Upzoning increases allowable building density in urban areas to accommodate growth and boost housing supply, while brownfield redevelopment focuses on cleaning and repurposing previously contaminated or underused industrial sites. Both approaches aim to revitalize cities, optimize land use, and address housing shortages through sustainable urban planning. Explore how upzoning and brownfield redevelopment shape the future of real estate development.
Why it is important
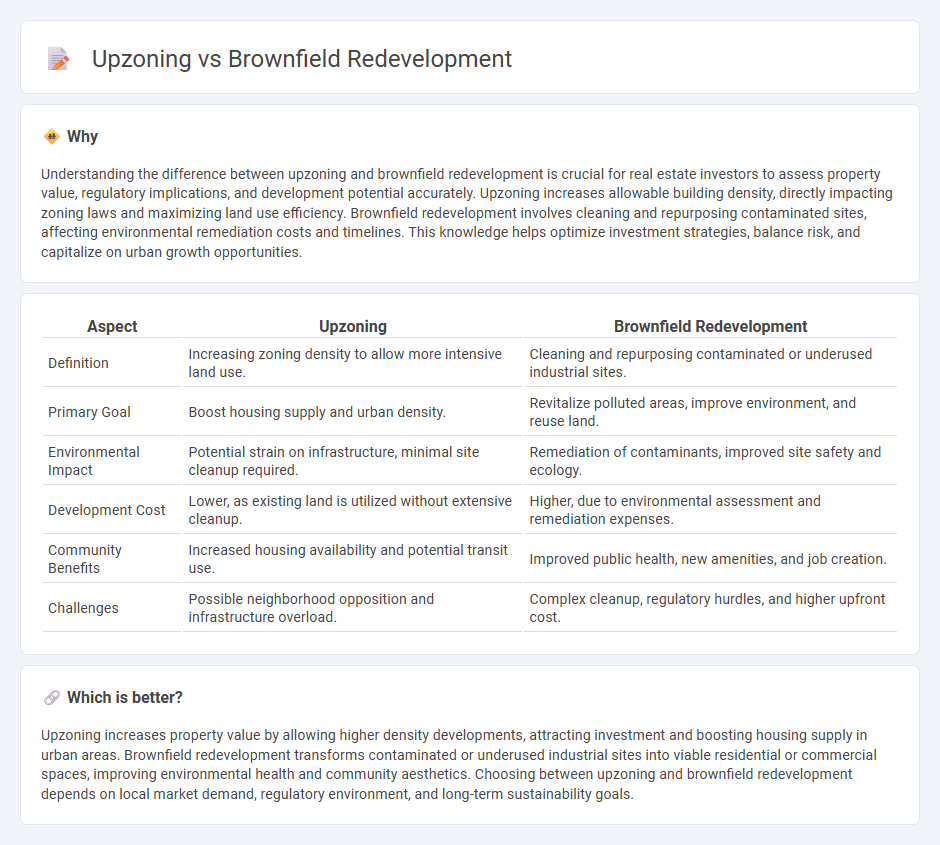
Understanding the difference between upzoning and brownfield redevelopment is crucial for real estate investors to assess property value, regulatory implications, and development potential accurately. Upzoning increases allowable building density, directly impacting zoning laws and maximizing land use efficiency. Brownfield redevelopment involves cleaning and repurposing contaminated sites, affecting environmental remediation costs and timelines. This knowledge helps optimize investment strategies, balance risk, and capitalize on urban growth opportunities.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Upzoning | Brownfield Redevelopment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Increasing zoning density to allow more intensive land use. | Cleaning and repurposing contaminated or underused industrial sites. |
| Primary Goal | Boost housing supply and urban density. | Revitalize polluted areas, improve environment, and reuse land. |
| Environmental Impact | Potential strain on infrastructure, minimal site cleanup required. | Remediation of contaminants, improved site safety and ecology. |
| Development Cost | Lower, as existing land is utilized without extensive cleanup. | Higher, due to environmental assessment and remediation expenses. |
| Community Benefits | Increased housing availability and potential transit use. | Improved public health, new amenities, and job creation. |
| Challenges | Possible neighborhood opposition and infrastructure overload. | Complex cleanup, regulatory hurdles, and higher upfront cost. |
Which is better?
Upzoning increases property value by allowing higher density developments, attracting investment and boosting housing supply in urban areas. Brownfield redevelopment transforms contaminated or underused industrial sites into viable residential or commercial spaces, improving environmental health and community aesthetics. Choosing between upzoning and brownfield redevelopment depends on local market demand, regulatory environment, and long-term sustainability goals.
Connection
Upzoning increases allowable building density in urban areas, which enhances the financial viability of redeveloping brownfield sites--previously contaminated or underutilized lands. Brownfield redevelopment transforms these sites into productive real estate assets, often spurring economic growth and urban revitalization. This synergy accelerates sustainable land use by promoting higher-density, mixed-use developments on previously neglected properties.
Key Terms
Contamination Remediation
Brownfield redevelopment involves cleaning up contaminated or polluted sites to prepare land for new use, prioritizing environmental remediation to ensure safety and compliance with health regulations. Upzoning allows increased land-use density but does not inherently address contamination risks, often requiring separate remediation initiatives when applied to brownfield areas. Explore effective strategies combining both approaches for sustainable urban growth and environmental health.
Land Use Regulation
Brownfield redevelopment involves the cleanup and repurposing of previously contaminated or underutilized industrial sites, promoting sustainable land use by revitalizing existing urban areas. Upzoning refers to changes in land use regulations that allow for higher-density development, enabling more intensive use of land through increased building heights or reduced setbacks. Explore how changes in land use policy shape urban growth, environmental impact, and community development.
Density Increase
Brownfield redevelopment involves transforming previously industrial or contaminated land into usable spaces, often increasing urban density by repurposing existing infrastructure. Upzoning permits higher density development through zoning changes, allowing more residential or commercial units on previously low-density land. Explore the impacts of these strategies on urban growth and sustainability to understand their roles in modern city planning.
Source and External Links
Anatomy of Brownfields Redevelopment - Brownfield redevelopment involves three stages: pre-development, development, and management, which include due diligence, environmental cleanup, financing, permitting, and marketing to enable infill development, job creation, and increased tax base.
What is Brownfield Redevelopment? A Guide for Developers - Brownfield redevelopment transforms abandoned or contaminated properties into productive spaces, driving economic revitalization, smart urban growth, and community benefits like job creation, higher property values, and improved quality of life.
Brownfields | US EPA - The EPA supports brownfield redevelopment with funding, technical assistance, and grants to assess, clean up, and sustainably reuse contaminated properties, enhancing local economies and quality of life through community-driven projects.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com