Digital twins in real estate offer dynamic, real-time representations of properties, enabling precise monitoring and management through integrated IoT sensors. Physical models provide tangible, three-dimensional replicas valuable for spatial visualization but lack real-time data integration and adaptability. Explore how digital twins are transforming property development and management efficiency.
Why it is important
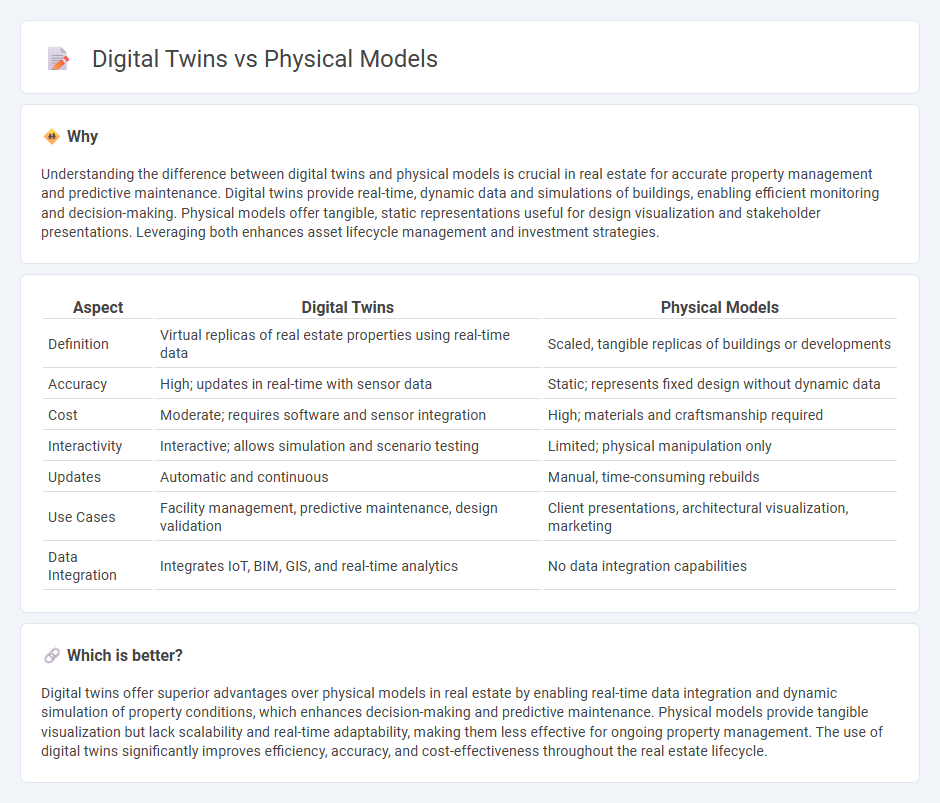
Understanding the difference between digital twins and physical models is crucial in real estate for accurate property management and predictive maintenance. Digital twins provide real-time, dynamic data and simulations of buildings, enabling efficient monitoring and decision-making. Physical models offer tangible, static representations useful for design visualization and stakeholder presentations. Leveraging both enhances asset lifecycle management and investment strategies.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Digital Twins | Physical Models |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Virtual replicas of real estate properties using real-time data | Scaled, tangible replicas of buildings or developments |
| Accuracy | High; updates in real-time with sensor data | Static; represents fixed design without dynamic data |
| Cost | Moderate; requires software and sensor integration | High; materials and craftsmanship required |
| Interactivity | Interactive; allows simulation and scenario testing | Limited; physical manipulation only |
| Updates | Automatic and continuous | Manual, time-consuming rebuilds |
| Use Cases | Facility management, predictive maintenance, design validation | Client presentations, architectural visualization, marketing |
| Data Integration | Integrates IoT, BIM, GIS, and real-time analytics | No data integration capabilities |
Which is better?
Digital twins offer superior advantages over physical models in real estate by enabling real-time data integration and dynamic simulation of property conditions, which enhances decision-making and predictive maintenance. Physical models provide tangible visualization but lack scalability and real-time adaptability, making them less effective for ongoing property management. The use of digital twins significantly improves efficiency, accuracy, and cost-effectiveness throughout the real estate lifecycle.
Connection
Digital twins create precise virtual replicas of physical real estate structures, enabling real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance. Physical models serve as tangible references that validate and enhance the accuracy of these digital representations. The integration of both technologies optimizes property management, design visualization, and decision-making processes in real estate development.
Key Terms
3D Visualization
Physical models provide tangible, scaled representations for spatial understanding, often limited by static features and lack of real-time updates. Digital twins enable dynamic 3D visualization with live data integration, facilitating accurate simulations and predictive analytics in real-time environments. Explore how digital twin technology revolutionizes 3D modeling and visualization in various industries.
Simulation
Simulation in physical models provides tangible experimentation but often lacks real-time data integration, limiting dynamic scenario analysis. Digital twins leverage IoT and real-time analytics to create highly accurate virtual replicas that simulate performance under varying conditions with predictive capabilities. Explore how digital twins transform simulation efficiency and decision-making in complex systems.
Sensor Integration
Sensor integration in physical models relies on direct attachment of devices to capture real-time data, often limited by scaling and environmental constraints. Digital twins utilize advanced sensor networks combined with IoT technology to provide continuous, precise monitoring and dynamic data feedback for accurate simulations. Explore the advantages of sensor integration in digital twins to enhance predictive maintenance and operational efficiency.
Source and External Links
Physical Model Definition, Examples & Limitation - This webpage provides an overview of physical models, including their definition, examples, and limitations, highlighting their role in understanding the literal object they represent.
Model - This article discusses models in general, including physical models like ship models, and explains their properties according to general model theory.
Model Classification - This webpage outlines the classification of models, including physical models, which are used as reduced-dimension representations of real-world systems.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com