Vertical farming buildings maximize urban space by integrating advanced hydroponic and aeroponic systems to produce fresh crops year-round, offering sustainable solutions for food security and reducing transportation emissions. Parking garages, while essential for urban mobility, occupy valuable land that could be repurposed for green infrastructure or mixed-use developments to enhance city living. Explore the transformative potential of vertical farming buildings in reshaping urban landscapes and promoting sustainability.
Why it is important
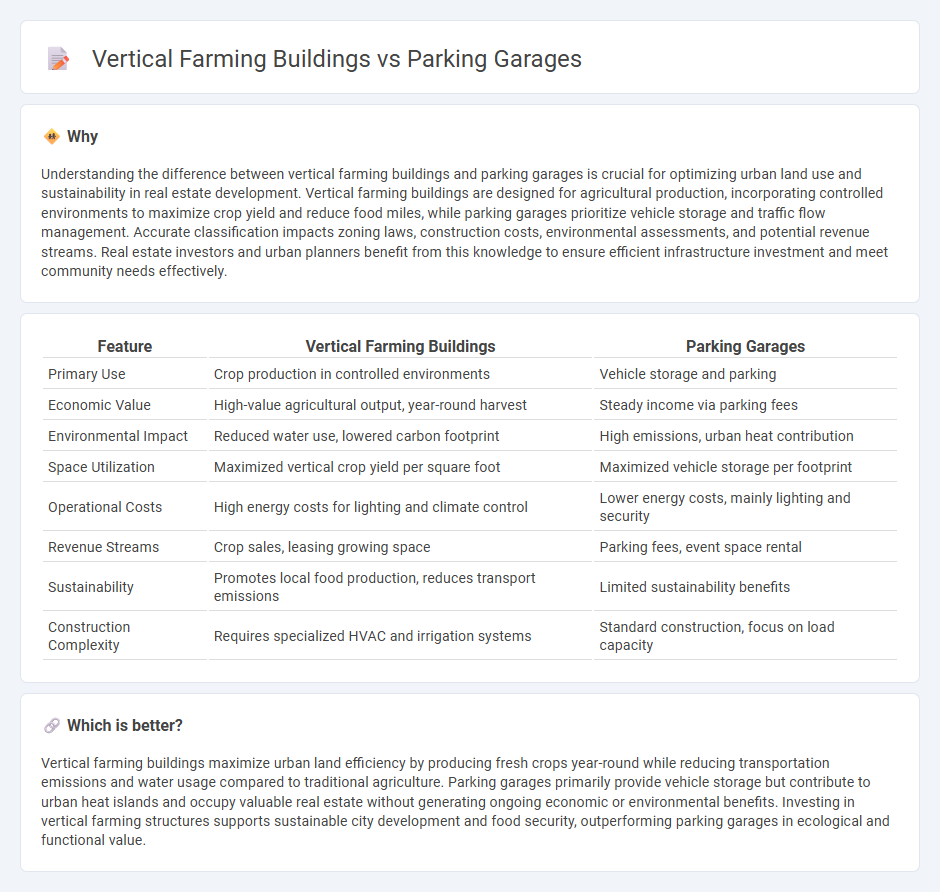
Understanding the difference between vertical farming buildings and parking garages is crucial for optimizing urban land use and sustainability in real estate development. Vertical farming buildings are designed for agricultural production, incorporating controlled environments to maximize crop yield and reduce food miles, while parking garages prioritize vehicle storage and traffic flow management. Accurate classification impacts zoning laws, construction costs, environmental assessments, and potential revenue streams. Real estate investors and urban planners benefit from this knowledge to ensure efficient infrastructure investment and meet community needs effectively.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Vertical Farming Buildings | Parking Garages |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Crop production in controlled environments | Vehicle storage and parking |
| Economic Value | High-value agricultural output, year-round harvest | Steady income via parking fees |
| Environmental Impact | Reduced water use, lowered carbon footprint | High emissions, urban heat contribution |
| Space Utilization | Maximized vertical crop yield per square foot | Maximized vehicle storage per footprint |
| Operational Costs | High energy costs for lighting and climate control | Lower energy costs, mainly lighting and security |
| Revenue Streams | Crop sales, leasing growing space | Parking fees, event space rental |
| Sustainability | Promotes local food production, reduces transport emissions | Limited sustainability benefits |
| Construction Complexity | Requires specialized HVAC and irrigation systems | Standard construction, focus on load capacity |
Which is better?
Vertical farming buildings maximize urban land efficiency by producing fresh crops year-round while reducing transportation emissions and water usage compared to traditional agriculture. Parking garages primarily provide vehicle storage but contribute to urban heat islands and occupy valuable real estate without generating ongoing economic or environmental benefits. Investing in vertical farming structures supports sustainable city development and food security, outperforming parking garages in ecological and functional value.
Connection
Vertical farming buildings and parking garages are connected through their shared use of urban infrastructure for maximizing space efficiency in real estate development. Both structures utilize multi-level designs to optimize land use in densely populated cities, providing solutions for food production and vehicle storage respectively. Integrating vertical farming within or atop parking garages can enhance sustainability by combining agricultural output with urban mobility needs.
Key Terms
Zoning Regulations
Zoning regulations distinctly impact parking garages and vertical farming buildings, where parking structures are often located in commercial or mixed-use zones with specific requirements for vehicle capacity and access. Vertical farming buildings typically fall under agricultural or special-use zones, subject to strict guidelines regarding environmental controls, building height, and water use. Explore zoning codes in your area to better understand how these regulations shape the development potential of each building type.
Structural Load Capacity
Parking garages are engineered with high structural load capacities to support multiple levels of heavy vehicles, often designed to handle loads ranging from 40 to 50 pounds per square foot or more. Vertical farming buildings, by contrast, typically require load capacities tailored to the weight of soil, water systems, and plant installations, usually ranging between 20 to 40 pounds per square foot depending on farming technology used. Explore further to understand how these structures optimize design for safety and functionality in their respective uses.
Land Use Efficiency
Vertical farming buildings significantly enhance land use efficiency by producing high yields on minimal footprints compared to traditional parking garages that primarily serve storage functions without generating food or renewable resources. These multi-story agricultural structures optimize urban spaces, reduce transportation emissions, and contribute to sustainable city planning. Explore the advantages of vertical farming over conventional land uses to understand its impact on urban resource management.
Source and External Links
Municipal Parking Facilities - NYC DOT - Offers municipal parking garages and lots across New York City, providing various payment options and a parking reservation system.
NYC Parking - Find. Compare. Save - A platform for finding and comparing parking options in New York City through an interactive map, including exclusive discounts.
Icon Parking - Provides safe and convenient parking across nearly 200 locations in New York City, offering daily and monthly parking options.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com