Tiny home communities offer affordable, sustainable living with a focus on minimalism and close-knit social environments, while multifamily housing provides higher-density options with diverse unit sizes and shared amenities that cater to urban lifestyles. Both real estate models address housing demands but differ significantly in space utilization, cost, and community dynamics. Explore the benefits and challenges of each to determine the best fit for your real estate investment or lifestyle needs.
Why it is important
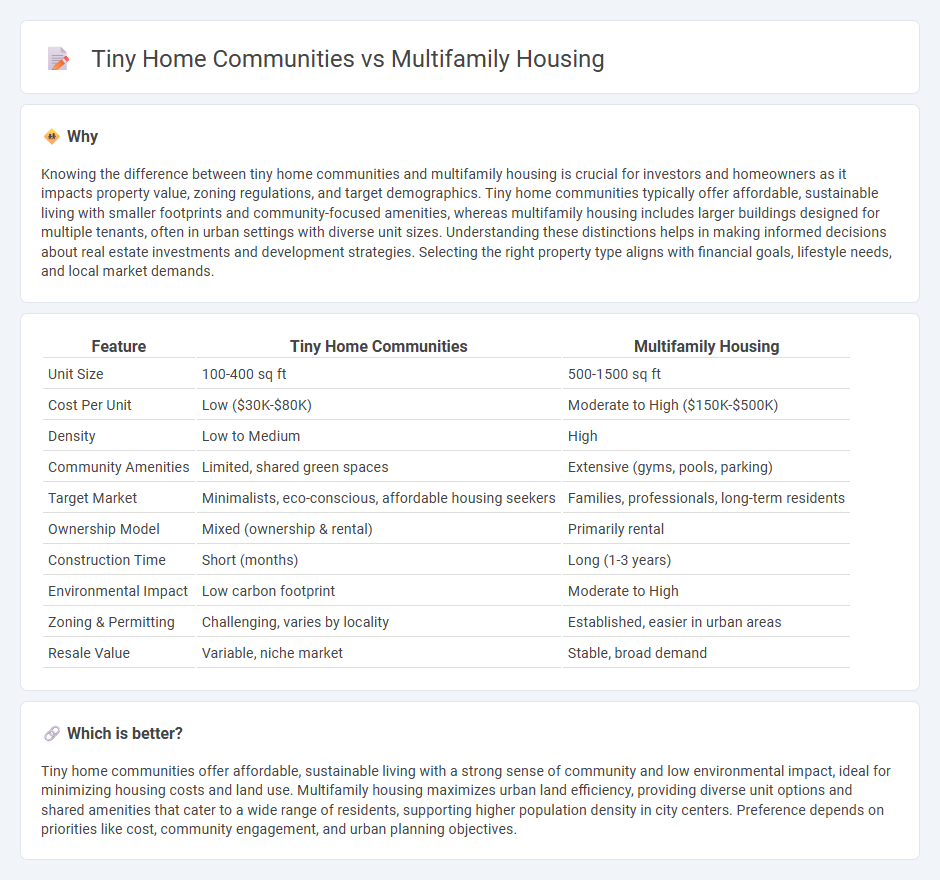
Knowing the difference between tiny home communities and multifamily housing is crucial for investors and homeowners as it impacts property value, zoning regulations, and target demographics. Tiny home communities typically offer affordable, sustainable living with smaller footprints and community-focused amenities, whereas multifamily housing includes larger buildings designed for multiple tenants, often in urban settings with diverse unit sizes. Understanding these distinctions helps in making informed decisions about real estate investments and development strategies. Selecting the right property type aligns with financial goals, lifestyle needs, and local market demands.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Tiny Home Communities | Multifamily Housing |
|---|---|---|
| Unit Size | 100-400 sq ft | 500-1500 sq ft |
| Cost Per Unit | Low ($30K-$80K) | Moderate to High ($150K-$500K) |
| Density | Low to Medium | High |
| Community Amenities | Limited, shared green spaces | Extensive (gyms, pools, parking) |
| Target Market | Minimalists, eco-conscious, affordable housing seekers | Families, professionals, long-term residents |
| Ownership Model | Mixed (ownership & rental) | Primarily rental |
| Construction Time | Short (months) | Long (1-3 years) |
| Environmental Impact | Low carbon footprint | Moderate to High |
| Zoning & Permitting | Challenging, varies by locality | Established, easier in urban areas |
| Resale Value | Variable, niche market | Stable, broad demand |
Which is better?
Tiny home communities offer affordable, sustainable living with a strong sense of community and low environmental impact, ideal for minimizing housing costs and land use. Multifamily housing maximizes urban land efficiency, providing diverse unit options and shared amenities that cater to a wide range of residents, supporting higher population density in city centers. Preference depends on priorities like cost, community engagement, and urban planning objectives.
Connection
Tiny home communities and multifamily housing both address urban density challenges by maximizing limited space to provide affordable, efficient living options. These housing models promote community-focused environments with shared amenities, reducing individual costs and environmental footprints. Developers increasingly integrate tiny homes within multifamily complexes to diversify housing stock and meet growing demand for flexible, sustainable urban living solutions.
Key Terms
Density
Multifamily housing typically offers higher density living, accommodating numerous residents within a single building and maximizing urban land use, whereas tiny home communities provide lower density with individual, compact units spread over larger areas. The density of multifamily housing supports efficient public transportation and infrastructure, while tiny home communities prioritize privacy and flexible space allocation. Explore detailed comparisons to understand which housing model best suits your urban development goals.
Zoning regulations
Zoning regulations play a crucial role in distinguishing multifamily housing from tiny home communities, often dictating density, land use, and building codes. Multifamily housing is typically allowed in residential zones with higher density allowances, while tiny home communities may face restrictions related to minimum lot sizes and sanitation requirements. Explore comprehensive zoning guidelines to understand how local laws impact the development and legality of these housing options.
Affordability
Multifamily housing offers cost efficiency by distributing expenses across multiple units, often resulting in lower rent per square foot compared to standalone homes. Tiny home communities emphasize minimal living spaces and reduced utility costs, making them highly affordable for individuals seeking low-maintenance lifestyles. Explore detailed comparisons to understand which option best fits your budget and lifestyle preferences.
Source and External Links
Multifamily Residential - Wikipedia - Multifamily residential housing involves multiple separate units within one building or complex, often including apartments and condominiums.
Multifamily Homes: Types and Trends | NAHB - Multifamily homes, such as apartment buildings and condominiums, account for 31.4% of U.S. housing and offer various amenities like fitness centers and smart home features.
What is Multifamily Housing and What are the Benefits? - Multifamily housing refers to properties with multiple households and offers benefits like affordability and reduced financial risks for homeowners and investors.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com