Green hushing occurs when companies underreport or hide their environmental efforts to avoid scrutiny, while social washing involves exaggerating social responsibility claims to enhance brand image without genuine impact. Both practices undermine consumer trust and hinder authentic corporate sustainability. Explore how these tactics affect marketing strategies and consumer perceptions in today's eco-conscious market.
Why it is important
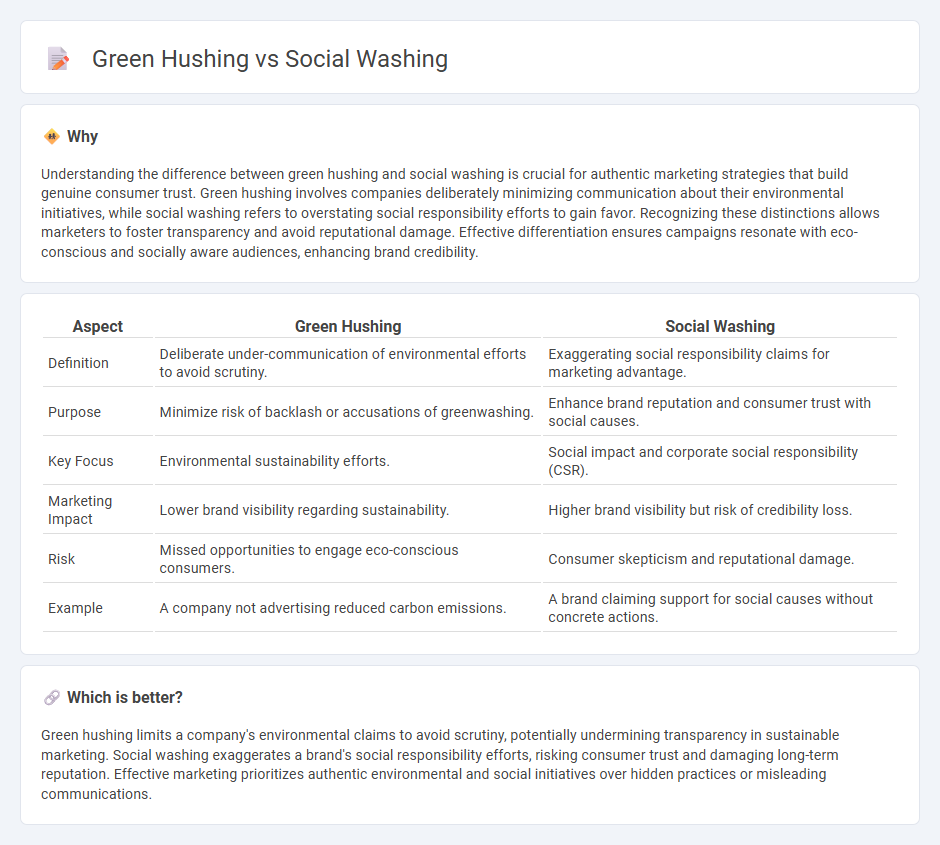
Understanding the difference between green hushing and social washing is crucial for authentic marketing strategies that build genuine consumer trust. Green hushing involves companies deliberately minimizing communication about their environmental initiatives, while social washing refers to overstating social responsibility efforts to gain favor. Recognizing these distinctions allows marketers to foster transparency and avoid reputational damage. Effective differentiation ensures campaigns resonate with eco-conscious and socially aware audiences, enhancing brand credibility.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Green Hushing | Social Washing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Deliberate under-communication of environmental efforts to avoid scrutiny. | Exaggerating social responsibility claims for marketing advantage. |
| Purpose | Minimize risk of backlash or accusations of greenwashing. | Enhance brand reputation and consumer trust with social causes. |
| Key Focus | Environmental sustainability efforts. | Social impact and corporate social responsibility (CSR). |
| Marketing Impact | Lower brand visibility regarding sustainability. | Higher brand visibility but risk of credibility loss. |
| Risk | Missed opportunities to engage eco-conscious consumers. | Consumer skepticism and reputational damage. |
| Example | A company not advertising reduced carbon emissions. | A brand claiming support for social causes without concrete actions. |
Which is better?
Green hushing limits a company's environmental claims to avoid scrutiny, potentially undermining transparency in sustainable marketing. Social washing exaggerates a brand's social responsibility efforts, risking consumer trust and damaging long-term reputation. Effective marketing prioritizes authentic environmental and social initiatives over hidden practices or misleading communications.
Connection
Green hushing and social washing intersect in marketing as strategies where companies obscure true environmental and social impacts to maintain a positive public image. Both involve selective communication, with green hushing minimizing public disclosure of genuine sustainability efforts, while social washing exaggerates social responsibility claims to influence consumer perception. These practices undermine transparency and consumer trust, complicating authentic corporate social responsibility initiatives.
Key Terms
Authenticity
Social washing involves companies exaggerating their social responsibility efforts to appeal to consumers, while green hushing refers to businesses deliberately minimizing or hiding their environmental achievements to avoid scrutiny. Authenticity in corporate communication is crucial as consumers increasingly demand transparency and genuine commitment to social and environmental causes. Discover how businesses can balance authenticity and responsibility to build lasting trust.
Transparency
Social washing involves companies exaggerating their social responsibility efforts, creating a misleading image of ethical practices, while green hushing refers to the deliberate underreporting or silence about environmental initiatives to avoid scrutiny or criticism. Transparency in social washing demands clear, verifiable disclosures to prevent misleading stakeholders, whereas green hushing undermines transparency by withholding positive sustainability actions that could encourage industry-wide progress. Explore strategies to enhance transparency and promote authentic communication in corporate social and environmental responsibility.
Consumer Trust
Social washing involves brands exaggerating their social responsibility efforts to enhance their public image, while green hushing refers to companies deliberately downplaying or hiding their environmental initiatives to avoid scrutiny. Both practices erode consumer trust by creating skepticism about the authenticity of corporate sustainability claims. Discover how transparent communication fosters genuine consumer confidence and strengthens brand loyalty.
Source and External Links
What is Social Washing? - Social washing involves companies presenting themselves as socially responsible while masking negative social impacts for financial gain.
On the rise: navigating the wave of greenwashing and social washing - Social washing occurs when companies obscure underlying social issues by portraying a positive image to safeguard their reputation and financial performance.
Social washing: social commitment or just a marketing strategy - Social washing is a deceptive practice where companies exaggerate or fake their social responsibility to attract consumers and improve their image.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com