Algorithmic bias in marketing algorithms can lead to unfair targeting and pricing disparities, impacting consumer trust and brand reputation. Dynamic pricing uses real-time data and machine learning to adjust prices based on demand, competition, and customer behavior, but may inadvertently reinforce biases if not carefully managed. Discover how understanding the balance between algorithmic fairness and dynamic pricing strategies can optimize marketing outcomes.
Why it is important
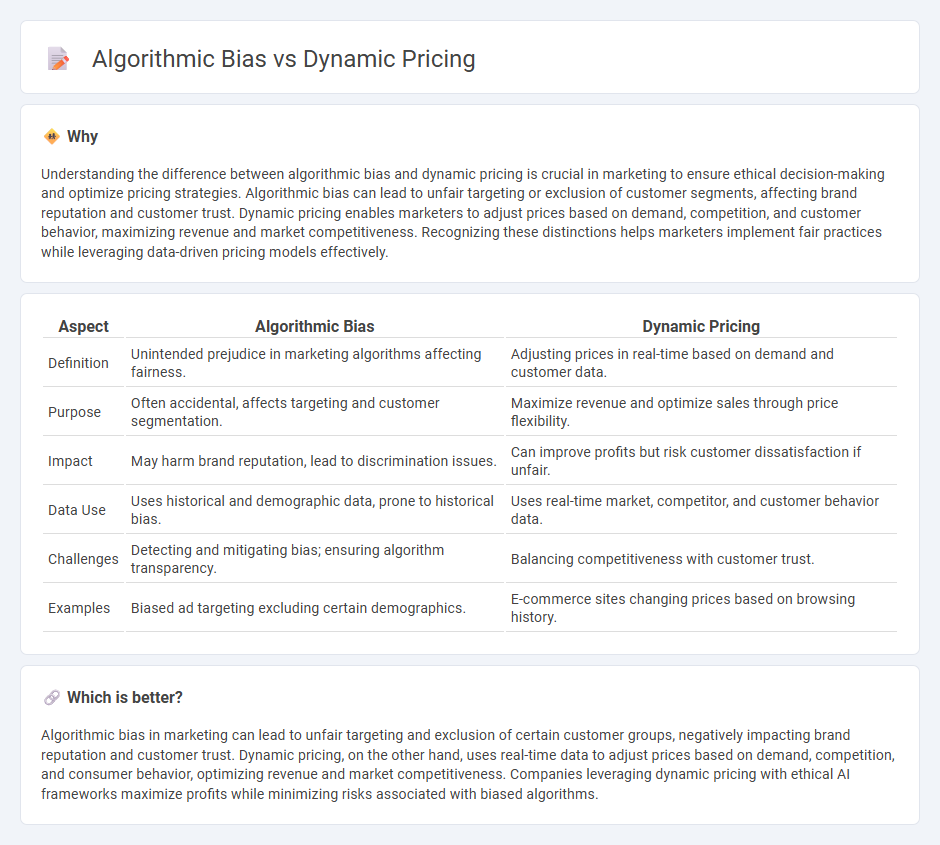
Understanding the difference between algorithmic bias and dynamic pricing is crucial in marketing to ensure ethical decision-making and optimize pricing strategies. Algorithmic bias can lead to unfair targeting or exclusion of customer segments, affecting brand reputation and customer trust. Dynamic pricing enables marketers to adjust prices based on demand, competition, and customer behavior, maximizing revenue and market competitiveness. Recognizing these distinctions helps marketers implement fair practices while leveraging data-driven pricing models effectively.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Algorithmic Bias | Dynamic Pricing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Unintended prejudice in marketing algorithms affecting fairness. | Adjusting prices in real-time based on demand and customer data. |
| Purpose | Often accidental, affects targeting and customer segmentation. | Maximize revenue and optimize sales through price flexibility. |
| Impact | May harm brand reputation, lead to discrimination issues. | Can improve profits but risk customer dissatisfaction if unfair. |
| Data Use | Uses historical and demographic data, prone to historical bias. | Uses real-time market, competitor, and customer behavior data. |
| Challenges | Detecting and mitigating bias; ensuring algorithm transparency. | Balancing competitiveness with customer trust. |
| Examples | Biased ad targeting excluding certain demographics. | E-commerce sites changing prices based on browsing history. |
Which is better?
Algorithmic bias in marketing can lead to unfair targeting and exclusion of certain customer groups, negatively impacting brand reputation and customer trust. Dynamic pricing, on the other hand, uses real-time data to adjust prices based on demand, competition, and consumer behavior, optimizing revenue and market competitiveness. Companies leveraging dynamic pricing with ethical AI frameworks maximize profits while minimizing risks associated with biased algorithms.
Connection
Algorithmic bias in marketing can lead to unfair dynamic pricing by influencing price adjustments based on skewed data patterns related to customer demographics. Machine learning models used for dynamic pricing may perpetuate existing biases, resulting in discriminatory pricing strategies that affect certain groups disproportionately. Addressing algorithmic bias is crucial for ensuring equitable pricing mechanisms and maintaining consumer trust in automated marketing systems.
Key Terms
Price Optimization
Dynamic pricing leverages real-time data and machine learning algorithms to adjust prices based on demand, competition, and customer behavior, enhancing revenue and market responsiveness. However, algorithmic bias in pricing models can lead to unfair price discrimination, disproportionately impacting certain customer groups and raising ethical concerns. Explore the nuances of price optimization strategies and the mitigation of algorithmic bias to ensure equitable and effective pricing solutions.
Machine Learning
Dynamic pricing leverages machine learning algorithms to adjust prices in real-time based on demand, customer behavior, and market conditions, aiming to maximize revenue and competitiveness. However, algorithmic bias in machine learning models can lead to unfair pricing strategies, disproportionately affecting certain customer groups based on biased training data or flawed feature selection. Explore how addressing algorithmic bias is crucial for ethical and effective dynamic pricing systems.
Fairness
Dynamic pricing adjusts product costs based on demand, customer behavior, and market conditions, often utilizing machine learning algorithms that can inadvertently perpetuate algorithmic bias. Algorithmic bias in dynamic pricing leads to unfair disparities where certain groups may face systematically higher prices due to biased data or flawed model assumptions. Explore methods to identify and mitigate bias in dynamic pricing systems to ensure fairness and equitable treatment for all consumers.
Source and External Links
Dynamic Pricing: What Is It & How It Effects E-Commerce - Dynamic pricing lets e-commerce businesses adjust prices in real time based on demand, competition, and data, enabling continuous price changes to optimize revenue and profitability.
What is Dynamic Pricing? - DealHub - Dynamic pricing is a strategy where prices fluctuate based on real-time market data including supply, demand, competitor pricing, and customer behavior to maximize revenue and improve pricing agility.
Dynamic pricing - Dynamic pricing, also known as surge or demand pricing, is a flexible pricing strategy where prices rise or fall based on current market demands, often used in industries like hospitality, retail, and transportation.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com