Phantom tagging in marketing involves assigning false or inflated conversion values to digital campaigns to manipulate performance data, while spoofing refers to disguising the source or identity of website visitors or ad traffic to deceive analytics systems. Both tactics can undermine data accuracy and lead to misinformed marketing decisions. Explore the nuances and implications of phantom tagging versus spoofing to enhance your data integrity strategies.
Why it is important
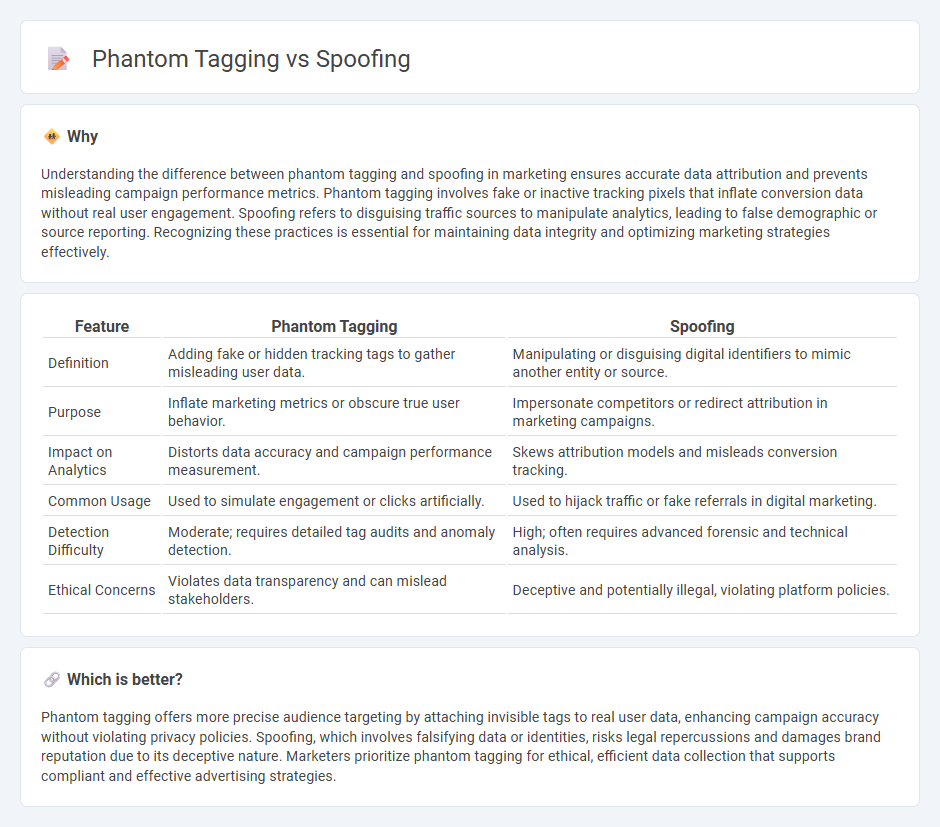
Understanding the difference between phantom tagging and spoofing in marketing ensures accurate data attribution and prevents misleading campaign performance metrics. Phantom tagging involves fake or inactive tracking pixels that inflate conversion data without real user engagement. Spoofing refers to disguising traffic sources to manipulate analytics, leading to false demographic or source reporting. Recognizing these practices is essential for maintaining data integrity and optimizing marketing strategies effectively.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Phantom Tagging | Spoofing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Adding fake or hidden tracking tags to gather misleading user data. | Manipulating or disguising digital identifiers to mimic another entity or source. |
| Purpose | Inflate marketing metrics or obscure true user behavior. | Impersonate competitors or redirect attribution in marketing campaigns. |
| Impact on Analytics | Distorts data accuracy and campaign performance measurement. | Skews attribution models and misleads conversion tracking. |
| Common Usage | Used to simulate engagement or clicks artificially. | Used to hijack traffic or fake referrals in digital marketing. |
| Detection Difficulty | Moderate; requires detailed tag audits and anomaly detection. | High; often requires advanced forensic and technical analysis. |
| Ethical Concerns | Violates data transparency and can mislead stakeholders. | Deceptive and potentially illegal, violating platform policies. |
Which is better?
Phantom tagging offers more precise audience targeting by attaching invisible tags to real user data, enhancing campaign accuracy without violating privacy policies. Spoofing, which involves falsifying data or identities, risks legal repercussions and damages brand reputation due to its deceptive nature. Marketers prioritize phantom tagging for ethical, efficient data collection that supports compliant and effective advertising strategies.
Connection
Phantom tagging and spoofing both manipulate digital marketing data to create artificial interactions that mislead tracking algorithms and analytics platforms. Phantom tagging generates fake user engagement through invisible tags, while spoofing disguises the origin of traffic to simulate legitimate user behavior. These deceptive practices distort campaign performance metrics, undermining accurate attribution and budget allocation in marketing strategies.
Key Terms
Brand Integrity
Spoofing involves creating fraudulent versions of a brand's digital presence to deceive consumers, undermining brand integrity and trust. Phantom tagging refers to artificially inflating product engagement metrics by adding fake tags or interactions, leading to distorted brand performance data. Explore effective strategies to safeguard your brand integrity against spoofing and phantom tagging threats.
Consumer Trust
Spoofing involves impersonating trusted entities to deceive consumers, while phantom tagging refers to the unauthorized use of real user data to manipulate digital advertising metrics. Both practices severely undermine consumer trust by compromising data integrity and privacy, leading to skepticism towards online interactions and advertisements. Explore more to understand how businesses can safeguard consumer trust against these deceptive tactics.
Engagement Metrics
Spoofing manipulates engagement metrics by generating fake interactions through bots or automated accounts, inflating likes, comments, and shares to create false popularity. Phantom tagging involves tagging users who have no relation to the content, coercing them to engage and artificially boosting visibility and interaction rates. Explore our detailed analysis to understand how these deceptive practices distort genuine engagement metrics and impact digital marketing strategies.
Source and External Links
What is Spoofing & How to Prevent it - Kaspersky - Spoofing is a cybercrime where attackers impersonate trusted entities via faked emails or websites to trick victims into harmful actions like fraudulent money transfers or data theft, often combining social engineering tactics.
Spoofing | Spoof Calls | What is a Spoofing Attack - Malwarebytes - Spoofing is when an attacker pretends to be another entity to gain trust, steal data, or access systems, with forms including email, caller ID, GPS, IP, and website spoofing designed to trick victims into revealing sensitive information or downloading malware.
What is Spoofing and How Can It Affect You? | Equifax(r) - Spoofing involves creating a fake identity, commonly seen in phone call or caller ID spoofing, where scammers falsify numbers to impersonate trusted organizations and steal personal information through scripted social engineering.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com