Microlearning delivers focused, bite-sized training modules that enhance retention and fit seamlessly into busy schedules, while simulation training offers immersive, hands-on experiences that replicate real-world scenarios to develop critical decision-making skills. Both methods improve employee performance and engagement, addressing different learning needs within management development programs. Explore how integrating microlearning and simulation training can optimize your organization's management training outcomes.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between microlearning and simulation training is crucial for effective management because microlearning delivers focused, bite-sized knowledge enhancing immediate skill acquisition, while simulation training provides immersive, hands-on experience to develop complex decision-making abilities. Managers who leverage microlearning can quickly upskill employees and address specific knowledge gaps, optimizing training efficiency and retention. Simulation training prepares teams for real-world challenges by replicating scenarios, improving critical thinking and problem-solving skills in a risk-free environment. This strategic distinction ensures tailored development approaches that maximize performance and organizational growth.
Comparison Table
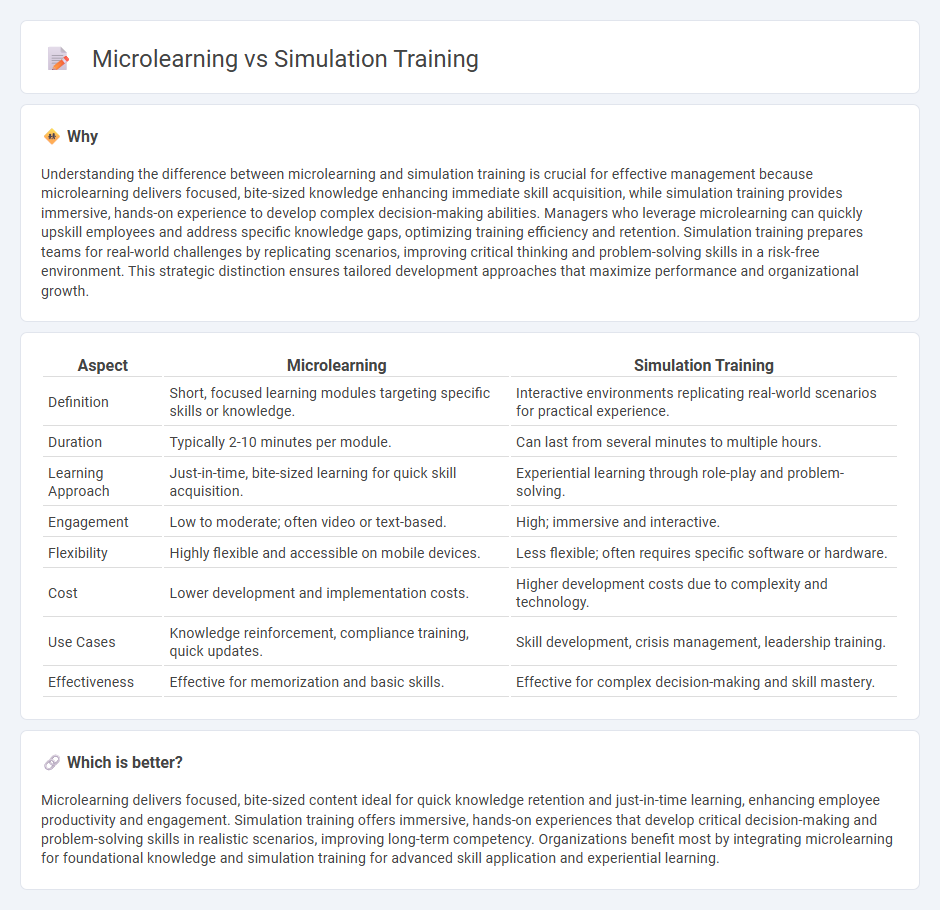
| Aspect | Microlearning | Simulation Training |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Short, focused learning modules targeting specific skills or knowledge. | Interactive environments replicating real-world scenarios for practical experience. |
| Duration | Typically 2-10 minutes per module. | Can last from several minutes to multiple hours. |
| Learning Approach | Just-in-time, bite-sized learning for quick skill acquisition. | Experiential learning through role-play and problem-solving. |
| Engagement | Low to moderate; often video or text-based. | High; immersive and interactive. |
| Flexibility | Highly flexible and accessible on mobile devices. | Less flexible; often requires specific software or hardware. |
| Cost | Lower development and implementation costs. | Higher development costs due to complexity and technology. |
| Use Cases | Knowledge reinforcement, compliance training, quick updates. | Skill development, crisis management, leadership training. |
| Effectiveness | Effective for memorization and basic skills. | Effective for complex decision-making and skill mastery. |
Which is better?
Microlearning delivers focused, bite-sized content ideal for quick knowledge retention and just-in-time learning, enhancing employee productivity and engagement. Simulation training offers immersive, hands-on experiences that develop critical decision-making and problem-solving skills in realistic scenarios, improving long-term competency. Organizations benefit most by integrating microlearning for foundational knowledge and simulation training for advanced skill application and experiential learning.
Connection
Microlearning and simulation training are connected through their shared goal of enhancing management skills by providing targeted, experiential learning in bite-sized formats. Simulation training replicates real-world management scenarios, allowing learners to practice decision-making and problem-solving within controlled environments, while microlearning delivers concise, focused content that reinforces key management concepts and behaviors. This combination accelerates skill acquisition and improves retention by engaging managers in interactive, contextually relevant exercises tailored to their development needs.
Key Terms
Experiential Learning
Simulation training offers immersive, hands-on experiences that replicate real-world scenarios for deep skill acquisition and decision-making improvements. Microlearning delivers bite-sized, focused content enhancing retention and flexibility, ideal for quick knowledge updates and just-in-time learning. Explore how combining these approaches leverages experiential learning to maximize practical skills and learner engagement.
Bite-sized Content
Simulation training offers immersive, realistic scenarios that enhance skills through hands-on practice, while microlearning delivers bite-sized content tailored for quick, focused knowledge acquisition. Bite-sized content specializes in concise, targeted learning modules that improve retention and flexibility, ideal for on-the-go learners seeking rapid skill development. Explore how integrating bite-sized content within simulation training can maximize learning efficiency and outcomes.
Skill Application
Simulation training offers immersive, hands-on experiences that closely mimic real-world scenarios, enhancing skill application through active participation and immediate feedback. Microlearning delivers concise, focused content targeting specific skills or knowledge, allowing learners to apply new information quickly in practical contexts. Explore detailed comparisons to understand which method best supports effective skill application.
Source and External Links
What Is Simulation Training? (+Benefits, Examples) - Simulation training involves immersive, realistic replications of work processes and scenarios, allowing learners to practice skills and decision-making in a risk-free environment, with applications in industries such as construction, engineering, aviation, and military sectors.
Simulation Training - Simulation training uses equipment or software to model real-world scenarios to better prepare learners for actual events by practicing tasks in a controlled, simulated environment, often leveraging virtual and augmented reality technologies.
Simulation Training | PSNet - Patient Safety Network - AHRQ - In healthcare, simulation training is crucial for developing technical and teamwork skills safely by allowing practice of rare, high-risk situations with real-time feedback, bridging classroom learning with clinical experience in a risk-free setting.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com