Leadership shadow refers to the subtle, often unconscious influence a leader's behavior and attitudes have on their team's culture and performance, contrasting sharply with autocratic leadership which is characterized by centralized decision-making and strict control. Autocratic leadership limits employee autonomy and discourages input, potentially stifling innovation, whereas leadership shadow shapes organizational dynamics through modeled behaviors and values. Explore the nuances between these leadership styles to understand their impact on organizational effectiveness.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between leadership shadow and autocratic leadership is crucial for effective management because the leadership shadow reflects the influence of a leader's behavior on organizational culture and employee motivation. Autocratic leadership, characterized by centralized decision-making and limited employee input, often stifles creativity and reduces team engagement. Recognizing these differences enables managers to adopt leadership styles that foster a positive work environment and enhance productivity. This knowledge helps in developing adaptive strategies that align leadership behaviors with organizational goals and employee well-being.
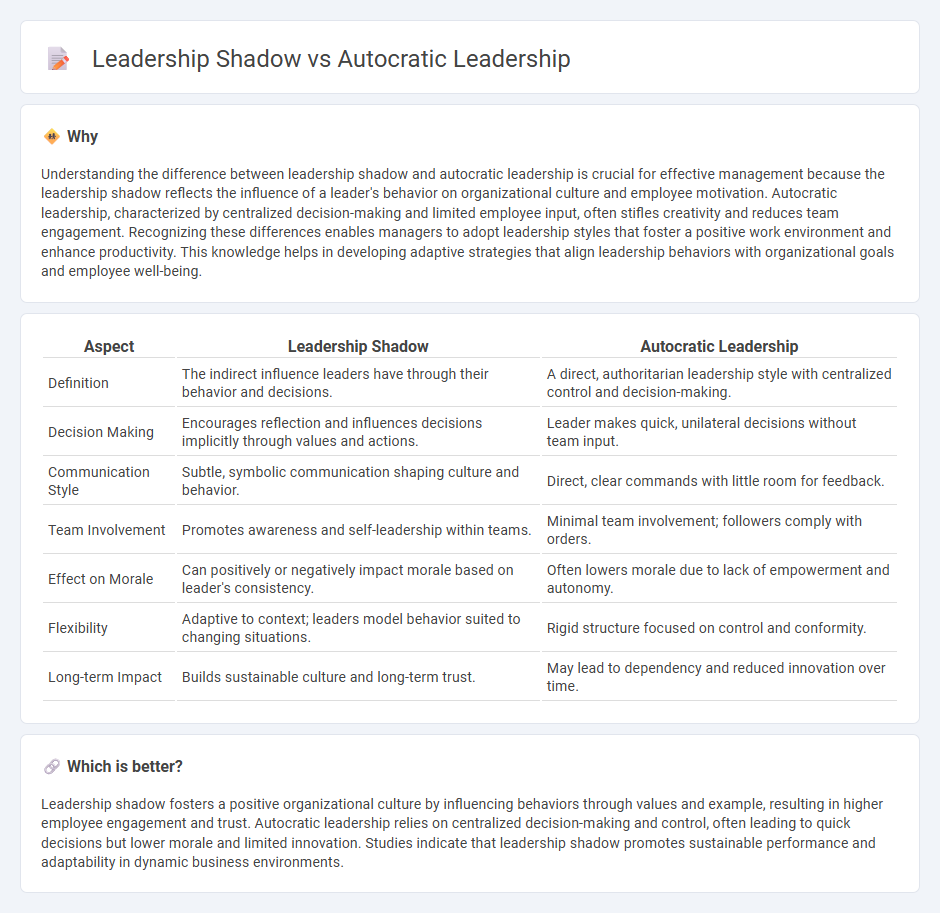
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Leadership Shadow | Autocratic Leadership |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The indirect influence leaders have through their behavior and decisions. | A direct, authoritarian leadership style with centralized control and decision-making. |
| Decision Making | Encourages reflection and influences decisions implicitly through values and actions. | Leader makes quick, unilateral decisions without team input. |
| Communication Style | Subtle, symbolic communication shaping culture and behavior. | Direct, clear commands with little room for feedback. |
| Team Involvement | Promotes awareness and self-leadership within teams. | Minimal team involvement; followers comply with orders. |
| Effect on Morale | Can positively or negatively impact morale based on leader's consistency. | Often lowers morale due to lack of empowerment and autonomy. |
| Flexibility | Adaptive to context; leaders model behavior suited to changing situations. | Rigid structure focused on control and conformity. |
| Long-term Impact | Builds sustainable culture and long-term trust. | May lead to dependency and reduced innovation over time. |
Which is better?
Leadership shadow fosters a positive organizational culture by influencing behaviors through values and example, resulting in higher employee engagement and trust. Autocratic leadership relies on centralized decision-making and control, often leading to quick decisions but lower morale and limited innovation. Studies indicate that leadership shadow promotes sustainable performance and adaptability in dynamic business environments.
Connection
Leadership shadow influences organizational culture by shaping employee behavior through modeled actions and values, while autocratic leadership intensifies this effect by enforcing strict control and unilateral decision-making. The autocratic leader's dominant presence casts a strong leadership shadow that often limits employee autonomy and innovation. This connection highlights how leadership styles directly impact workplace dynamics and employee engagement.
Key Terms
Decision-making
Autocratic leadership centralizes decision-making authority in a single leader, ensuring quick and clear directives but often limiting team input and creativity. Leadership shadow refers to the indirect influence a leader's behavior and values have on organizational culture and decision dynamics, shaping how decisions are made beyond explicit commands. Explore further to understand how these contrasting leadership styles impact effective decision-making processes.
Influence
Autocratic leadership relies on centralized authority, where decision-making power is concentrated in the leader, exerting influence through control and directive commands. Leadership shadow refers to the unintended influence leaders have on organizational culture and behavior, often shaping norms and values beyond formal authority. Explore more to understand how influence operates differently in these leadership dynamics.
Accountability
Autocratic leadership centralizes decision-making authority, enforcing strict accountability through clear hierarchical structures and direct commands. In contrast, the leadership shadow emphasizes accountability by recognizing the implicit influence of a leader's behavior on organizational culture and employee responsibility. Explore the impact of these leadership styles on fostering accountability in your team.
Source and External Links
Autocratic Leadership: Definition & Examples - Describes autocratic leadership as a centralized management style where decisions are made by a single leader without input from others, emphasizing strict control and efficiency.
Autocratic Leadership Style: Definition, Examples, Pros & Cons - Explains that autocratic leadership involves making decisions without input from others, often leading to quick decisions but potentially lower employee morale and creativity.
What Is Autocratic Leadership? - Discusses autocratic leadership as a style where a single leader holds all decision-making power, prioritizing control and efficiency over collaboration and creativity.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com