Continuous performance management emphasizes regular feedback, goal setting, and employee development to enhance productivity and engagement, contrasting sharply with forced ranking's rigid system of categorizing employees into predetermined performance tiers. Forced ranking often undermines team morale by fostering competition instead of collaboration, while continuous performance management supports a growth mindset and adaptive improvement. Explore how integrating continuous performance management can transform organizational culture and drive sustainable success.
Why it is important
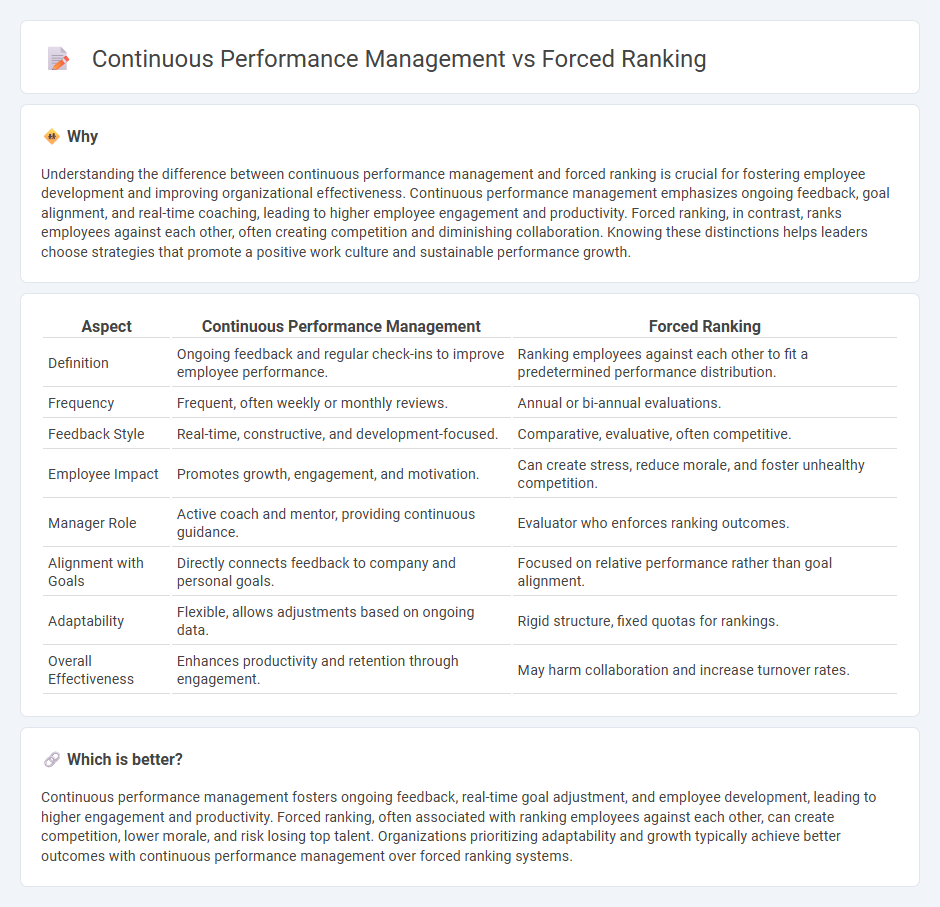
Understanding the difference between continuous performance management and forced ranking is crucial for fostering employee development and improving organizational effectiveness. Continuous performance management emphasizes ongoing feedback, goal alignment, and real-time coaching, leading to higher employee engagement and productivity. Forced ranking, in contrast, ranks employees against each other, often creating competition and diminishing collaboration. Knowing these distinctions helps leaders choose strategies that promote a positive work culture and sustainable performance growth.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Continuous Performance Management | Forced Ranking |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ongoing feedback and regular check-ins to improve employee performance. | Ranking employees against each other to fit a predetermined performance distribution. |
| Frequency | Frequent, often weekly or monthly reviews. | Annual or bi-annual evaluations. |
| Feedback Style | Real-time, constructive, and development-focused. | Comparative, evaluative, often competitive. |
| Employee Impact | Promotes growth, engagement, and motivation. | Can create stress, reduce morale, and foster unhealthy competition. |
| Manager Role | Active coach and mentor, providing continuous guidance. | Evaluator who enforces ranking outcomes. |
| Alignment with Goals | Directly connects feedback to company and personal goals. | Focused on relative performance rather than goal alignment. |
| Adaptability | Flexible, allows adjustments based on ongoing data. | Rigid structure, fixed quotas for rankings. |
| Overall Effectiveness | Enhances productivity and retention through engagement. | May harm collaboration and increase turnover rates. |
Which is better?
Continuous performance management fosters ongoing feedback, real-time goal adjustment, and employee development, leading to higher engagement and productivity. Forced ranking, often associated with ranking employees against each other, can create competition, lower morale, and risk losing top talent. Organizations prioritizing adaptability and growth typically achieve better outcomes with continuous performance management over forced ranking systems.
Connection
Continuous performance management enables real-time feedback and ongoing employee development, creating a dynamic environment where performance metrics are constantly assessed. Forced ranking, a method that ranks employees against each other, relies on the consistent data generated by continuous performance systems to make comparative evaluations more accurate and current. Combining these approaches allows organizations to identify top performers and underachievers with timely insights, driving strategic talent management and workforce optimization.
Key Terms
Evaluation Frequency
Forced ranking typically evaluates employee performance annually, creating a competitive ranking system that may overlook ongoing development. Continuous performance management emphasizes frequent, real-time feedback and regular check-ins, fostering continuous improvement and adaptability. Explore how evaluation frequency impacts employee growth and organizational success by diving deeper into these performance management approaches.
Employee Comparison
Forced ranking systems rank employees against each other, often creating a competitive environment that may impact morale and teamwork negatively, while continuous performance management emphasizes ongoing feedback and regular check-ins to support employee growth and collaboration. Forced ranking categorizes employees into strict performance tiers, which can lead to employee dissatisfaction and turnover, whereas continuous performance management encourages dynamic development and real-time adjustments based on individual progress. Explore detailed insights on how these approaches affect employee comparison and overall organizational performance.
Feedback Mechanism
Forced ranking relies on comparative feedback by ranking employees against each other, often leading to competitive tension and limited development dialogue. Continuous performance management emphasizes regular, real-time feedback focusing on individual progress and growth, fostering a culture of continuous improvement. Explore strategies to optimize feedback mechanisms for enhanced employee engagement and performance outcomes.
Source and External Links
What Is Forced Ranking? | HR Glossary - Forced ranking is a performance appraisal system categorizing employees into top, average, and low performers based on predefined criteria.
Employee Ranking Systems - Forced ranking is a method that categorizes employees into predetermined groups, helping identify top performers and areas for improvement.
Forced Ranking - Gamestorming - Forced ranking involves making difficult decisions by ranking items relative to each other, often used in decision-making processes.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com