Job crafting empowers employees to redesign tasks, relationships, and perceptions to better fit their strengths and interests, enhancing engagement and performance. Proactive behavior involves self-initiated actions aimed at anticipating and addressing future challenges or opportunities within the workplace. Explore how integrating job crafting with proactive behavior drives innovation and organizational success.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between job crafting and proactive behavior is crucial for effective management because job crafting focuses on employees individually redesigning their roles to enhance job satisfaction and performance, while proactive behavior encompasses broader anticipatory actions aimed at improving work processes and organizational outcomes. Distinguishing these concepts enables managers to tailor development strategies that foster employee engagement and drive innovation within the organization. Properly leveraging job crafting can reduce turnover rates by empowering employees to align tasks with their strengths, whereas encouraging proactive behavior supports adaptability and resilience in dynamic business environments. This nuanced knowledge helps optimize resource allocation and cultivates a motivated workforce aligned with strategic goals.
Comparison Table
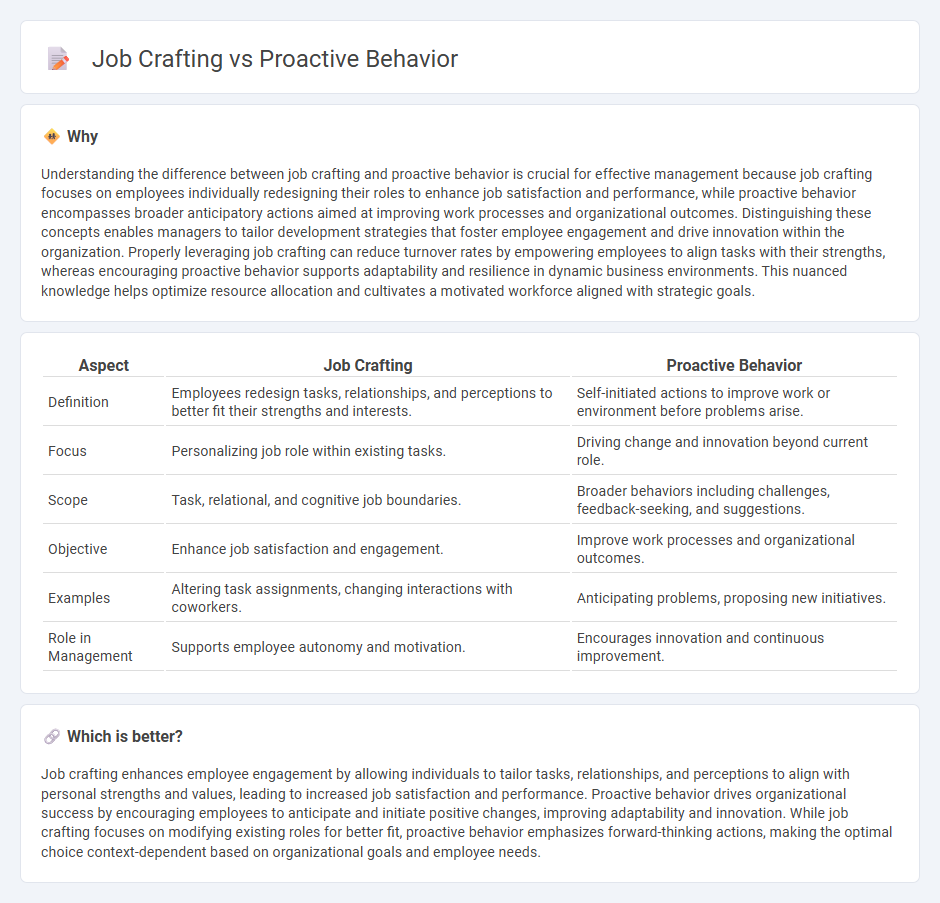
| Aspect | Job Crafting | Proactive Behavior |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Employees redesign tasks, relationships, and perceptions to better fit their strengths and interests. | Self-initiated actions to improve work or environment before problems arise. |
| Focus | Personalizing job role within existing tasks. | Driving change and innovation beyond current role. |
| Scope | Task, relational, and cognitive job boundaries. | Broader behaviors including challenges, feedback-seeking, and suggestions. |
| Objective | Enhance job satisfaction and engagement. | Improve work processes and organizational outcomes. |
| Examples | Altering task assignments, changing interactions with coworkers. | Anticipating problems, proposing new initiatives. |
| Role in Management | Supports employee autonomy and motivation. | Encourages innovation and continuous improvement. |
Which is better?
Job crafting enhances employee engagement by allowing individuals to tailor tasks, relationships, and perceptions to align with personal strengths and values, leading to increased job satisfaction and performance. Proactive behavior drives organizational success by encouraging employees to anticipate and initiate positive changes, improving adaptability and innovation. While job crafting focuses on modifying existing roles for better fit, proactive behavior emphasizes forward-thinking actions, making the optimal choice context-dependent based on organizational goals and employee needs.
Connection
Job crafting empowers employees to reshape their tasks, relationships, and perceptions at work, directly fostering proactive behavior by encouraging initiative and self-driven change. Proactive behavior, characterized by anticipatory actions and problem-solving, enhances job crafting by motivating individuals to seek opportunities for improvement and align their roles with personal strengths and interests. This dynamic interaction promotes higher job satisfaction, engagement, and organizational performance.
Key Terms
Initiative
Proactive behavior involves taking initiative to improve work processes and outcomes, while job crafting specifically refers to employees actively reshaping their job tasks and relationships to better align with their strengths and interests. Initiative in proactive behavior drives employees to anticipate changes and act ahead of time, whereas in job crafting, initiative manifests through personalized adjustments that enhance job satisfaction and engagement. Explore deeper insights into how initiative uniquely empowers proactive behavior and job crafting for workplace success.
Autonomy
Proactive behavior in the workplace involves employees taking initiative to improve their tasks and environment, often leading to increased autonomy by shaping their roles and responsibilities. Job crafting specifically refers to employees customizing their job boundaries, relationships, and perceptions to better fit their strengths and preferences, thereby enhancing their sense of autonomy. Explore how these concepts interrelate and impact employee motivation by delving deeper into autonomy's role in job design and performance.
Role Redefinition
Role redefinition in proactive behavior involves employees actively seeking to expand or modify their job responsibilities to better align with their strengths and interests, fostering personal and organizational growth. Job crafting emphasizes role redefinition as employees deliberately adjust job tasks, relationships, and cognitive perceptions to enhance work meaning and satisfaction. Explore more about how role redefinition shapes employee engagement and performance.
Source and External Links
What Does Proactive Mean? Mastering Proactivity in the Workplace - Proactive behavior involves anticipating future needs and challenges, taking initiative, and planning ahead to prevent problems rather than simply reacting to them.
Proactivity - Wikipedia - Proactive behavior refers to self-initiated actions aimed at solving problems before they occur, taking control, and making early changes instead of waiting or adjusting to situations.
PROACTIVE BEHAVIOR: MEANING, IMPACT, RECOMMENDATIONS - Proactive individuals constantly scan for opportunities, set ambitious, change-oriented goals, and focus on making a real impact in their environment.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com