Employee ghosting occurs when employees abruptly stop communicating and fail to show up for work without notice, creating operational disruptions and increased workload for remaining staff. Employee attrition refers to the gradual loss of employees through resignation or retirement, often managed through strategic workforce planning to minimize impact. Explore more about differentiating these phenomena and their effects on talent management strategies.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between employee ghosting and employee attrition is crucial for effective management because ghosting indicates sudden, unexplained departures, causing immediate operational disruptions, whereas attrition reflects a gradual, predictable workforce decline. Identifying ghosting patterns helps managers address engagement and communication issues, reducing turnover shock. Recognizing attrition trends enables strategic workforce planning and succession development. Accurate distinction enhances talent retention strategies and organizational stability.
Comparison Table
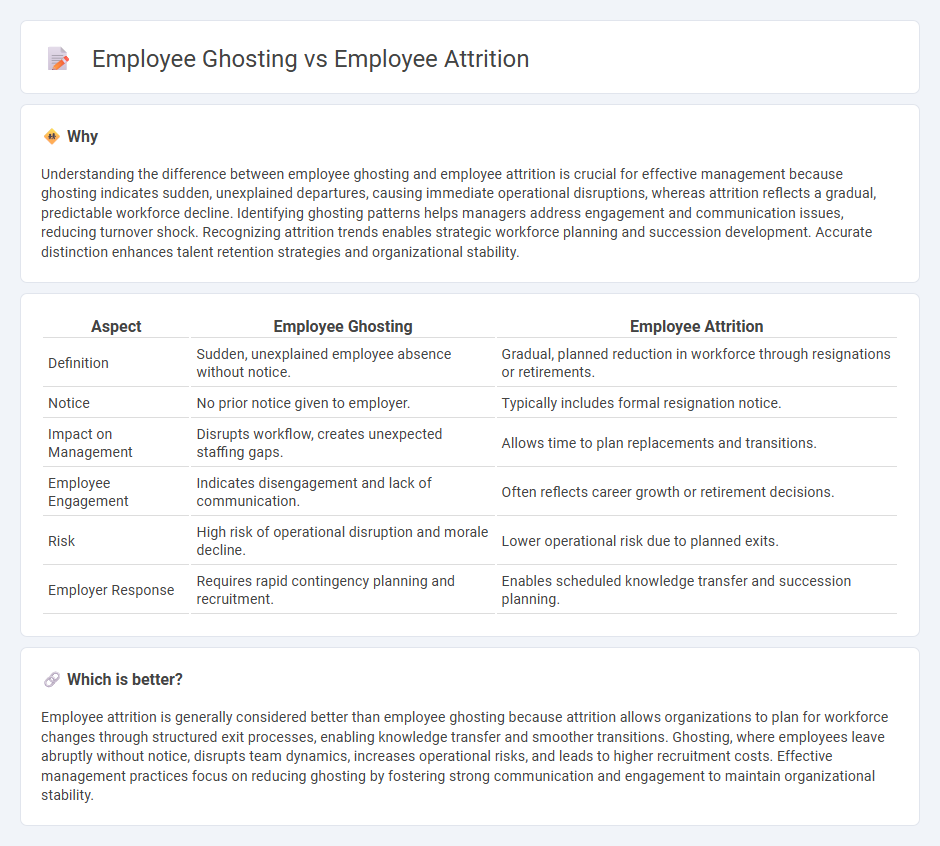
| Aspect | Employee Ghosting | Employee Attrition |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Sudden, unexplained employee absence without notice. | Gradual, planned reduction in workforce through resignations or retirements. |
| Notice | No prior notice given to employer. | Typically includes formal resignation notice. |
| Impact on Management | Disrupts workflow, creates unexpected staffing gaps. | Allows time to plan replacements and transitions. |
| Employee Engagement | Indicates disengagement and lack of communication. | Often reflects career growth or retirement decisions. |
| Risk | High risk of operational disruption and morale decline. | Lower operational risk due to planned exits. |
| Employer Response | Requires rapid contingency planning and recruitment. | Enables scheduled knowledge transfer and succession planning. |
Which is better?
Employee attrition is generally considered better than employee ghosting because attrition allows organizations to plan for workforce changes through structured exit processes, enabling knowledge transfer and smoother transitions. Ghosting, where employees leave abruptly without notice, disrupts team dynamics, increases operational risks, and leads to higher recruitment costs. Effective management practices focus on reducing ghosting by fostering strong communication and engagement to maintain organizational stability.
Connection
Employee ghosting, where workers abruptly stop communicating without notice, significantly contributes to increased employee attrition by disrupting workforce stability and productivity. High rates of ghosting signal underlying issues in management practices, such as poor engagement or inadequate onboarding processes, which directly escalate turnover rates. Addressing employee ghosting through improved communication and support strategies reduces attrition and fosters a more committed and stable workforce.
Key Terms
Retention
Employee attrition refers to the gradual loss of employees through retirement, resignation, or other voluntary exits, impacting workforce stability and increasing recruitment costs. Employee ghosting happens when employees abruptly stop communicating and fail to show up at work without notice, creating immediate operational disruptions and challenging retention strategies. Explore effective retention techniques to reduce both attrition and ghosting rates.
Turnover
Employee attrition refers to the gradual loss of employees through retirement, resignation, or other permanent exits, impacting overall turnover rates and workforce planning. Employee ghosting occurs when employees unexpectedly stop showing up or communicating, causing sudden disruptions and affecting short-term staffing stability. Explore strategies to manage these issues and reduce turnover effectively.
Disengagement
Employee attrition often results from ongoing disengagement, leading to voluntary resignation or retirement, whereas employee ghosting manifests abruptly with sudden, uncommunicated absences signaling severe disengagement or dissatisfaction. Both phenomena highlight critical challenges in workforce management, affecting productivity, team morale, and organizational culture. Explore strategies to detect early disengagement signs and address employee retention effectively.
Source and External Links
Attrition Definition, Types, Causes & Mitigation Tips - SHRM - Attrition is a gradual reduction in workforce due to retirement, resignations, deaths, or elimination of positions that are not immediately filled, often driven by factors like inadequate compensation, work-life imbalance, unrealistic workloads, poor management, cultural misalignment, and lack of career advancement opportunities.
Employee Attrition: Meaning, Impact & Attrition Rate Calculation - AIHR - Employee attrition occurs when employees leave the organization and are not replaced for a significant period, impacting operational continuity and often resulting from voluntary resignations, company restructuring, or demographic shifts in the workforce.
Employee Attrition 101: Definition, Types, Best Practices and More - splashBI - Attrition refers to employees leaving the company faster than new hires are brought in, with common types including voluntary (resignations), involuntary (layoffs, policy violations), retirement, and demographic-specific departures.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com