Leadership in management contrasts sharply between gig leadership and autocratic leadership, with gig leadership emphasizing flexibility, autonomy, and project-based roles, while autocratic leadership centers on centralized decision-making and strict control. Gig leadership thrives in dynamic, digital economies where innovation and adaptability are crucial, whereas autocratic leadership is more prevalent in traditional, hierarchical organizations requiring obedience and consistency. Explore the distinctive impacts and benefits of gig and autocratic leadership to enhance your management strategy.
Why it is important
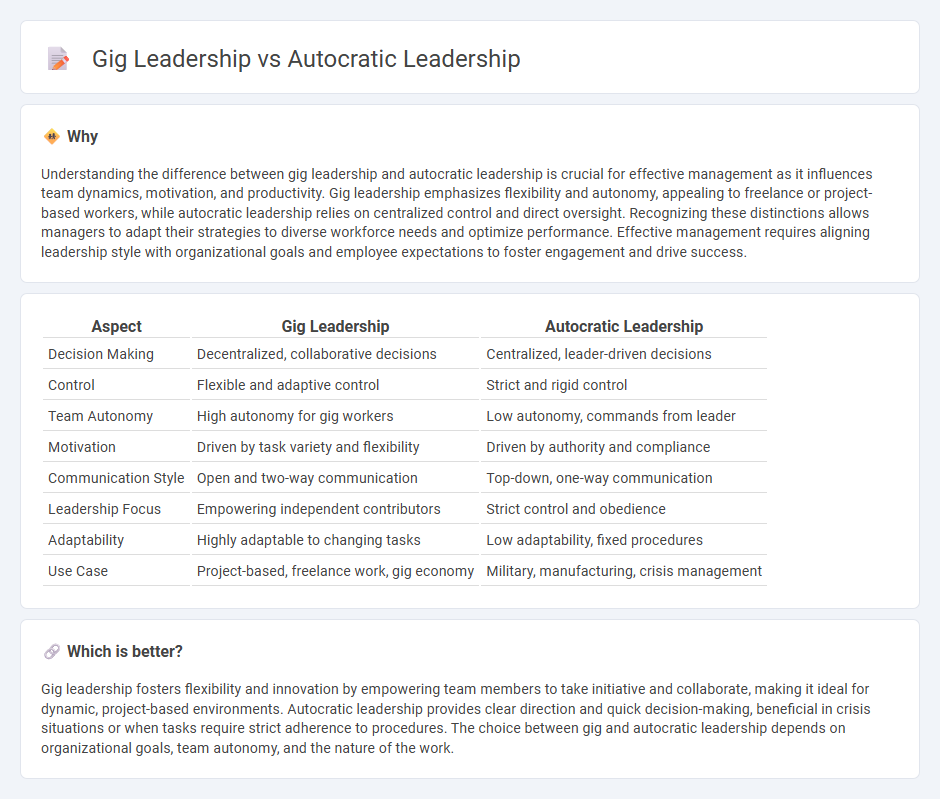
Understanding the difference between gig leadership and autocratic leadership is crucial for effective management as it influences team dynamics, motivation, and productivity. Gig leadership emphasizes flexibility and autonomy, appealing to freelance or project-based workers, while autocratic leadership relies on centralized control and direct oversight. Recognizing these distinctions allows managers to adapt their strategies to diverse workforce needs and optimize performance. Effective management requires aligning leadership style with organizational goals and employee expectations to foster engagement and drive success.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Gig Leadership | Autocratic Leadership |
|---|---|---|
| Decision Making | Decentralized, collaborative decisions | Centralized, leader-driven decisions |
| Control | Flexible and adaptive control | Strict and rigid control |
| Team Autonomy | High autonomy for gig workers | Low autonomy, commands from leader |
| Motivation | Driven by task variety and flexibility | Driven by authority and compliance |
| Communication Style | Open and two-way communication | Top-down, one-way communication |
| Leadership Focus | Empowering independent contributors | Strict control and obedience |
| Adaptability | Highly adaptable to changing tasks | Low adaptability, fixed procedures |
| Use Case | Project-based, freelance work, gig economy | Military, manufacturing, crisis management |
Which is better?
Gig leadership fosters flexibility and innovation by empowering team members to take initiative and collaborate, making it ideal for dynamic, project-based environments. Autocratic leadership provides clear direction and quick decision-making, beneficial in crisis situations or when tasks require strict adherence to procedures. The choice between gig and autocratic leadership depends on organizational goals, team autonomy, and the nature of the work.
Connection
Gig leadership and autocratic leadership connect through their emphasis on clear direction and control over tasks, although gig leadership adapts to flexible, project-based work environments while autocratic leadership relies on top-down decision-making. Both styles prioritize efficiency and task completion, with gig leaders managing diverse, temporary teams and autocratic leaders enforcing strict authority to drive performance. Understanding these connections helps optimize leadership strategies in dynamic organizational settings.
Key Terms
Decision-making
Autocratic leadership centralizes decision-making power in a single leader, ensuring rapid and consistent choices often without input from team members, which suits high-stakes or crisis environments. Gig leadership distributes decision-making across independent contractors or freelancers, promoting flexibility and innovation but sometimes resulting in less cohesive strategic direction due to varied individual priorities. Explore these leadership styles further to understand their impact on organizational agility and team dynamics.
Authority
Autocratic leadership centralizes authority, with decision-making power held by a single leader who directs tasks and enforces strict control over team members. Gig leadership, by contrast, distributes authority among independent contractors or freelancers, fostering autonomy and flexible collaboration without hierarchical constraints. Explore how these leadership models impact organizational efficiency and workforce engagement.
Flexibility
Autocratic leadership features rigid decision-making processes with minimal employee input, resulting in limited flexibility for adapting to dynamic work environments. In contrast, gig leadership embraces flexibility by empowering independent contractors to manage their schedules and tasks, promoting agility and responsiveness. Explore how these leadership styles impact organizational performance and employee satisfaction to understand which approach suits your business needs best.
Source and External Links
Autocratic Leadership: Definition & Examples - AIHR - Autocratic leadership is a management style where a single leader holds all decision-making power without input from group members, enforcing strict obedience and clear authority, often effective in scenarios requiring discipline and precision.
Autocratic Leadership Style: Definition, Examples, Pros & Cons - This leadership style involves unilateral decision-making with limited stakeholder input, a highly structured environment, and clearly defined rules, which may boost efficiency but can reduce creativity and employee morale.
What Is Autocratic Leadership? | Rasmussen University - Autocratic leadership is characterized by a dominant leader who makes all decisions independently, discourages input or feedback, demands loyalty, prioritizes task completion over collaboration, and creates an environment focused on rules and hierarchy.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com