Reverse mentorship leverages the expertise of younger or less experienced employees to guide senior leaders, fostering fresh perspectives and innovation. Peer mentorship involves colleagues at similar levels sharing knowledge and support to enhance professional growth and collaboration. Explore how both approaches transform organizational dynamics and leadership development.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between reverse mentorship and peer mentorship is crucial for effectively leveraging diverse expertise and fostering innovation within an organization. Reverse mentorship pairs junior employees with senior leaders to share fresh perspectives and technological insights, enhancing leadership adaptability. Peer mentorship involves colleagues at similar levels collaborating for mutual skill development and support, boosting team cohesion. Recognizing these distinctions enables tailored mentorship strategies that optimize knowledge transfer and professional growth.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Reverse Mentorship | Peer Mentorship |
|---|---|---|
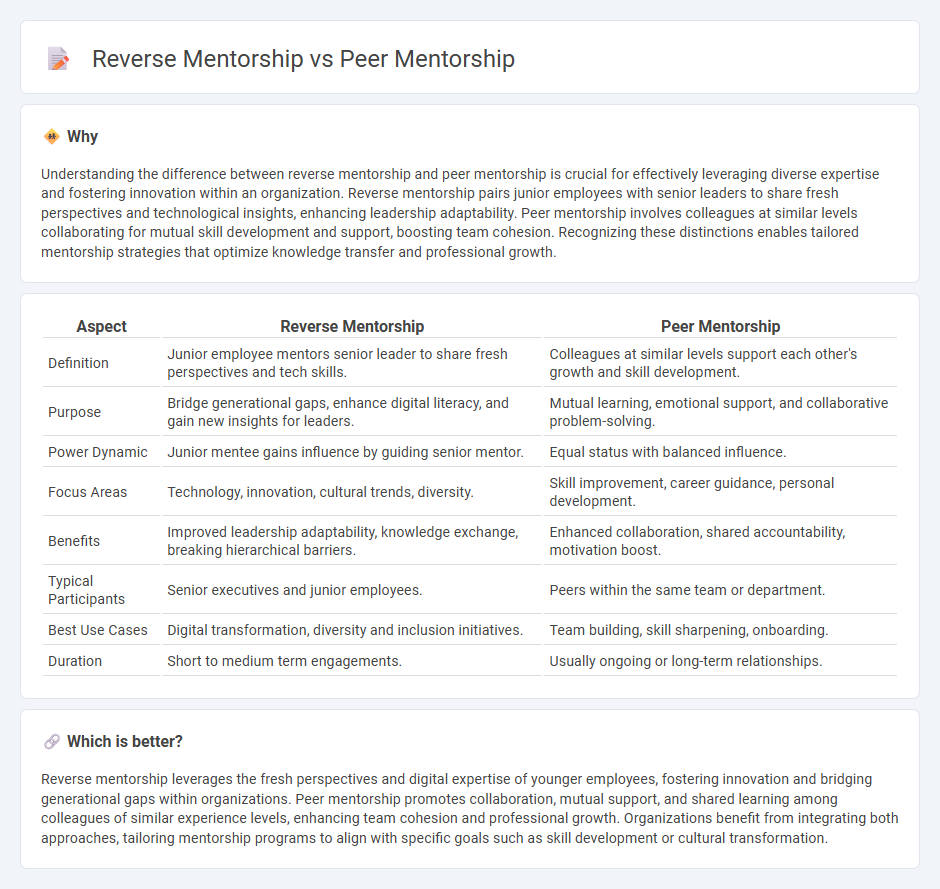
| Definition | Junior employee mentors senior leader to share fresh perspectives and tech skills. | Colleagues at similar levels support each other's growth and skill development. |
| Purpose | Bridge generational gaps, enhance digital literacy, and gain new insights for leaders. | Mutual learning, emotional support, and collaborative problem-solving. |
| Power Dynamic | Junior mentee gains influence by guiding senior mentor. | Equal status with balanced influence. |
| Focus Areas | Technology, innovation, cultural trends, diversity. | Skill improvement, career guidance, personal development. |
| Benefits | Improved leadership adaptability, knowledge exchange, breaking hierarchical barriers. | Enhanced collaboration, shared accountability, motivation boost. |
| Typical Participants | Senior executives and junior employees. | Peers within the same team or department. |
| Best Use Cases | Digital transformation, diversity and inclusion initiatives. | Team building, skill sharpening, onboarding. |
| Duration | Short to medium term engagements. | Usually ongoing or long-term relationships. |
Which is better?
Reverse mentorship leverages the fresh perspectives and digital expertise of younger employees, fostering innovation and bridging generational gaps within organizations. Peer mentorship promotes collaboration, mutual support, and shared learning among colleagues of similar experience levels, enhancing team cohesion and professional growth. Organizations benefit from integrating both approaches, tailoring mentorship programs to align with specific goals such as skill development or cultural transformation.
Connection
Reverse mentorship and peer mentorship are connected through their focus on knowledge exchange and skill development across different experience levels and roles within an organization. Both approaches foster collaborative learning environments where diverse perspectives drive innovation and improve leadership effectiveness. Implementing these mentorship models enhances organizational agility by bridging generational gaps and promoting continuous professional growth.
Key Terms
Knowledge Transfer
Peer mentorship facilitates knowledge transfer through mutual sharing of skills and experiences among colleagues with similar expertise, fostering collaborative learning environments. Reverse mentorship enables junior employees to impart fresh perspectives, technological skills, and contemporary industry trends to senior staff, enhancing organizational agility. Explore how these mentorship models can optimize knowledge transfer effectively within your team.
Leadership Development
Peer mentorship fosters leadership development by enabling individuals at similar career stages to share experiences, challenges, and strategies, enhancing mutual growth and collaboration skills. Reverse mentorship accelerates leadership skills by connecting senior leaders with younger employees, promoting fresh perspectives, technological literacy, and adaptability critical for modern leadership. Explore each approach's impact on leadership development to determine the best fit for your organizational culture and goals.
Generational Diversity
Peer mentorship fosters knowledge sharing among individuals of similar age or experience, enhancing collaboration within generational groups like Millennials or Gen Z. Reverse mentorship bridges generational diversity by allowing younger employees to share insights on technology, social media, and contemporary trends with senior leaders. Explore how organizations leverage these strategies to maximize cross-generational learning and innovation.
Source and External Links
Peer mentoring - Peer mentoring involves an experienced individual supporting someone new to a specific experience, such as students or patients, focusing on education, support, and motivation, often within similar life situations or challenges.
What is Peer Mentoring? - Peer mentoring is a reciprocal mentorship where two people of similar experience share advice and learn from each other, commonly used in workplaces to foster professional development on an equal footing.
Peer Mentor Programs: What They Are and How to Start One - Peer mentoring programs emphasize lateral relationships between mentors and mentees close in age or experience, promoting collaboration, small-goal setting, and creating ground rules to facilitate effective, pressure-free exchanges.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com