Shadow boards consist of emerging leaders providing fresh perspectives directly to senior executives, fostering innovation and agile decision-making. Stakeholder panels engage external parties, including customers and community members, to ensure diverse interests shape strategic directions and corporate responsibility. Explore further to understand how these governance tools enhance organizational effectiveness and inclusive leadership.
Why it is important
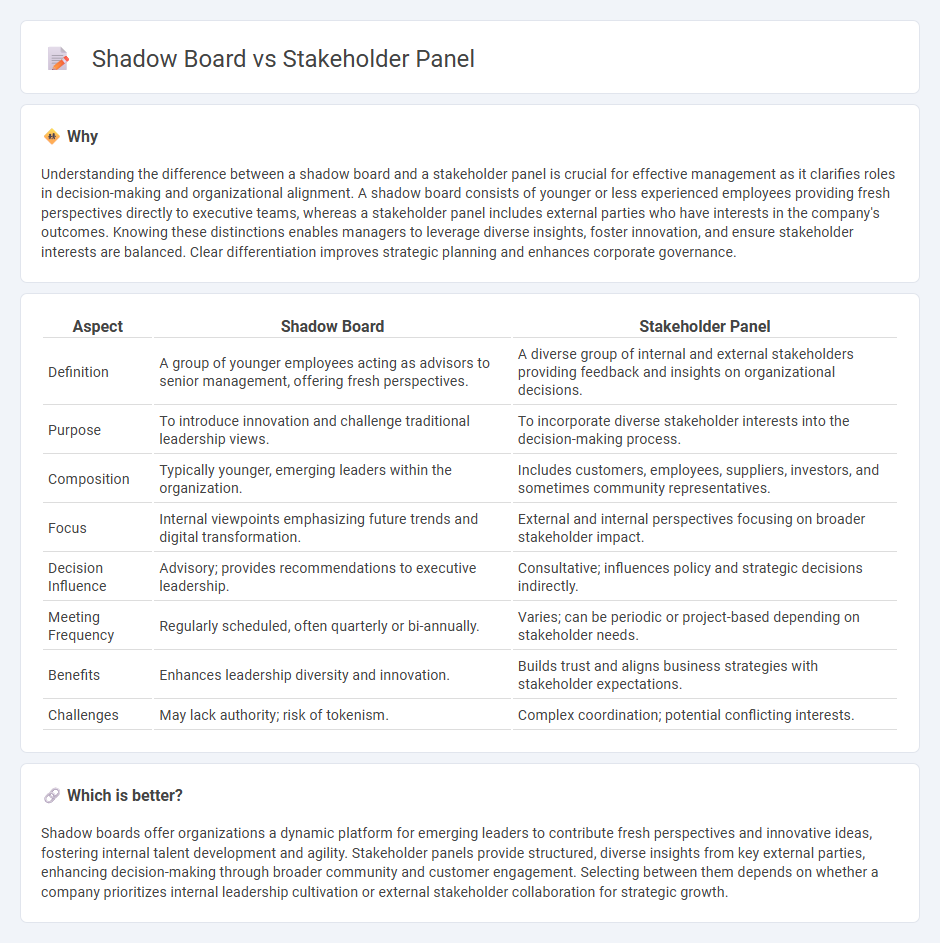
Understanding the difference between a shadow board and a stakeholder panel is crucial for effective management as it clarifies roles in decision-making and organizational alignment. A shadow board consists of younger or less experienced employees providing fresh perspectives directly to executive teams, whereas a stakeholder panel includes external parties who have interests in the company's outcomes. Knowing these distinctions enables managers to leverage diverse insights, foster innovation, and ensure stakeholder interests are balanced. Clear differentiation improves strategic planning and enhances corporate governance.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Shadow Board | Stakeholder Panel |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A group of younger employees acting as advisors to senior management, offering fresh perspectives. | A diverse group of internal and external stakeholders providing feedback and insights on organizational decisions. |
| Purpose | To introduce innovation and challenge traditional leadership views. | To incorporate diverse stakeholder interests into the decision-making process. |
| Composition | Typically younger, emerging leaders within the organization. | Includes customers, employees, suppliers, investors, and sometimes community representatives. |
| Focus | Internal viewpoints emphasizing future trends and digital transformation. | External and internal perspectives focusing on broader stakeholder impact. |
| Decision Influence | Advisory; provides recommendations to executive leadership. | Consultative; influences policy and strategic decisions indirectly. |
| Meeting Frequency | Regularly scheduled, often quarterly or bi-annually. | Varies; can be periodic or project-based depending on stakeholder needs. |
| Benefits | Enhances leadership diversity and innovation. | Builds trust and aligns business strategies with stakeholder expectations. |
| Challenges | May lack authority; risk of tokenism. | Complex coordination; potential conflicting interests. |
Which is better?
Shadow boards offer organizations a dynamic platform for emerging leaders to contribute fresh perspectives and innovative ideas, fostering internal talent development and agility. Stakeholder panels provide structured, diverse insights from key external parties, enhancing decision-making through broader community and customer engagement. Selecting between them depends on whether a company prioritizes internal leadership cultivation or external stakeholder collaboration for strategic growth.
Connection
A shadow board and a stakeholder panel both enhance organizational decision-making by incorporating diverse perspectives beyond traditional leadership. A shadow board typically consists of emerging employees providing fresh insights, while a stakeholder panel includes representatives from key external stakeholders such as customers or partners. Their connection lies in fostering inclusive governance, improving innovation, and aligning management strategies with varied internal and external interests.
Key Terms
Representation
Stakeholder panels prioritize diverse representation by including various internal and external parties such as employees, customers, and community members to ensure broad perspectives in decision-making. Shadow boards consist mainly of emerging leaders or younger employees who provide fresh insights and innovative ideas to complement executive decisions. Explore the differences further to understand how each structure enhances organizational governance.
Decision-making
A stakeholder panel involves diverse representatives who provide input and feedback to influence strategic decisions, ensuring alignment with broad organizational interests. A shadow board comprises younger or emerging leaders who simulate decision-making processes to challenge senior management and foster innovation. Explore deeper insights into how these governance structures enhance decision-making dynamics in modern organizations.
Perspective diversity
Stakeholder panels prioritize diverse interests by incorporating representatives from various groups affected by business decisions, fostering a broad range of perspectives. Shadow boards consist of younger employees or emerging leaders who challenge existing management with fresh viewpoints and innovative ideas. Explore how these approaches enhance organizational insight and strategic decision-making.
Source and External Links
The LibrarIN Stakeholder Panel - A diverse group of 29 members from Europe, representing various libraries and organizations, aiming to bring innovation to libraries through collaboration and expertise sharing.
Ipieca Stakeholder Panel - Comprises independent experts in sustainability reporting, focusing on the energy sector to ensure Guidance captures key challenges and supports transparent reporting.
InnoSocial Stakeholder Panels - A series of discussions gathering over 70 representatives from various stakeholder groups to refine the InnoSocial Toolkit for inclusive innovation and social entrepreneurship in education.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com