Digital body language encompasses nonverbal cues conveyed through virtual interactions, including response times, emoji usage, and message tone, which influence team dynamics and communication effectiveness. Asynchronous messaging allows team members to engage across different time zones and schedules, promoting flexibility but requiring clear, intentional messaging to avoid misunderstandings. Explore how mastering digital body language enhances asynchronous communication and boosts remote team management success.
Why it is important
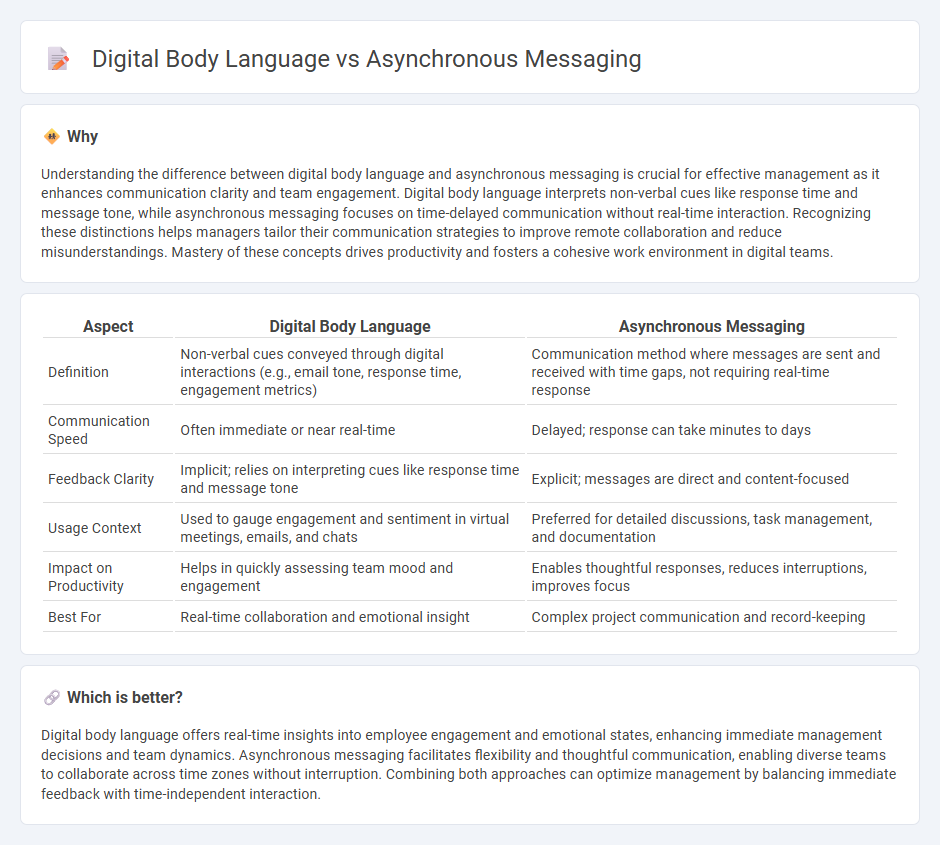
Understanding the difference between digital body language and asynchronous messaging is crucial for effective management as it enhances communication clarity and team engagement. Digital body language interprets non-verbal cues like response time and message tone, while asynchronous messaging focuses on time-delayed communication without real-time interaction. Recognizing these distinctions helps managers tailor their communication strategies to improve remote collaboration and reduce misunderstandings. Mastery of these concepts drives productivity and fosters a cohesive work environment in digital teams.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Digital Body Language | Asynchronous Messaging |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Non-verbal cues conveyed through digital interactions (e.g., email tone, response time, engagement metrics) | Communication method where messages are sent and received with time gaps, not requiring real-time response |
| Communication Speed | Often immediate or near real-time | Delayed; response can take minutes to days |
| Feedback Clarity | Implicit; relies on interpreting cues like response time and message tone | Explicit; messages are direct and content-focused |
| Usage Context | Used to gauge engagement and sentiment in virtual meetings, emails, and chats | Preferred for detailed discussions, task management, and documentation |
| Impact on Productivity | Helps in quickly assessing team mood and engagement | Enables thoughtful responses, reduces interruptions, improves focus |
| Best For | Real-time collaboration and emotional insight | Complex project communication and record-keeping |
Which is better?
Digital body language offers real-time insights into employee engagement and emotional states, enhancing immediate management decisions and team dynamics. Asynchronous messaging facilitates flexibility and thoughtful communication, enabling diverse teams to collaborate across time zones without interruption. Combining both approaches can optimize management by balancing immediate feedback with time-independent interaction.
Connection
Digital body language and asynchronous messaging intersect by enabling effective communication cues despite time gaps, enhancing remote management efficiency. Understanding digital body language, such as response times and message tone, allows managers to gauge team sentiment and engagement in asynchronous platforms like email or project management tools. This connection fosters clearer collaboration, reduces misunderstandings, and improves workflow in distributed work environments.
Key Terms
Communication Channels
Asynchronous messaging, characterized by delayed responses in platforms like email and chat, contrasts with digital body language, which interprets real-time online behaviors such as typing indicators, read receipts, and reaction emojis. These communication channels offer unique insights, where asynchronous messaging allows thoughtful expression while digital body language enhances understanding of engagement and emotional context. Explore how leveraging these channels can optimize communication effectiveness in remote and hybrid work environments.
Feedback Loops
Asynchronous messaging enables flexible communication by allowing participants to respond at their convenience, which can slow feedback loops and reduce immediate interaction cues present in synchronous exchanges. Digital body language, including response time, message tone, and emoji usage, serves as critical indicators within asynchronous feedback loops to interpret user sentiment and engagement levels accurately. Explore deeper into how optimizing feedback loops through understanding these subtle digital cues can enhance remote teamwork and customer interactions.
Context Interpretation
Asynchronous messaging allows users to communicate without real-time interaction, making context interpretation reliant on message tone, phrasing, and timing. Digital body language, which includes cues such as response speed, message length, and engagement patterns, enhances understanding by providing non-verbal signals that clarify intent and emotion. Explore how combining these elements improves communication accuracy and remote collaboration effectiveness.
Source and External Links
What is An Asynchronous Messaging? + Its Importance - Asynchronous messaging refers to a communication method where parties can send messages without needing to be concurrently active, allowing users to multitask while waiting for a response.
What is asynchronous messaging + how does it work? - Asynchronous messaging enables customers to start, pause, and resume conversations at their convenience, maintaining a continuous thread of communication.
What is asynchronous messaging? - Asynchronous messaging involves exchanging messages at irregular intervals, allowing communication without the need for an immediate response.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com