Distributed workforce leverages remote employees working across multiple locations, enhancing flexibility and access to global talent pools. Autonomous teams operate independently within organizations, making decisions and managing workflows without constant supervision, driving innovation and accountability. Explore how integrating both approaches can transform modern management for greater efficiency and engagement.
Why it is important
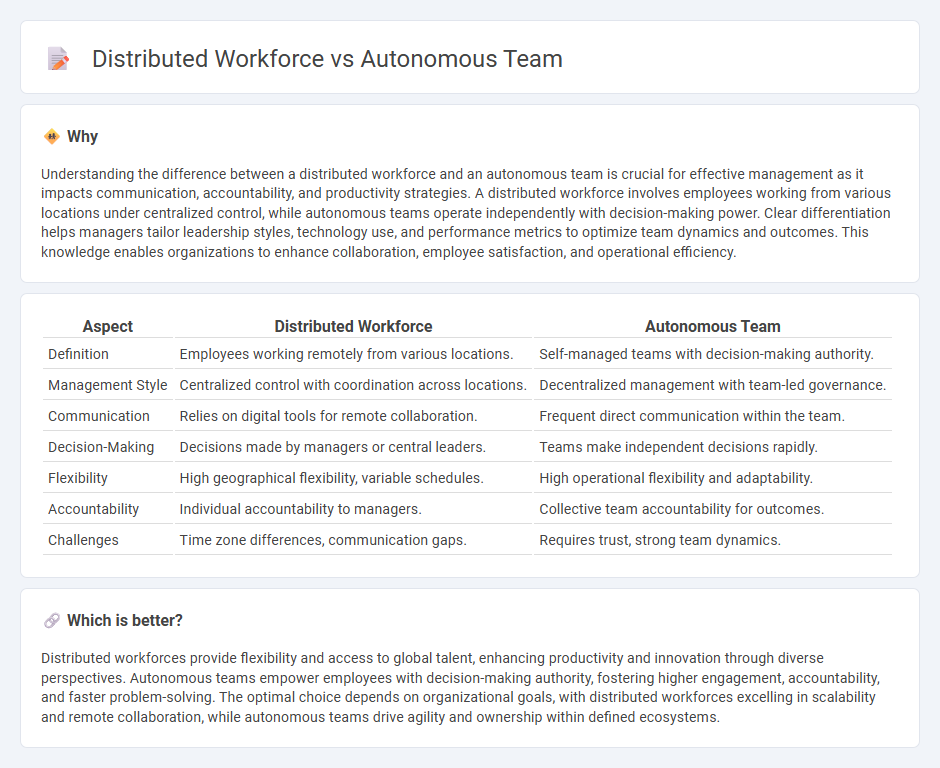
Understanding the difference between a distributed workforce and an autonomous team is crucial for effective management as it impacts communication, accountability, and productivity strategies. A distributed workforce involves employees working from various locations under centralized control, while autonomous teams operate independently with decision-making power. Clear differentiation helps managers tailor leadership styles, technology use, and performance metrics to optimize team dynamics and outcomes. This knowledge enables organizations to enhance collaboration, employee satisfaction, and operational efficiency.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Distributed Workforce | Autonomous Team |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Employees working remotely from various locations. | Self-managed teams with decision-making authority. |
| Management Style | Centralized control with coordination across locations. | Decentralized management with team-led governance. |
| Communication | Relies on digital tools for remote collaboration. | Frequent direct communication within the team. |
| Decision-Making | Decisions made by managers or central leaders. | Teams make independent decisions rapidly. |
| Flexibility | High geographical flexibility, variable schedules. | High operational flexibility and adaptability. |
| Accountability | Individual accountability to managers. | Collective team accountability for outcomes. |
| Challenges | Time zone differences, communication gaps. | Requires trust, strong team dynamics. |
Which is better?
Distributed workforces provide flexibility and access to global talent, enhancing productivity and innovation through diverse perspectives. Autonomous teams empower employees with decision-making authority, fostering higher engagement, accountability, and faster problem-solving. The optimal choice depends on organizational goals, with distributed workforces excelling in scalability and remote collaboration, while autonomous teams drive agility and ownership within defined ecosystems.
Connection
Distributed workforce relies on autonomous teams to maintain productivity and decision-making efficiency across different locations. Autonomous teams empower employees with decentralized control, enabling seamless collaboration and rapid problem-solving despite geographical dispersion. This synergy enhances organizational agility and supports scalable management in dynamic business environments.
Key Terms
Decision-Making Authority
Autonomous teams possess high decision-making authority, enabling swift, independent choices without constant managerial approval, which enhances agility and accountability. Distributed workforces operate across diverse locations but often maintain centralized decision-making structures, potentially slowing response times. Explore how these dynamics impact organizational efficiency and employee empowerment by learning more.
Collaboration Tools
Autonomous teams leverage collaboration tools like Slack, Trello, and Zoom to enhance self-managed project workflows and real-time decision-making, fostering agility and accountability. Distributed workforces depend heavily on cloud platforms such as Microsoft Teams and Google Workspace, enabling seamless communication and document sharing across multiple time zones and locations. Explore how selecting the right collaboration tools can optimize productivity and connectivity for both autonomous teams and distributed workforces.
Geographic Dispersion
Autonomous teams operate independently with decision-making authority, often within a single location, enabling focused collaboration and streamlined communication. Distributed workforces consist of employees spread across multiple geographic locations, leveraging technology to maintain productivity despite physical separation. Explore the key differences in managing geographic dispersion and enhancing team efficiency in both models.
Source and External Links
Autonomous Work Group - Wikipedia - An autonomous work group is a team that manages its own work and practices with minimal external supervision, often selecting and training new members and making decisions collaboratively.
Autonomous Work Group - An autonomous work group operates independently, making decisions without direct management supervision, and often handles tasks like hiring and training new members.
How to Create an Autonomous Team - Creating an autonomous team involves giving team members the freedom to set their own pace and workflow, allowing them to respond quickly to new information and make decisions independently.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com