Distributed workforce models enable organizations to operate with employees working remotely across various locations, enhancing flexibility and global talent access. Gig workforce strategies rely on independent contractors or freelancers engaged for specific tasks or projects, offering scalability and cost efficiency. Discover how these workforce structures impact productivity and business agility in modern management.
Why it is important
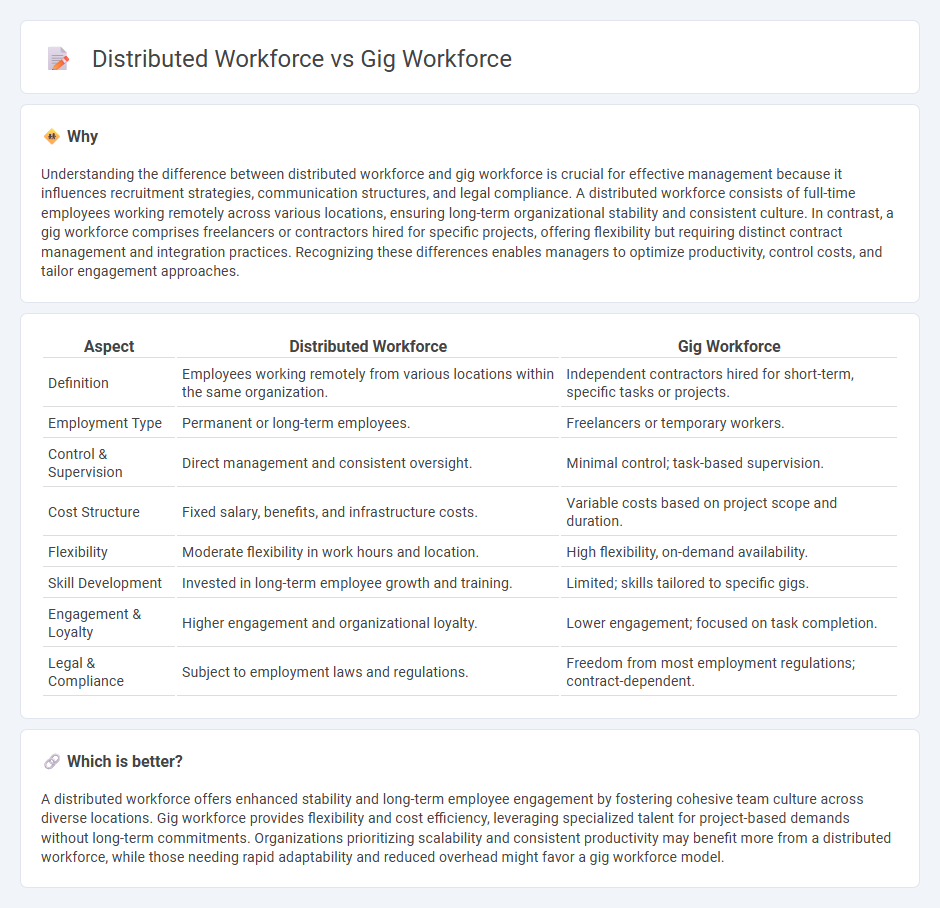
Understanding the difference between distributed workforce and gig workforce is crucial for effective management because it influences recruitment strategies, communication structures, and legal compliance. A distributed workforce consists of full-time employees working remotely across various locations, ensuring long-term organizational stability and consistent culture. In contrast, a gig workforce comprises freelancers or contractors hired for specific projects, offering flexibility but requiring distinct contract management and integration practices. Recognizing these differences enables managers to optimize productivity, control costs, and tailor engagement approaches.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Distributed Workforce | Gig Workforce |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Employees working remotely from various locations within the same organization. | Independent contractors hired for short-term, specific tasks or projects. |
| Employment Type | Permanent or long-term employees. | Freelancers or temporary workers. |
| Control & Supervision | Direct management and consistent oversight. | Minimal control; task-based supervision. |
| Cost Structure | Fixed salary, benefits, and infrastructure costs. | Variable costs based on project scope and duration. |
| Flexibility | Moderate flexibility in work hours and location. | High flexibility, on-demand availability. |
| Skill Development | Invested in long-term employee growth and training. | Limited; skills tailored to specific gigs. |
| Engagement & Loyalty | Higher engagement and organizational loyalty. | Lower engagement; focused on task completion. |
| Legal & Compliance | Subject to employment laws and regulations. | Freedom from most employment regulations; contract-dependent. |
Which is better?
A distributed workforce offers enhanced stability and long-term employee engagement by fostering cohesive team culture across diverse locations. Gig workforce provides flexibility and cost efficiency, leveraging specialized talent for project-based demands without long-term commitments. Organizations prioritizing scalability and consistent productivity may benefit more from a distributed workforce, while those needing rapid adaptability and reduced overhead might favor a gig workforce model.
Connection
Distributed workforce models leverage the flexibility and remote capabilities inherent in gig workforce structures, enabling organizations to access diverse talent pools globally. Both approaches rely on digital platforms and cloud-based tools to coordinate tasks, ensuring efficient communication and project management across time zones. Integrating gig workers into distributed teams enhances scalability and operational agility, critical for evolving business environments.
Key Terms
Flexibility
The gig workforce offers unparalleled flexibility by allowing individuals to choose projects, set their schedules, and work from various locations without long-term commitments. The distributed workforce provides flexibility through decentralized teams that operate across different time zones, enhancing global collaboration and work-life balance. Explore more about the distinct flexibility benefits and challenges of gig versus distributed workforces.
Remote Collaboration
The gig workforce consists of freelancers or contract workers engaged for specific projects, often working independently with flexible schedules, while the distributed workforce includes full-time employees spread across various geographic locations collaborating as a cohesive unit. Remote collaboration tools such as Slack, Zoom, and Asana play pivotal roles in both models, enabling real-time communication and seamless project management despite physical separation. Explore in-depth strategies to enhance remote collaboration efficiency within gig and distributed workforces.
Talent Sourcing
Gig workforce leverages independent contractors for short-term projects, offering flexibility and specialized skills, while distributed workforce consists of full-time remote employees working across various locations, enhancing collaboration and continuity. Talent sourcing for gig workers emphasizes rapid access to niche expertise via platforms like Upwork or Fiverr, whereas distributed workforce sourcing prioritizes long-term cultural fit and remote work capabilities through comprehensive recruitment processes and tools. Explore key strategies to optimize talent sourcing for both gig and distributed workforces to boost organizational agility.
Source and External Links
ADP Research: Insights Into the Gig Workforce - This report provides insights into the gig workforce, highlighting its impact on businesses and the prevalence of gig workers across various industries.
Wikipedia: Gig Worker - Defines gig workers as independent contractors, online platform workers, and temporary workers, noting their global presence and challenges.
Maryville Online: What Is the Gig Economy? - Explains the gig economy as a system where people earn money from on-demand work, highlighting shifts in workforce demographics and the preference for flexible work arrangements.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com