Lazy management focuses on minimal intervention, relying on established processes and routine monitoring to maintain operations with low effort and cost. Active management involves continuous oversight, decision-making, and dynamic adjustments to optimize performance and address emerging challenges. Discover how these management styles impact organizational success and efficiency.
Why it is important
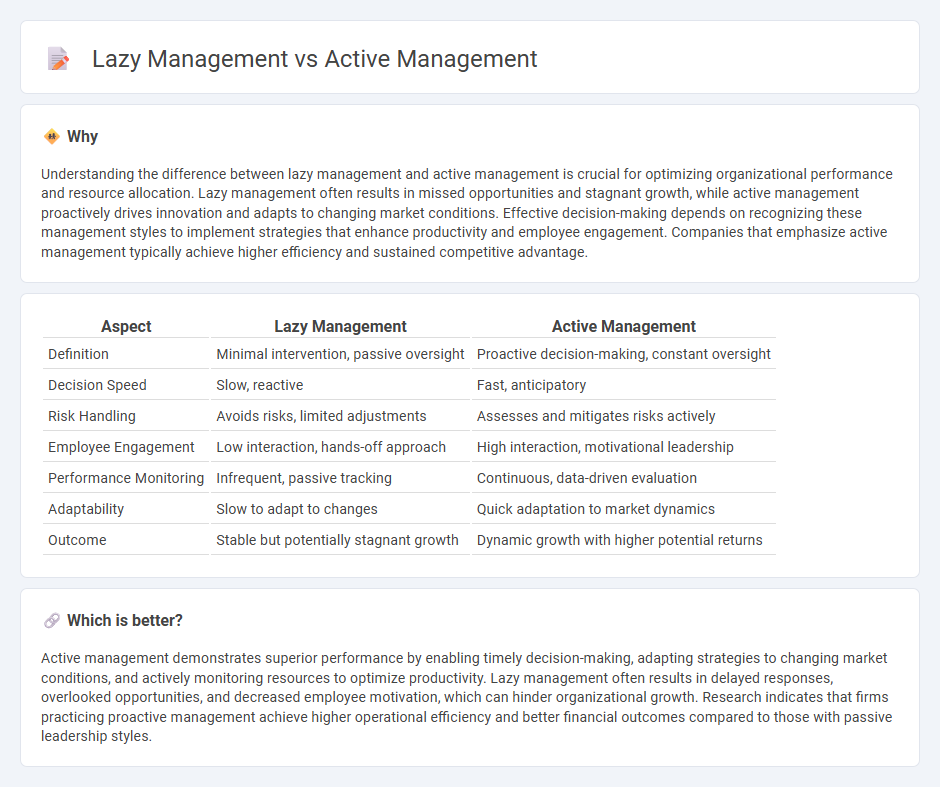
Understanding the difference between lazy management and active management is crucial for optimizing organizational performance and resource allocation. Lazy management often results in missed opportunities and stagnant growth, while active management proactively drives innovation and adapts to changing market conditions. Effective decision-making depends on recognizing these management styles to implement strategies that enhance productivity and employee engagement. Companies that emphasize active management typically achieve higher efficiency and sustained competitive advantage.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Lazy Management | Active Management |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Minimal intervention, passive oversight | Proactive decision-making, constant oversight |
| Decision Speed | Slow, reactive | Fast, anticipatory |
| Risk Handling | Avoids risks, limited adjustments | Assesses and mitigates risks actively |
| Employee Engagement | Low interaction, hands-off approach | High interaction, motivational leadership |
| Performance Monitoring | Infrequent, passive tracking | Continuous, data-driven evaluation |
| Adaptability | Slow to adapt to changes | Quick adaptation to market dynamics |
| Outcome | Stable but potentially stagnant growth | Dynamic growth with higher potential returns |
Which is better?
Active management demonstrates superior performance by enabling timely decision-making, adapting strategies to changing market conditions, and actively monitoring resources to optimize productivity. Lazy management often results in delayed responses, overlooked opportunities, and decreased employee motivation, which can hinder organizational growth. Research indicates that firms practicing proactive management achieve higher operational efficiency and better financial outcomes compared to those with passive leadership styles.
Connection
Lazy management and active management represent opposite approaches in organizational leadership, where lazy management involves minimal intervention and reliance on employees' self-direction, potentially leading to decreased productivity and accountability. Active management emphasizes continuous oversight, strategic planning, and proactive problem-solving to optimize performance and drive business objectives. Both styles impact workforce motivation, operational efficiency, and company culture, influencing long-term success and adaptability in dynamic markets.
Key Terms
Decision-making
Active management involves continuous decision-making and frequent portfolio adjustments based on market analysis, aiming to outperform benchmarks through skilled asset selection and timing. Lazy management, or passive management, relies on long-term investment in index funds or ETFs, minimizing decisions to reduce costs and maintain market-average returns. Explore the advantages and strategies of both approaches for informed investment decisions.
Engagement
Active management emphasizes continuous employee engagement through regular feedback, goal-setting, and personalized support to boost productivity and morale. Lazy management often neglects these practices, leading to disengagement, reduced motivation, and higher turnover rates. Discover how integrating active engagement strategies can transform workforce performance and satisfaction.
Oversight
Active management emphasizes continuous oversight through frequent portfolio analysis, real-time market monitoring, and tactical adjustments to capitalize on emerging opportunities. Lazy management relies on minimal oversight, often employing passive index tracking with periodic rebalancing to maintain alignment with target allocations. Discover how differing oversight approaches impact investment performance and risk management strategies.
Source and External Links
Active management - Active management is an investing approach where the investor selects specific investments to try to outperform the market, offering flexibility to tailor risk, emphasize income, and align with personal goals, though it tends to be more costly and potentially less tax-efficient than passive management.
Active Management - Overview, How It Works, Process - Active management uses human judgment and research to select securities believed to be mispriced, aiming to generate returns above a benchmark, though most active managers struggle to consistently beat passive funds and charge higher fees.
What Is Active Management? - Active management involves selecting investments through fundamental or quantitative research and includes security selection, asset allocation, and sustainability analysis; it remains the dominant investing approach despite being contrasted with passive strategies.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com