A growth mindset embraces challenges as opportunities for learning and development, fostering resilience and continuous improvement in management practices. In contrast, an avoidance mindset resists change, hindering innovation and limiting team potential by focusing on fear of failure rather than progress. Explore key strategies to cultivate a growth mindset and enhance leadership effectiveness.
Why it is important
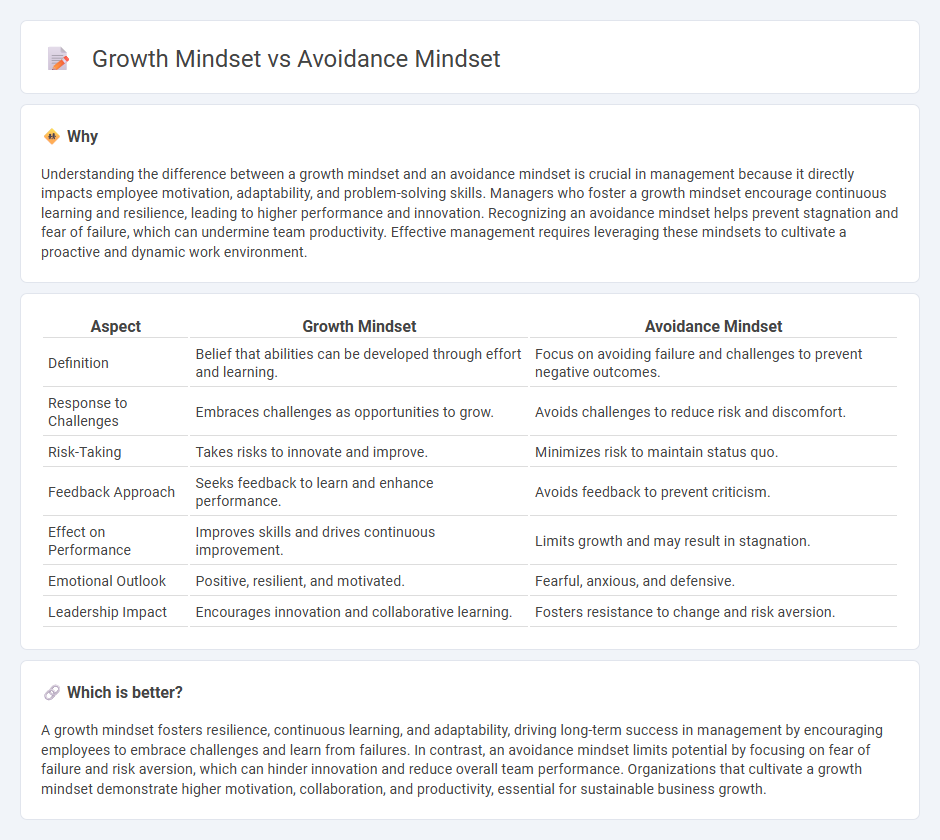
Understanding the difference between a growth mindset and an avoidance mindset is crucial in management because it directly impacts employee motivation, adaptability, and problem-solving skills. Managers who foster a growth mindset encourage continuous learning and resilience, leading to higher performance and innovation. Recognizing an avoidance mindset helps prevent stagnation and fear of failure, which can undermine team productivity. Effective management requires leveraging these mindsets to cultivate a proactive and dynamic work environment.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Growth Mindset | Avoidance Mindset |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Belief that abilities can be developed through effort and learning. | Focus on avoiding failure and challenges to prevent negative outcomes. |
| Response to Challenges | Embraces challenges as opportunities to grow. | Avoids challenges to reduce risk and discomfort. |
| Risk-Taking | Takes risks to innovate and improve. | Minimizes risk to maintain status quo. |
| Feedback Approach | Seeks feedback to learn and enhance performance. | Avoids feedback to prevent criticism. |
| Effect on Performance | Improves skills and drives continuous improvement. | Limits growth and may result in stagnation. |
| Emotional Outlook | Positive, resilient, and motivated. | Fearful, anxious, and defensive. |
| Leadership Impact | Encourages innovation and collaborative learning. | Fosters resistance to change and risk aversion. |
Which is better?
A growth mindset fosters resilience, continuous learning, and adaptability, driving long-term success in management by encouraging employees to embrace challenges and learn from failures. In contrast, an avoidance mindset limits potential by focusing on fear of failure and risk aversion, which can hinder innovation and reduce overall team performance. Organizations that cultivate a growth mindset demonstrate higher motivation, collaboration, and productivity, essential for sustainable business growth.
Connection
A growth mindset fosters continuous learning and resilience, enabling managers to embrace challenges and improve performance. In contrast, an avoidance mindset leads to fear of failure, limiting risk-taking and innovation within teams. Understanding the interplay between these mindsets helps organizations promote adaptive leadership and enhance overall management effectiveness.
Key Terms
Fear of Failure
The avoidance mindset is characterized by a fear of failure that leads individuals to evade challenges and resist taking risks, limiting personal and professional growth. In contrast, the growth mindset embraces failure as a crucial learning opportunity, encouraging persistence and resilience despite setbacks. Discover how shifting from fear-based avoidance to growth-oriented thinking can transform your approach to challenges.
Embracing Challenges
An avoidance mindset views challenges as threats to avoid, leading to missed opportunities for learning and personal development. In contrast, a growth mindset embraces challenges as essential for improvement, fostering resilience and creativity. Explore more strategies to cultivate a growth mindset and transform obstacles into opportunities for success.
Resilience
The avoidance mindset centers on evading challenges to prevent failure, often limiting resilience by fostering fear of setbacks. Conversely, the growth mindset embraces obstacles as opportunities for learning, strengthening resilience through persistence and adaptability. Explore strategies to cultivate a growth mindset and enhance your resilience for lasting success.
Source and External Links
The 5 Types of Avoidance Behavior - This article outlines five main types of avoidance behavior: situational, cognitive, protective, somatic, and substitution, helping individuals address their specific avoidance patterns.
Avoidance Behavior: Examples, Impacts, & How to Overcome - This webpage provides examples and impacts of avoidance behavior while offering strategies to overcome it, including understanding its various forms and effects.
Avoidance coping - This Wikipedia page describes avoidance coping as a mechanism to deal with stress by avoiding the source of stress, which can manifest in various behaviors like substance abuse or social withdrawal.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com