Reverse logistics solutions focus on the efficient return and recycling of products, minimizing waste and reducing costs in the supply chain. Cold chain logistics ensure temperature-sensitive goods are maintained within required thermal conditions during transportation and storage to preserve quality and safety. Explore how tailored logistics strategies optimize supply chains and enhance operational efficiency.
Why it is important
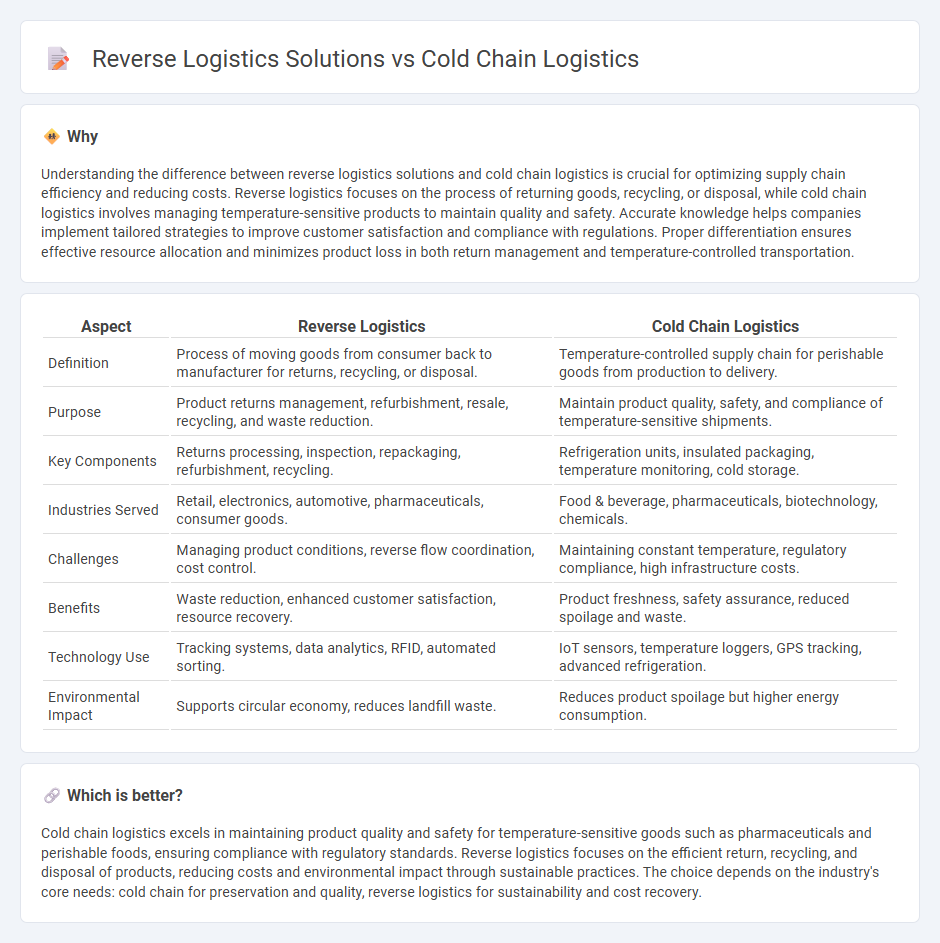
Understanding the difference between reverse logistics solutions and cold chain logistics is crucial for optimizing supply chain efficiency and reducing costs. Reverse logistics focuses on the process of returning goods, recycling, or disposal, while cold chain logistics involves managing temperature-sensitive products to maintain quality and safety. Accurate knowledge helps companies implement tailored strategies to improve customer satisfaction and compliance with regulations. Proper differentiation ensures effective resource allocation and minimizes product loss in both return management and temperature-controlled transportation.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Reverse Logistics | Cold Chain Logistics |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Process of moving goods from consumer back to manufacturer for returns, recycling, or disposal. | Temperature-controlled supply chain for perishable goods from production to delivery. |
| Purpose | Product returns management, refurbishment, resale, recycling, and waste reduction. | Maintain product quality, safety, and compliance of temperature-sensitive shipments. |
| Key Components | Returns processing, inspection, repackaging, refurbishment, recycling. | Refrigeration units, insulated packaging, temperature monitoring, cold storage. |
| Industries Served | Retail, electronics, automotive, pharmaceuticals, consumer goods. | Food & beverage, pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, chemicals. |
| Challenges | Managing product conditions, reverse flow coordination, cost control. | Maintaining constant temperature, regulatory compliance, high infrastructure costs. |
| Benefits | Waste reduction, enhanced customer satisfaction, resource recovery. | Product freshness, safety assurance, reduced spoilage and waste. |
| Technology Use | Tracking systems, data analytics, RFID, automated sorting. | IoT sensors, temperature loggers, GPS tracking, advanced refrigeration. |
| Environmental Impact | Supports circular economy, reduces landfill waste. | Reduces product spoilage but higher energy consumption. |
Which is better?
Cold chain logistics excels in maintaining product quality and safety for temperature-sensitive goods such as pharmaceuticals and perishable foods, ensuring compliance with regulatory standards. Reverse logistics focuses on the efficient return, recycling, and disposal of products, reducing costs and environmental impact through sustainable practices. The choice depends on the industry's core needs: cold chain for preservation and quality, reverse logistics for sustainability and cost recovery.
Connection
Reverse logistics solutions and cold chain logistics are interconnected through the management of temperature-sensitive returns and recycling processes, ensuring product quality and safety during transit. Effective reverse logistics strategies incorporate cold chain protocols to handle perishable goods, such as pharmaceuticals and food, enabling proper storage and transportation that prevent spoilage. Integration of these logistics systems reduces waste, optimizes inventory recovery, and maintains regulatory compliance in the supply chain.
Key Terms
**Cold Chain Logistics:**
Cold chain logistics ensures the continuous temperature-controlled supply chain for perishable goods such as pharmaceuticals, fresh produce, and frozen food, maintaining product integrity from origin to destination. It demands specialized refrigeration equipment, real-time temperature monitoring, and compliance with strict regulatory standards like the FDA and WHO for safe storage and transport. Explore more about cutting-edge cold chain logistics technologies and best practices to enhance supply chain efficiency and product quality.
Temperature Control
Cold chain logistics ensures the integrity of temperature-sensitive products, such as pharmaceuticals and perishables, through specialized refrigeration and monitoring systems that maintain optimal temperature ranges from production to delivery. Reverse logistics solutions, on the other hand, emphasize temperature control in the management of returns, recalls, and recycling of sensitive goods to prevent spoilage and maintain quality during transit back to manufacturers or disposal sites. Explore detailed strategies and technologies used in temperature-controlled logistics by learning more about cold chain versus reverse logistics solutions.
Refrigerated Transport
Cold chain logistics emphasizes maintaining temperature-sensitive goods through refrigerated transport, ensuring product integrity for pharmaceuticals, perishables, and temperature-critical items. Reverse logistics solutions manage the return flow of products, often requiring specialized refrigerated transport to preserve freshness and safety during returns or recall processes. Explore more to understand how refrigerated transport optimizes both forward cold chain and reverse logistics operations.
Source and External Links
Cold Chain Logistics: The Ultimate Guide for 2025 - Crowley - Cold chain logistics is the complex process of moving temperature-controlled goods like foods, beverages, and pharmaceuticals from origin to end customers, requiring careful management of temperature throughout all supply chain phases to ensure product safety and quality.
Cold Chain Logistics: A Comprehensive Guide | SafetyCulture - Cold chain logistics involves specialized storage and transport of temperature-sensitive goods using equipment, technology, and procedures to maintain required temperatures, ensuring product quality, regulatory compliance, and public health safety.
A guide to cold chain logistics - Everstream Analytics - Cold chain logistics encompasses managing temperature-sensitive products throughout procurement, packaging, storage, transportation, and delivery, relying on proper equipment, routes, timing, and visibility to maintain consistent temperatures preventing spoilage or quality loss.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com