Reverse logistics focuses on the process of moving goods from consumers back to manufacturers for returns, recycling, or disposal, optimizing sustainability and cost management. Distribution logistics involves the efficient planning and execution of delivering products from warehouses to end customers, ensuring timely order fulfillment and inventory control. Explore more to understand how these logistics strategies impact supply chain efficiency and business profitability.
Why it is important
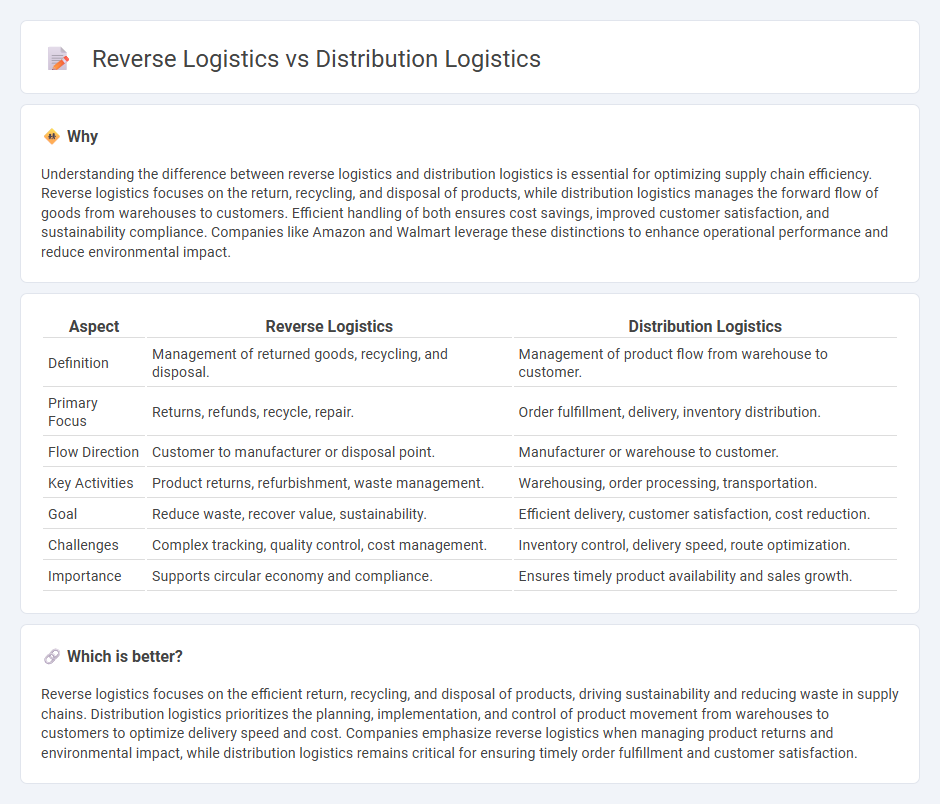
Understanding the difference between reverse logistics and distribution logistics is essential for optimizing supply chain efficiency. Reverse logistics focuses on the return, recycling, and disposal of products, while distribution logistics manages the forward flow of goods from warehouses to customers. Efficient handling of both ensures cost savings, improved customer satisfaction, and sustainability compliance. Companies like Amazon and Walmart leverage these distinctions to enhance operational performance and reduce environmental impact.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Reverse Logistics | Distribution Logistics |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Management of returned goods, recycling, and disposal. | Management of product flow from warehouse to customer. |
| Primary Focus | Returns, refunds, recycle, repair. | Order fulfillment, delivery, inventory distribution. |
| Flow Direction | Customer to manufacturer or disposal point. | Manufacturer or warehouse to customer. |
| Key Activities | Product returns, refurbishment, waste management. | Warehousing, order processing, transportation. |
| Goal | Reduce waste, recover value, sustainability. | Efficient delivery, customer satisfaction, cost reduction. |
| Challenges | Complex tracking, quality control, cost management. | Inventory control, delivery speed, route optimization. |
| Importance | Supports circular economy and compliance. | Ensures timely product availability and sales growth. |
Which is better?
Reverse logistics focuses on the efficient return, recycling, and disposal of products, driving sustainability and reducing waste in supply chains. Distribution logistics prioritizes the planning, implementation, and control of product movement from warehouses to customers to optimize delivery speed and cost. Companies emphasize reverse logistics when managing product returns and environmental impact, while distribution logistics remains critical for ensuring timely order fulfillment and customer satisfaction.
Connection
Reverse logistics and distribution logistics are interconnected through the efficient management of product flow between consumers and manufacturers, enhancing supply chain sustainability. Reverse logistics handles the return, recycling, and disposal of goods, while distribution logistics focuses on the delivery and storage of products to end customers. Integrating data systems in both processes optimizes inventory control and reduces operational costs.
Key Terms
**Distribution Logistics:**
Distribution logistics involves the efficient movement of goods from manufacturers to end consumers, focusing on transportation, warehousing, and inventory management to ensure timely delivery. It optimizes supply chain operations by reducing costs, improving order accuracy, and enhancing customer satisfaction through effective distribution strategies. Explore more to understand how distribution logistics drives competitive advantage in supply chain management.
Transportation
Distribution logistics primarily involves the forward movement of goods from manufacturers to end consumers, focusing on efficient transportation modes, route optimization, and timely delivery to meet customer demand. Reverse logistics centers on the transportation of returned, defective, or recyclable products from consumers back to manufacturers or disposal facilities, emphasizing cost reduction, sustainability, and regulatory compliance. Explore the critical differences and best practices in transportation strategies within distribution and reverse logistics to optimize supply chain performance.
Warehousing
Distribution logistics centers on efficient storage, handling, and movement of goods from warehouses to end consumers, ensuring timely delivery and inventory accuracy. Reverse logistics involves managing returned products and recycling materials through dedicated warehouse processes that emphasize inspection, refurbishing, and proper disposal. Explore the nuances of warehousing strategies in both logistics types to optimize supply chain performance.
Source and External Links
What is Distribution Logistics? - Distribution logistics involves planning, controlling, and managing all processes to move products from production or storage to the end customer, aiming to optimize cost, efficiency, and customer satisfaction through transport, warehouse, order fulfillment, inventory, returns management, and supply chain coordination.
Distribution Logistics and its importance in companies - Distribution logistics ensures efficient and effective product flow from origin to consumption by coordinating transportation, storage, order processing, and delivery to meet customer needs while reducing costs and enhancing competitiveness.
Distribution Logistics: Definition and Applications - Distribution logistics is the complex process of delivering goods from manufacturers to consumers using advanced technologies and strategic channel management to ensure timely, safe, and cost-effective deliveries in a globalized market.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com