Silent quitting refers to employees limiting their work effort strictly to their job description, avoiding extra tasks or engagement beyond basic responsibilities. Job withdrawal encompasses broader behaviors such as absenteeism, reduced productivity, and disengagement from workplace culture, often signaling deeper dissatisfaction. Explore our insights to understand how these behaviors impact organizational performance and employee retention.
Why it is important
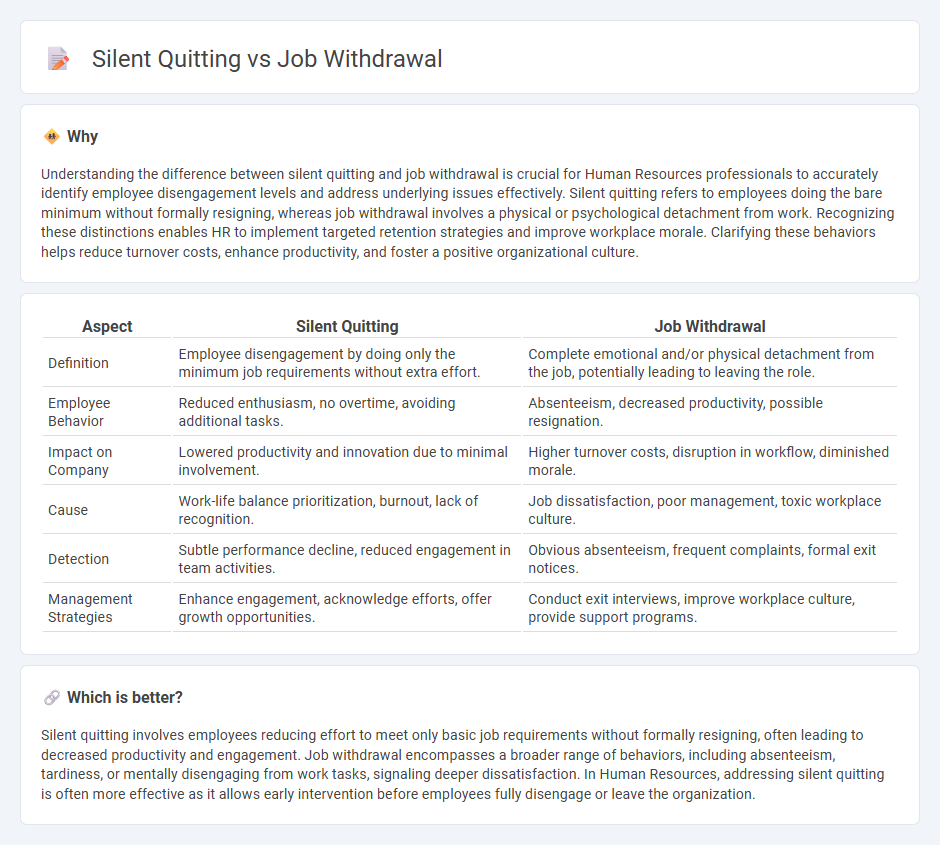
Understanding the difference between silent quitting and job withdrawal is crucial for Human Resources professionals to accurately identify employee disengagement levels and address underlying issues effectively. Silent quitting refers to employees doing the bare minimum without formally resigning, whereas job withdrawal involves a physical or psychological detachment from work. Recognizing these distinctions enables HR to implement targeted retention strategies and improve workplace morale. Clarifying these behaviors helps reduce turnover costs, enhance productivity, and foster a positive organizational culture.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Silent Quitting | Job Withdrawal |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Employee disengagement by doing only the minimum job requirements without extra effort. | Complete emotional and/or physical detachment from the job, potentially leading to leaving the role. |
| Employee Behavior | Reduced enthusiasm, no overtime, avoiding additional tasks. | Absenteeism, decreased productivity, possible resignation. |
| Impact on Company | Lowered productivity and innovation due to minimal involvement. | Higher turnover costs, disruption in workflow, diminished morale. |
| Cause | Work-life balance prioritization, burnout, lack of recognition. | Job dissatisfaction, poor management, toxic workplace culture. |
| Detection | Subtle performance decline, reduced engagement in team activities. | Obvious absenteeism, frequent complaints, formal exit notices. |
| Management Strategies | Enhance engagement, acknowledge efforts, offer growth opportunities. | Conduct exit interviews, improve workplace culture, provide support programs. |
Which is better?
Silent quitting involves employees reducing effort to meet only basic job requirements without formally resigning, often leading to decreased productivity and engagement. Job withdrawal encompasses a broader range of behaviors, including absenteeism, tardiness, or mentally disengaging from work tasks, signaling deeper dissatisfaction. In Human Resources, addressing silent quitting is often more effective as it allows early intervention before employees fully disengage or leave the organization.
Connection
Silent quitting and job withdrawal are interconnected as both reflect employee disengagement and a deliberate reduction in work effort without formal resignation. Silent quitting involves employees meeting only basic job requirements, avoiding extra tasks or involvement, signaling a psychological withdrawal from their roles. Job withdrawal encompasses a broader range of behaviors including absenteeism, reduced productivity, and eventual turnover, with silent quitting often serving as an initial stage in this disengagement process.
Key Terms
Disengagement
Job withdrawal involves employees physically distancing themselves from their tasks or workplace, which may include absenteeism or turnover, reflecting clear signs of disengagement. Silent quitting refers to employees doing only the minimum required work without extra effort, demonstrating psychological disengagement while remaining present. Explore deeper insights on how these behaviors impact organizational performance and employee well-being.
Turnover
Job withdrawal involves employees actively disengaging from work tasks and seeking alternative employment, leading to higher turnover rates and recruitment challenges for organizations. Silent quitting, characterized by employees doing only the minimum required work without overtly resigning, can result in reduced productivity and gradual turnover as disengaged workers remain but contribute less. Explore how these behaviors impact turnover to develop effective retention strategies.
Presenteeism
Job withdrawal reflects an employee's gradual disengagement, characterized by reduced effort and commitment, whereas silent quitting involves performing only assigned tasks without extra initiative. Both behaviors contribute to presenteeism, where employees are physically present but mentally unproductive, leading to decreased organizational performance and increased healthcare costs. Explore further to understand how addressing these issues can improve workplace wellbeing and efficiency.
Source and External Links
How to Write a Letter of Withdrawal to an Employer - Job withdrawal involves formally withdrawing oneself from the hiring process, often by sending a letter of withdrawal due to reasons like accepting another job, relocating, or experiencing a poor hiring process.
Employee Withdrawal: What if People Suddenly ... - Employee withdrawal refers to behaviors indicating disengagement from the organization, including physical actions like absenteeism or quitting, and psychological withdrawal like low productivity and burnout.
Reducing Work Withdrawal Behaviors When Faced with ... - Work withdrawal behavior is a negative employee response to obstacles at work manifested through physical and psychological disengagement, with research emphasizing the role of stress, cognitive flexibility, and control in influencing such behavior.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com