Silent quitting occurs when employees disengage from extra work without formally resigning, often leading to reduced productivity and morale. Resenteeism involves employees attending work despite dissatisfaction or burnout, resulting in decreased efficiency and increased errors. Explore the differences to better understand their impact on workforce management.
Why it is important
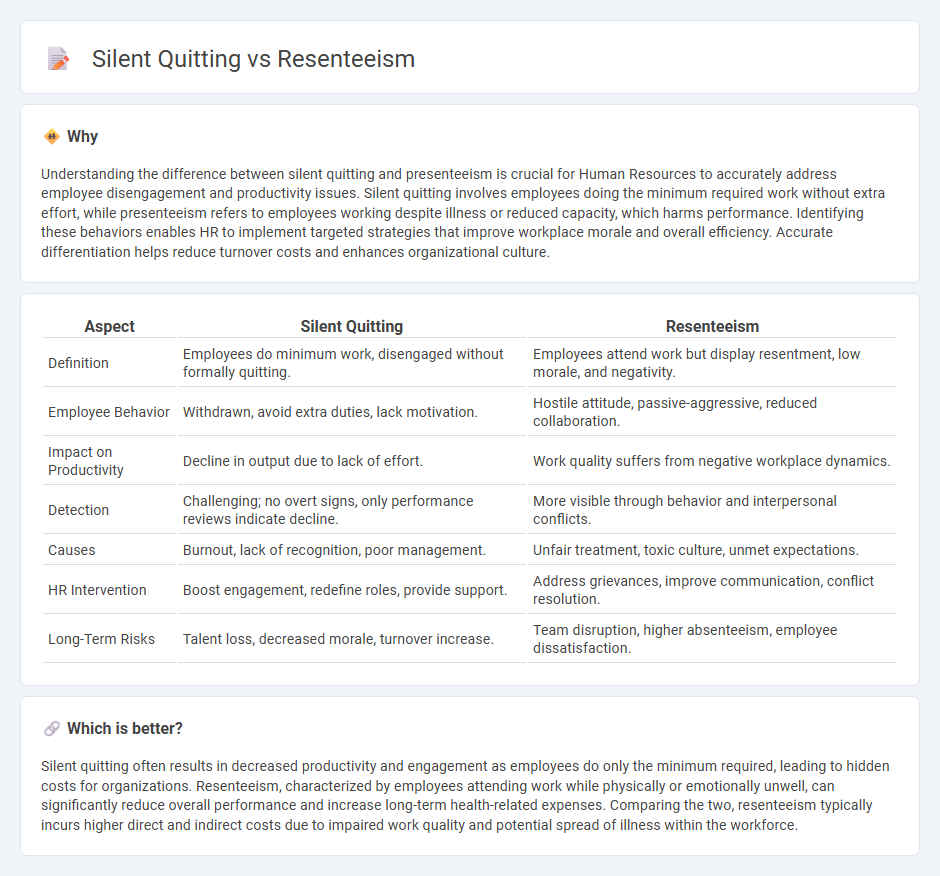
Understanding the difference between silent quitting and presenteeism is crucial for Human Resources to accurately address employee disengagement and productivity issues. Silent quitting involves employees doing the minimum required work without extra effort, while presenteeism refers to employees working despite illness or reduced capacity, which harms performance. Identifying these behaviors enables HR to implement targeted strategies that improve workplace morale and overall efficiency. Accurate differentiation helps reduce turnover costs and enhances organizational culture.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Silent Quitting | Resenteeism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Employees do minimum work, disengaged without formally quitting. | Employees attend work but display resentment, low morale, and negativity. |
| Employee Behavior | Withdrawn, avoid extra duties, lack motivation. | Hostile attitude, passive-aggressive, reduced collaboration. |
| Impact on Productivity | Decline in output due to lack of effort. | Work quality suffers from negative workplace dynamics. |
| Detection | Challenging; no overt signs, only performance reviews indicate decline. | More visible through behavior and interpersonal conflicts. |
| Causes | Burnout, lack of recognition, poor management. | Unfair treatment, toxic culture, unmet expectations. |
| HR Intervention | Boost engagement, redefine roles, provide support. | Address grievances, improve communication, conflict resolution. |
| Long-Term Risks | Talent loss, decreased morale, turnover increase. | Team disruption, higher absenteeism, employee dissatisfaction. |
Which is better?
Silent quitting often results in decreased productivity and engagement as employees do only the minimum required, leading to hidden costs for organizations. Resenteeism, characterized by employees attending work while physically or emotionally unwell, can significantly reduce overall performance and increase long-term health-related expenses. Comparing the two, resenteeism typically incurs higher direct and indirect costs due to impaired work quality and potential spread of illness within the workforce.
Connection
Silent quitting and resenteeism are interconnected through their impact on workplace engagement and productivity. Silent quitting occurs when employees reduce effort and withdraw from discretionary tasks without formally resigning, fostering feelings of dissatisfaction and mistrust that contribute to resenteeism, or the tendency to work while emotionally disengaged. Both phenomena undermine organizational culture and can lead to increased turnover rates and decreased overall performance.
Key Terms
Employee Engagement
Resenteeism, the act of employees grudgingly showing up to work without genuine engagement, contrasts sharply with silent quitting, where employees withdraw effort and commitment while remaining physically present. Both behaviors reflect low employee engagement and can significantly impact productivity, morale, and retention rates. Explore effective strategies to boost engagement and reduce workplace disengagement today.
Job Satisfaction
Resenteeism reflects employees physically present but mentally disengaged due to low job satisfaction, often resulting in decreased productivity and increased workplace stress. Silent quitting involves employees strictly adhering to their job descriptions without extra effort, driven by dissatisfaction or lack of motivation. Explore more about how job satisfaction impacts these workplace behaviors and strategies to improve engagement.
Discretionary Effort
Resenteeism reflects employees' reduced effort due to perceived unfair treatment, leading to minimal discretionary effort despite physical presence. Silent quitting involves employees consciously limiting work to assigned tasks, withholding extra effort beyond formal responsibilities. Explore in-depth strategies to address both issues and enhance workplace engagement.
Source and External Links
Resenteeism - Wikipedia - Resenteeism is professional dissatisfaction when individuals stay in unfulfilling jobs, feeling resentment and entrapment, often linked to the post-pandemic work climate and poor workplace culture.
Resenteeism: Can You Spot the Signs in Your Workplace? - AIHR - Resenteeism occurs when employees remain in jobs despite dissatisfaction or disengagement due to factors like financial constraints, lack of alternatives, and rigid workplace policies, impacting productivity and workplace culture.
What is Resenteeism and How to Fix It in the Workplace - Resenteeism describes employees who feel frustrated or disgruntled with their jobs but stay due to job market concerns, often showing vocal discontent and negatively affecting company culture.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com