Blind hiring eliminates bias by anonymizing candidate information such as names and demographics during the recruitment process, promoting diversity and fairness. Structured interviews rely on standardized questions and scoring rubrics to objectively evaluate candidate competencies, enhancing the reliability and validity of hiring decisions. Explore these recruitment methods to discover how they can improve your talent acquisition strategy.
Why it is important
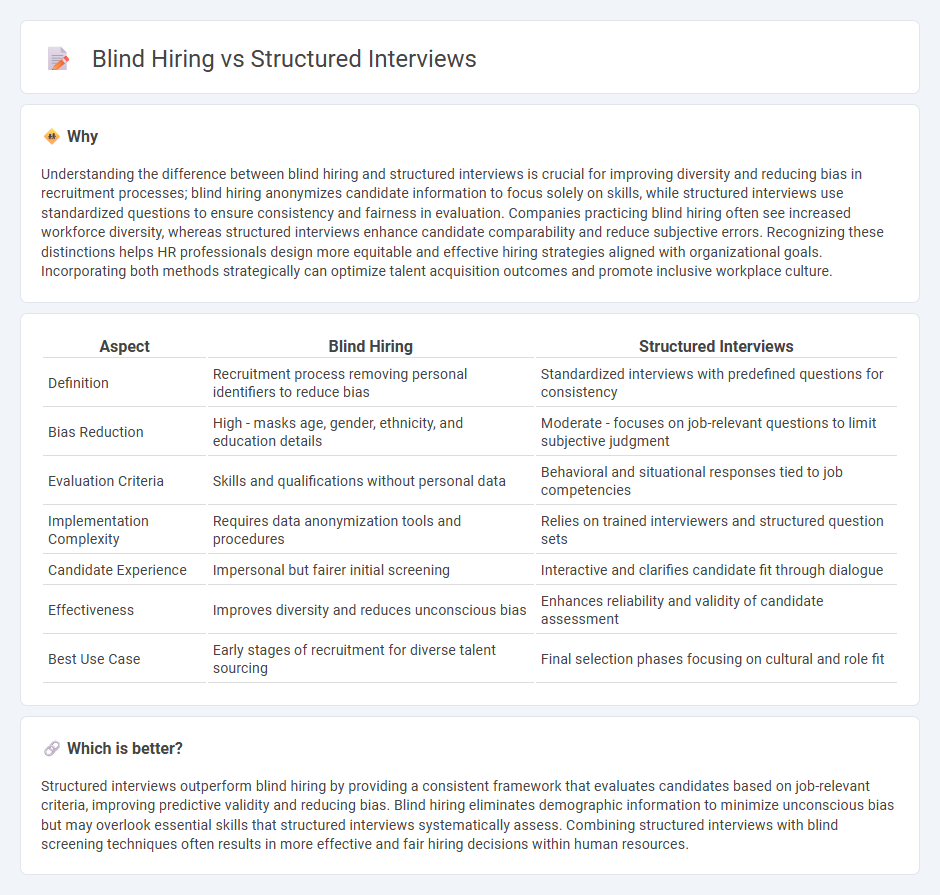
Understanding the difference between blind hiring and structured interviews is crucial for improving diversity and reducing bias in recruitment processes; blind hiring anonymizes candidate information to focus solely on skills, while structured interviews use standardized questions to ensure consistency and fairness in evaluation. Companies practicing blind hiring often see increased workforce diversity, whereas structured interviews enhance candidate comparability and reduce subjective errors. Recognizing these distinctions helps HR professionals design more equitable and effective hiring strategies aligned with organizational goals. Incorporating both methods strategically can optimize talent acquisition outcomes and promote inclusive workplace culture.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Blind Hiring | Structured Interviews |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Recruitment process removing personal identifiers to reduce bias | Standardized interviews with predefined questions for consistency |
| Bias Reduction | High - masks age, gender, ethnicity, and education details | Moderate - focuses on job-relevant questions to limit subjective judgment |
| Evaluation Criteria | Skills and qualifications without personal data | Behavioral and situational responses tied to job competencies |
| Implementation Complexity | Requires data anonymization tools and procedures | Relies on trained interviewers and structured question sets |
| Candidate Experience | Impersonal but fairer initial screening | Interactive and clarifies candidate fit through dialogue |
| Effectiveness | Improves diversity and reduces unconscious bias | Enhances reliability and validity of candidate assessment |
| Best Use Case | Early stages of recruitment for diverse talent sourcing | Final selection phases focusing on cultural and role fit |
Which is better?
Structured interviews outperform blind hiring by providing a consistent framework that evaluates candidates based on job-relevant criteria, improving predictive validity and reducing bias. Blind hiring eliminates demographic information to minimize unconscious bias but may overlook essential skills that structured interviews systematically assess. Combining structured interviews with blind screening techniques often results in more effective and fair hiring decisions within human resources.
Connection
Blind hiring techniques, which remove demographic information from applications, enhance fairness by reducing unconscious bias in candidate selection. Structured interviews implement standardized questions and scoring criteria, ensuring consistency and objectivity in evaluating candidates' qualifications. Together, blind hiring and structured interviews create a more equitable recruitment process that prioritizes skills and experience over personal characteristics.
Key Terms
Standardization
Structured interviews emphasize standardization by using consistent questions and scoring rubrics to reduce interviewer bias and ensure fair candidate evaluation. Blind hiring removes identifying details such as names and demographics to minimize unconscious bias, but may lack the comprehensive standardization found in structured interviews. Explore deeper insights into how these methods enhance hiring fairness and accuracy.
Unconscious Bias
Structured interviews provide a consistent framework, minimizing unconscious bias by evaluating all candidates against the same criteria, thereby enhancing fairness and objectivity in hiring. Blind hiring techniques, which remove identifying information such as names or demographic details, further reduce the influence of unconscious bias by focusing solely on skills and qualifications. Explore more about how combining these methods can create a more inclusive and equitable recruitment process.
Candidate Anonymity
Structured interviews provide a consistent framework that evaluates candidates based on predetermined criteria, enhancing fairness but often revealing personal information. Blind hiring techniques emphasize candidate anonymity by removing identifiable details such as names, gender, and educational background to reduce bias in the selection process. Explore how integrating candidate anonymity in hiring can create a more equitable recruitment experience.
Source and External Links
Guides: Use structured interviewing - Google re:Work - Structured interviews involve asking candidates a consistent set of vetted questions evaluated by standardized rubrics, improving fairness and predictive validity in hiring decisions.
Structured interview - Wikipedia - Structured interviews are a standardized quantitative research method where each respondent is asked the same questions in the same order, often with fixed-choice answers to ensure reliable aggregation and comparisons.
Structured Interviews: Definition, Benefits, Challenges & Examples - Structured interviews use predetermined questions and evaluation criteria for consistent candidate assessment, contrasting with unstructured interviews that are more conversational and flexible.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com