Silent quitting involves employees performing only their assigned tasks without extra effort, reflecting minimal engagement yet still fulfilling job responsibilities. Disengagement, however, signifies a deeper emotional and psychological withdrawal from work, often resulting in decreased productivity and morale. Explore these concepts to understand their impact on workforce management and employee retention strategies.
Why it is important
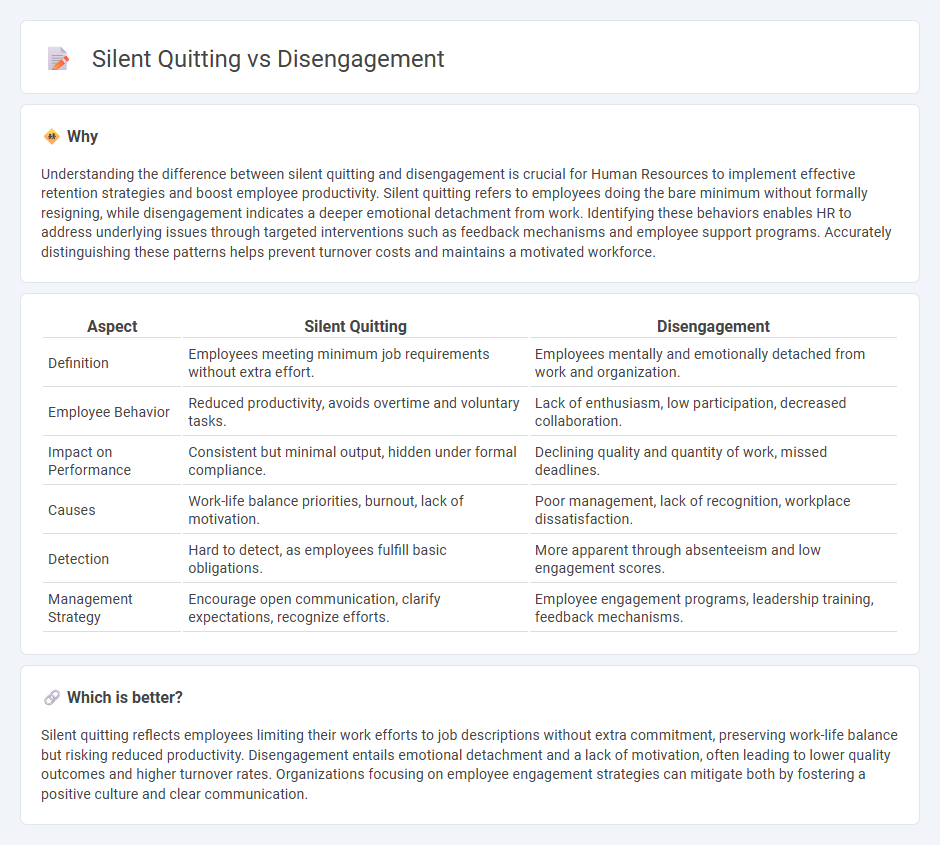
Understanding the difference between silent quitting and disengagement is crucial for Human Resources to implement effective retention strategies and boost employee productivity. Silent quitting refers to employees doing the bare minimum without formally resigning, while disengagement indicates a deeper emotional detachment from work. Identifying these behaviors enables HR to address underlying issues through targeted interventions such as feedback mechanisms and employee support programs. Accurately distinguishing these patterns helps prevent turnover costs and maintains a motivated workforce.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Silent Quitting | Disengagement |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Employees meeting minimum job requirements without extra effort. | Employees mentally and emotionally detached from work and organization. |
| Employee Behavior | Reduced productivity, avoids overtime and voluntary tasks. | Lack of enthusiasm, low participation, decreased collaboration. |
| Impact on Performance | Consistent but minimal output, hidden under formal compliance. | Declining quality and quantity of work, missed deadlines. |
| Causes | Work-life balance priorities, burnout, lack of motivation. | Poor management, lack of recognition, workplace dissatisfaction. |
| Detection | Hard to detect, as employees fulfill basic obligations. | More apparent through absenteeism and low engagement scores. |
| Management Strategy | Encourage open communication, clarify expectations, recognize efforts. | Employee engagement programs, leadership training, feedback mechanisms. |
Which is better?
Silent quitting reflects employees limiting their work efforts to job descriptions without extra commitment, preserving work-life balance but risking reduced productivity. Disengagement entails emotional detachment and a lack of motivation, often leading to lower quality outcomes and higher turnover rates. Organizations focusing on employee engagement strategies can mitigate both by fostering a positive culture and clear communication.
Connection
Silent quitting reflects a growing trend of employee disengagement where workers fulfill only their job descriptions without extra effort. Disengaged employees exhibit decreased productivity, lower job satisfaction, and increased turnover risk, directly impacting organizational performance. Understanding this connection enables HR to implement targeted strategies such as employee engagement programs and open communication to mitigate silent quitting.
Key Terms
Employee Engagement
Disengagement refers to employees emotionally withdrawing from their work, resulting in reduced productivity and lack of enthusiasm, whereas silent quitting involves employees doing the bare minimum without voicing dissatisfaction. Both phenomena negatively impact employee engagement, leading to higher turnover rates and decreased organizational performance. Explore effective strategies to boost employee engagement and prevent workforce disengagement.
Organizational Commitment
Disengagement represents a decline in employees' emotional and cognitive attachment to organizational goals, while silent quitting involves minimal effort and withdrawal from extra-role duties without formally resigning. Both behaviors critically undermine organizational commitment, reducing productivity and increasing turnover risk. Explore further to understand strategies for enhancing employee engagement and loyalty.
Work Motivation
Disengagement involves a decline in work motivation characterized by reduced effort, interest, and emotional connection to job tasks, whereas silent quitting refers to employees doing the bare minimum to meet job requirements without overtly expressing dissatisfaction. Both phenomena signal underlying motivational issues, such as lack of recognition, limited growth opportunities, and misalignment with organizational goals, which negatively impact productivity and morale. Explore effective strategies to boost work motivation and prevent disengagement and silent quitting in your workforce.
Source and External Links
5 Stages of Employee Disengagement (and How to Fix It) - Employee disengagement is a state where people lack motivation, commitment, and enthusiasm at work, progressing through five stages from discontent to complete disengagement, impacting productivity and morale significantly.
Emotional Disengagement - Marshall Digital Scholar - Emotional disengagement involves detaching oneself from negative emotional experiences by avoiding or suppressing these emotions, which can prevent closure and prolong psychological pain despite appearing as a coping mechanism.
DISENGAGEMENT definition | Cambridge English Dictionary - Disengagement is the fact of stopping being involved in something, such as social or political activities, and can refer to withdrawal from commitments or obligations.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com