Blind hiring eliminates unconscious bias by focusing solely on candidates' skills and qualifications, enhancing diversity and inclusion within organizations. Internal mobility promotes employee growth and retention by encouraging career advancement and skill development from within the company. Explore how combining these strategies can optimize talent acquisition and workforce development.
Why it is important
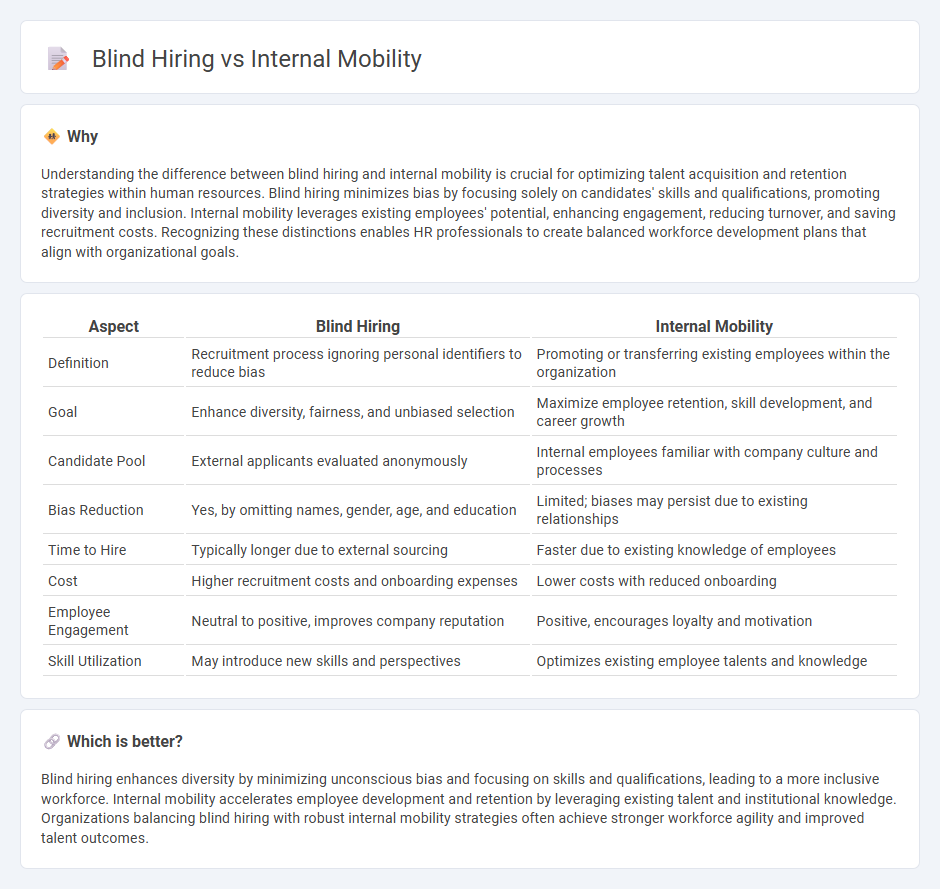
Understanding the difference between blind hiring and internal mobility is crucial for optimizing talent acquisition and retention strategies within human resources. Blind hiring minimizes bias by focusing solely on candidates' skills and qualifications, promoting diversity and inclusion. Internal mobility leverages existing employees' potential, enhancing engagement, reducing turnover, and saving recruitment costs. Recognizing these distinctions enables HR professionals to create balanced workforce development plans that align with organizational goals.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Blind Hiring | Internal Mobility |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Recruitment process ignoring personal identifiers to reduce bias | Promoting or transferring existing employees within the organization |
| Goal | Enhance diversity, fairness, and unbiased selection | Maximize employee retention, skill development, and career growth |
| Candidate Pool | External applicants evaluated anonymously | Internal employees familiar with company culture and processes |
| Bias Reduction | Yes, by omitting names, gender, age, and education | Limited; biases may persist due to existing relationships |
| Time to Hire | Typically longer due to external sourcing | Faster due to existing knowledge of employees |
| Cost | Higher recruitment costs and onboarding expenses | Lower costs with reduced onboarding |
| Employee Engagement | Neutral to positive, improves company reputation | Positive, encourages loyalty and motivation |
| Skill Utilization | May introduce new skills and perspectives | Optimizes existing employee talents and knowledge |
Which is better?
Blind hiring enhances diversity by minimizing unconscious bias and focusing on skills and qualifications, leading to a more inclusive workforce. Internal mobility accelerates employee development and retention by leveraging existing talent and institutional knowledge. Organizations balancing blind hiring with robust internal mobility strategies often achieve stronger workforce agility and improved talent outcomes.
Connection
Blind hiring eliminates biases by focusing on skills and qualifications, fostering a more diverse talent pool within Human Resources. Internal mobility leverages this diverse pool by promoting employees based on merit and potential rather than traditional criteria. Together, they enhance workforce agility and inclusivity, driving better organizational performance.
Key Terms
**Internal Mobility:**
Internal mobility enhances employee retention by promoting career growth within the organization, leveraging existing talent, and reducing recruitment costs. Companies that prioritize internal mobility experience higher employee engagement and faster onboarding processes due to familiarization with company culture and workflows. Explore effective internal mobility strategies to unlock your workforce's full potential.
Talent Development
Internal mobility enhances talent development by promoting employee growth through skill-building and career progression within the organization, resulting in increased retention and engagement. Blind hiring focuses on reducing bias by evaluating candidates solely on skills and qualifications without considering demographic factors, which can diversify talent pools but may overlook internal employee potential. Explore further to understand how balancing internal mobility and blind hiring strategies can optimize talent development and workforce effectiveness.
Succession Planning
Internal mobility enhances succession planning by leveraging existing employee skills and company knowledge, ensuring leadership continuity and reducing onboarding time. Blind hiring aims to minimize biases by anonymizing candidate information, but may overlook cultural fit crucial for succession roles. Explore how integrating both strategies can optimize your organization's leadership pipeline.
Source and External Links
Internal Mobility: What Is It And Why Organizations Need It? - Fuel50 - Internal mobility is the movement of employees within an organization to different roles, departments, or locations, including promotions, lateral moves, job rotations, and secondments, aimed at developing a versatile workforce and improving retention.
Internal Mobility: What Is It and Why Do You Need It? - Gloat - Internal mobility involves vertical and horizontal employee moves within a company, and fostering it requires embracing role-to-role mobility, providing experiential learning opportunities, and empowering employees with career ownership.
What is Internal Mobility and Why is it Important? - Phenom - Internal mobility refers to moving employees to new roles or development opportunities within the same organization, supported by career pathing and talent marketplaces to boost retention, reduce hiring time, and encourage upskilling.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com