Blind recruitment minimizes unconscious bias by anonymizing candidate information, thereby promoting diversity and inclusion within organizations. Internal recruitment leverages existing employees' knowledge and company culture fit to fill vacancies quickly and cost-effectively. Discover how choosing between blind recruitment and internal recruitment can transform your talent acquisition strategy.
Why it is important
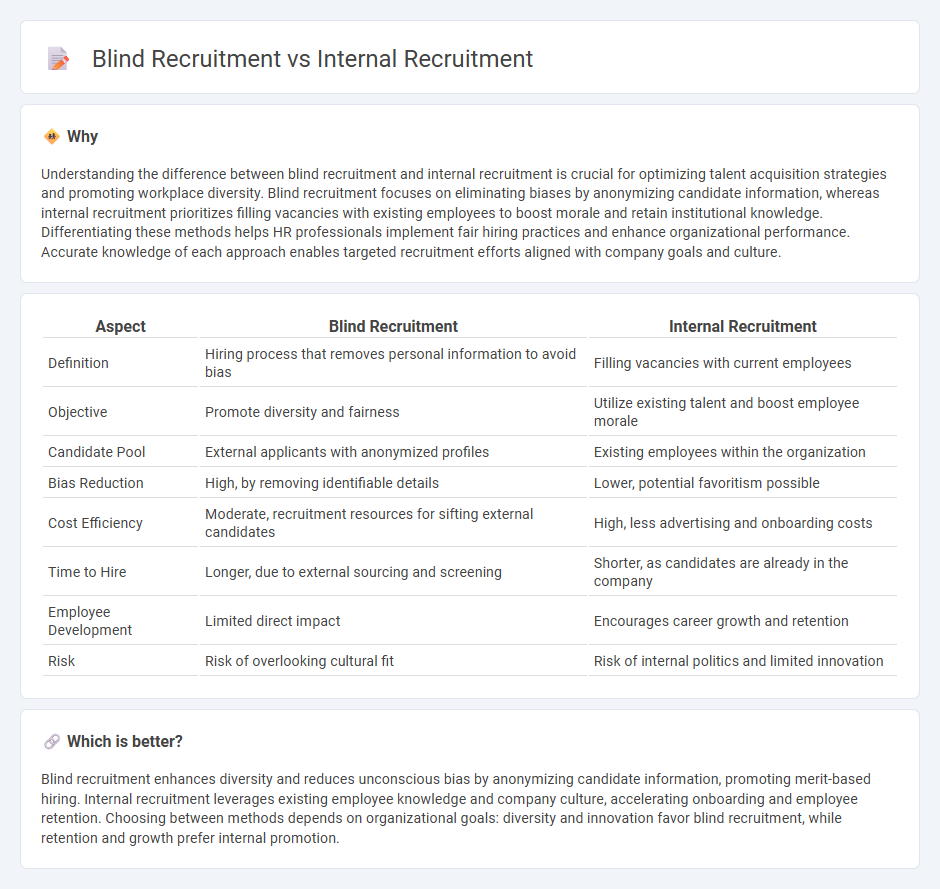
Understanding the difference between blind recruitment and internal recruitment is crucial for optimizing talent acquisition strategies and promoting workplace diversity. Blind recruitment focuses on eliminating biases by anonymizing candidate information, whereas internal recruitment prioritizes filling vacancies with existing employees to boost morale and retain institutional knowledge. Differentiating these methods helps HR professionals implement fair hiring practices and enhance organizational performance. Accurate knowledge of each approach enables targeted recruitment efforts aligned with company goals and culture.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Blind Recruitment | Internal Recruitment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Hiring process that removes personal information to avoid bias | Filling vacancies with current employees |
| Objective | Promote diversity and fairness | Utilize existing talent and boost employee morale |
| Candidate Pool | External applicants with anonymized profiles | Existing employees within the organization |
| Bias Reduction | High, by removing identifiable details | Lower, potential favoritism possible |
| Cost Efficiency | Moderate, recruitment resources for sifting external candidates | High, less advertising and onboarding costs |
| Time to Hire | Longer, due to external sourcing and screening | Shorter, as candidates are already in the company |
| Employee Development | Limited direct impact | Encourages career growth and retention |
| Risk | Risk of overlooking cultural fit | Risk of internal politics and limited innovation |
Which is better?
Blind recruitment enhances diversity and reduces unconscious bias by anonymizing candidate information, promoting merit-based hiring. Internal recruitment leverages existing employee knowledge and company culture, accelerating onboarding and employee retention. Choosing between methods depends on organizational goals: diversity and innovation favor blind recruitment, while retention and growth prefer internal promotion.
Connection
Blind recruitment enhances internal recruitment by minimizing unconscious bias and promoting diversity within existing talent pools. Implementing anonymized candidate assessments focuses on skills and qualifications, improving the fairness of internal promotions and lateral moves. This connection supports equitable workforce development and optimizes talent utilization in Human Resources.
Key Terms
Talent Pool
Internal recruitment leverages existing employee talent pools, maximizing familiarity with company culture and reducing onboarding time, while blind recruitment emphasizes unbiased selection by anonymizing candidate data to enhance diversity and inclusivity. Companies prioritizing talent pool quality benefit from internal recruitment's ability to retain in-house expertise, whereas blind recruitment broadens the candidate base beyond internal networks. Explore more strategies to optimize your talent acquisition process.
Unconscious Bias
Internal recruitment leverages existing employee knowledge and reduces onboarding time, while blind recruitment minimizes unconscious bias by eliminating identifiable candidate information. Unconscious bias, such as gender or ethnic preferences, can influence hiring decisions and impact diversity; blind recruitment techniques ensure fairer evaluation of skills and qualifications. Explore effective strategies to balance internal mobility and bias mitigation for stronger organizational hiring outcomes.
Diversity
Internal recruitment leverages existing employee talent pools, enhancing retention and familiarity but may limit diversity by favoring similar backgrounds. Blind recruitment removes identifiable candidate information to reduce unconscious bias, promoting broader diversity and inclusion across gender, ethnicity, and experience. Explore how these strategies impact workforce diversity and optimize hiring outcomes in your organization.
Source and External Links
8 internal recruitment methods you need to know - Augeo - Internal recruitment involves methods like promotions, transfers, referrals, and role changes to fill vacancies from within a company, encouraging employee motivation and career growth.
What Is Internal Recruitment? 7 Internal Recruitment Methods - AIHR - Internal recruitment is the process of filling job openings from current employees, emphasizing clear communication, transparency, fairness, and employee development to ensure successful internal hiring.
Internal Recruitment: What, Why, How and When - Paycor - Internal recruiting fills jobs from existing staff, commonly through promotions, transfers, temporary-to-permanent changes, and employee referrals, saving resources and fostering loyalty.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com