Skills adjacency mapping identifies related abilities to facilitate employee development and internal mobility, whereas competency frameworks define specific behaviors and attributes required for job success. Both approaches optimize talent management by aligning workforce capabilities with organizational goals through structured skill categorization and performance standards. Explore how integrating these methods can enhance strategic human resource planning and employee growth.
Why it is important
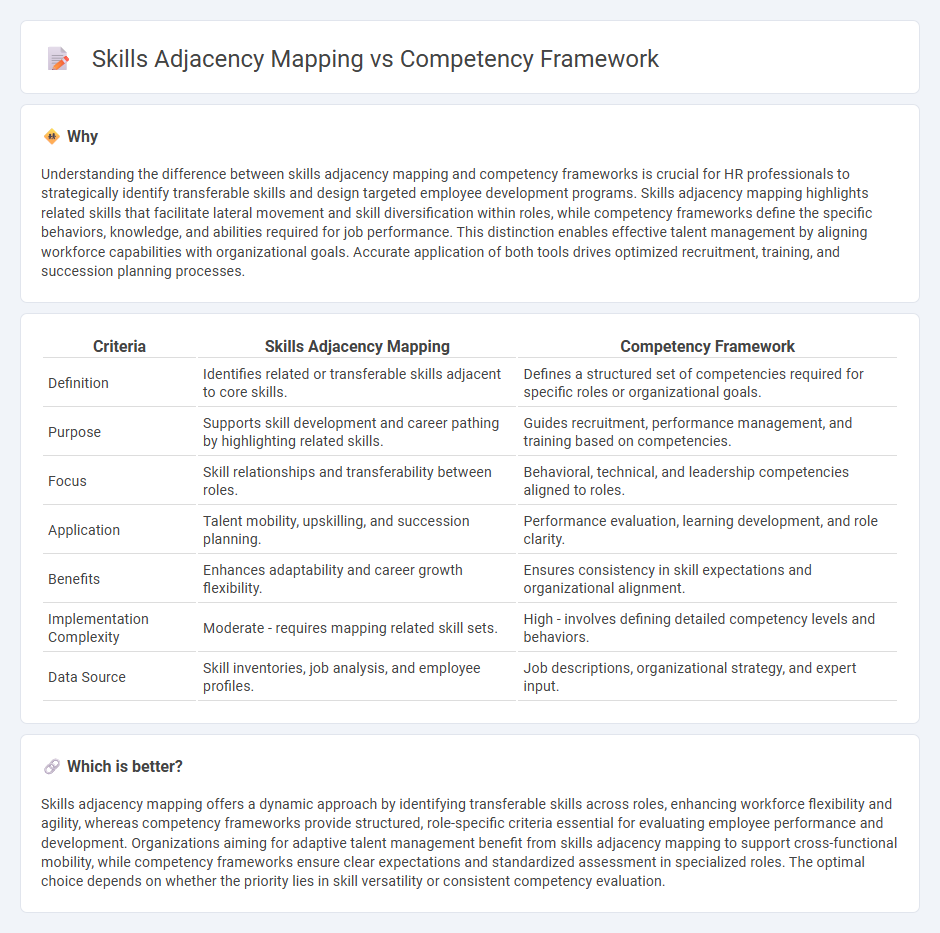
Understanding the difference between skills adjacency mapping and competency frameworks is crucial for HR professionals to strategically identify transferable skills and design targeted employee development programs. Skills adjacency mapping highlights related skills that facilitate lateral movement and skill diversification within roles, while competency frameworks define the specific behaviors, knowledge, and abilities required for job performance. This distinction enables effective talent management by aligning workforce capabilities with organizational goals. Accurate application of both tools drives optimized recruitment, training, and succession planning processes.
Comparison Table
| Criteria | Skills Adjacency Mapping | Competency Framework |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Identifies related or transferable skills adjacent to core skills. | Defines a structured set of competencies required for specific roles or organizational goals. |
| Purpose | Supports skill development and career pathing by highlighting related skills. | Guides recruitment, performance management, and training based on competencies. |
| Focus | Skill relationships and transferability between roles. | Behavioral, technical, and leadership competencies aligned to roles. |
| Application | Talent mobility, upskilling, and succession planning. | Performance evaluation, learning development, and role clarity. |
| Benefits | Enhances adaptability and career growth flexibility. | Ensures consistency in skill expectations and organizational alignment. |
| Implementation Complexity | Moderate - requires mapping related skill sets. | High - involves defining detailed competency levels and behaviors. |
| Data Source | Skill inventories, job analysis, and employee profiles. | Job descriptions, organizational strategy, and expert input. |
Which is better?
Skills adjacency mapping offers a dynamic approach by identifying transferable skills across roles, enhancing workforce flexibility and agility, whereas competency frameworks provide structured, role-specific criteria essential for evaluating employee performance and development. Organizations aiming for adaptive talent management benefit from skills adjacency mapping to support cross-functional mobility, while competency frameworks ensure clear expectations and standardized assessment in specialized roles. The optimal choice depends on whether the priority lies in skill versatility or consistent competency evaluation.
Connection
Skills adjacency mapping and competency frameworks are interconnected tools in human resources that enhance talent management by identifying related skills and defining performance standards. Skills adjacency mapping helps uncover transferable skills across roles, while competency frameworks establish the specific behaviors and abilities required for success in those roles. Integrating these approaches supports effective workforce planning, targeted training, and career development initiatives.
Key Terms
Competency Model
A Competency Model defines a structured framework outlining essential skills, behaviors, and attributes required for effective job performance, aligning individual capabilities with organizational goals. Skills adjacency mapping identifies and links related competencies to facilitate targeted development and seamless role transitions. Explore detailed insights to enhance workforce planning and talent management strategies.
Skill Gaps
Competency frameworks provide structured descriptions of roles and required abilities, while skills adjacency mapping identifies related skills to bridge gaps effectively. Skill gaps are pinpointed by comparing current competencies with those outlined in frameworks, enabling targeted development plans that enhance workforce capabilities. Explore how integrating these methodologies can optimize skill gap analysis and talent management strategies.
Transferable Skills
Competency frameworks systematically outline the core abilities required for job performance, emphasizing transferable skills such as communication, problem-solving, and adaptability that apply across various roles. Skills adjacency mapping identifies related skills that bridge different functions or industries, enabling smoother transitions and expanding career mobility by highlighting transferable competencies. Explore how integrating these approaches enhances talent development and workforce agility.
Source and External Links
The Competency Framework - A competency framework is a model that outlines the behaviors and skills required for performance excellence across multiple roles within an organization, defining core values and competencies to guide staff expectations, evaluation, and development.
What Is a Competency Model? Expert Guidance on ... - A competency model defines the knowledge, skills, and behaviors needed for success in roles, and examples like the European e-Competence Framework and DDI model show how these frameworks support workforce development, leadership growth, and talent management.
Competency Framework: Definition and How To Develop ... - Competency frameworks measure the skills, judgment, and attributes required for effective job performance by grouping behaviors into categories and subgroups, which helps in hiring, training needs identification, job descriptions, and HR policy development.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com