The internal gig economy leverages employees for short-term projects within their organization, fostering flexibility and skill development without formal role changes. Secondment involves temporarily assigning an employee to a different position or department, often to gain experience or support business needs while maintaining employment continuity. Explore how these HR strategies optimize workforce agility and talent utilization in your company.
Why it is important
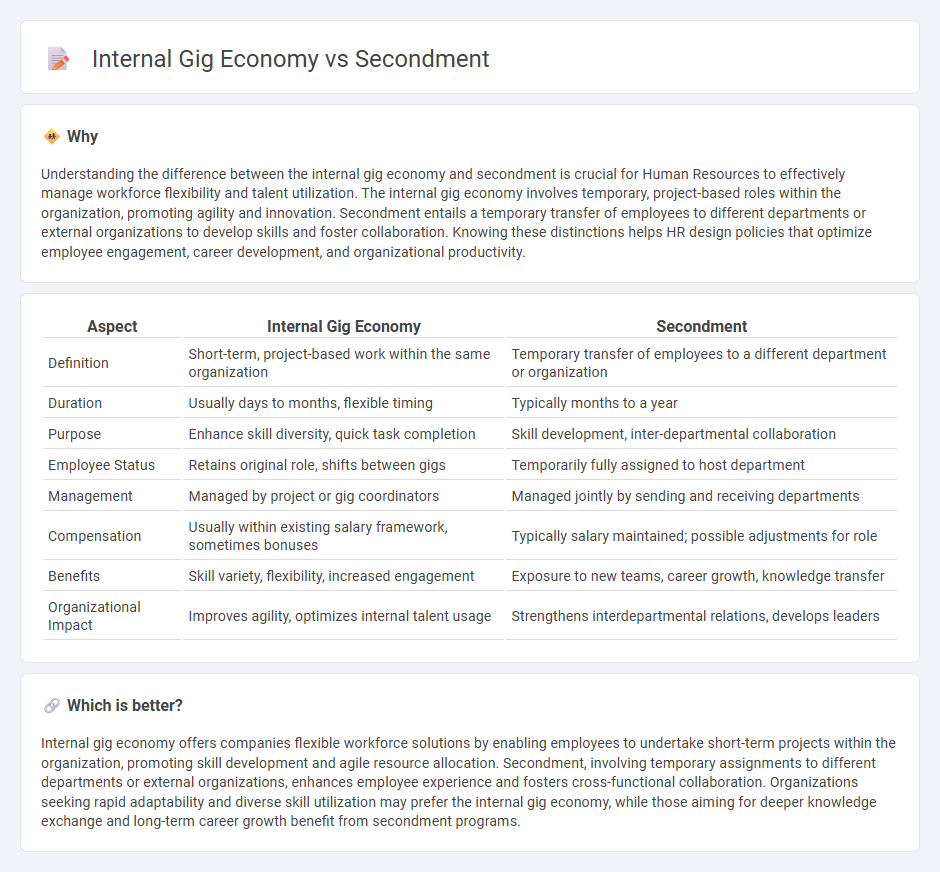
Understanding the difference between the internal gig economy and secondment is crucial for Human Resources to effectively manage workforce flexibility and talent utilization. The internal gig economy involves temporary, project-based roles within the organization, promoting agility and innovation. Secondment entails a temporary transfer of employees to different departments or external organizations to develop skills and foster collaboration. Knowing these distinctions helps HR design policies that optimize employee engagement, career development, and organizational productivity.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Internal Gig Economy | Secondment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Short-term, project-based work within the same organization | Temporary transfer of employees to a different department or organization |
| Duration | Usually days to months, flexible timing | Typically months to a year |
| Purpose | Enhance skill diversity, quick task completion | Skill development, inter-departmental collaboration |
| Employee Status | Retains original role, shifts between gigs | Temporarily fully assigned to host department |
| Management | Managed by project or gig coordinators | Managed jointly by sending and receiving departments |
| Compensation | Usually within existing salary framework, sometimes bonuses | Typically salary maintained; possible adjustments for role |
| Benefits | Skill variety, flexibility, increased engagement | Exposure to new teams, career growth, knowledge transfer |
| Organizational Impact | Improves agility, optimizes internal talent usage | Strengthens interdepartmental relations, develops leaders |
Which is better?
Internal gig economy offers companies flexible workforce solutions by enabling employees to undertake short-term projects within the organization, promoting skill development and agile resource allocation. Secondment, involving temporary assignments to different departments or external organizations, enhances employee experience and fosters cross-functional collaboration. Organizations seeking rapid adaptability and diverse skill utilization may prefer the internal gig economy, while those aiming for deeper knowledge exchange and long-term career growth benefit from secondment programs.
Connection
Internal gig economy and secondment are connected through their shared focus on flexible workforce utilization within organizations. Both models enable employees to take on diverse roles and projects, improving skill development and increasing organizational agility. Companies leveraging internal gig economy platforms often use secondments to facilitate temporary assignments that align employees' expertise with evolving business needs.
Key Terms
Temporary Placement
Temporary placement within secondment arrangements offers employees short-term assignments in different departments or external organizations, providing skill diversification and career growth opportunities. In contrast, the internal gig economy enables on-demand project-based work within the company, promoting agility and resource optimization. Explore how these flexible workforce models transform talent management strategies.
Skill Utilization
Secondment programs enable employees to utilize and develop specialized skills by temporarily assigning them to different roles within or outside the organization, fostering deep expertise and cross-functional knowledge. Internal gig economy platforms offer on-demand project opportunities that match employee skills with organizational needs, promoting agility and continuous upskilling through diverse, short-term assignments. Discover how combining secondments with internal gig opportunities can maximize skill utilization and workforce flexibility.
Talent Mobility
Talent mobility drives organizational agility by leveraging secondment programs and the internal gig economy to optimize workforce skills and project alignment. Secondments provide temporary, structured assignments fostering skill development and cross-functional collaboration, whereas internal gig platforms enable spontaneous, project-based engagements enhancing workforce flexibility and innovation. Explore strategic approaches to integrate both models for maximizing talent potential and organizational resilience.
Source and External Links
Secondment | HR & Payroll Glossary - Paylocity - This webpage explains that a secondment is a temporary work arrangement where an employee is reassigned to a different role within their organization or with an external partner.
What Is Secondment? Meaning + Examples - Velocity Global - This article defines secondment as a temporary work arrangement where an employee is assigned to a different organization or department, maintaining employment with their original employer.
Secondment - Wikipedia - A secondment is described as the temporary assignment of an employee from one organization to another, often retaining their salary and rights while working under the host organization's supervision.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com