Emotional salary encompasses non-monetary benefits such as recognition, work-life balance, and job satisfaction that enhance employee motivation and loyalty beyond traditional compensation. Compensation refers to the tangible financial rewards an employee receives, including salary, bonuses, and benefits. Explore how integrating emotional salary strategies can transform human resources practices and boost organizational performance.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between emotional salary and compensation is crucial in Human Resources to effectively attract, retain, and motivate employees by addressing both financial and psychological needs. Emotional salary encompasses non-monetary benefits such as recognition, work-life balance, and job satisfaction, which significantly influence employee engagement. Compensation refers strictly to monetary rewards like salary, bonuses, and benefits, forming the tangible aspect of employee remuneration. Prioritizing both elements helps HR professionals design comprehensive employee value propositions that enhance organizational performance.
Comparison Table
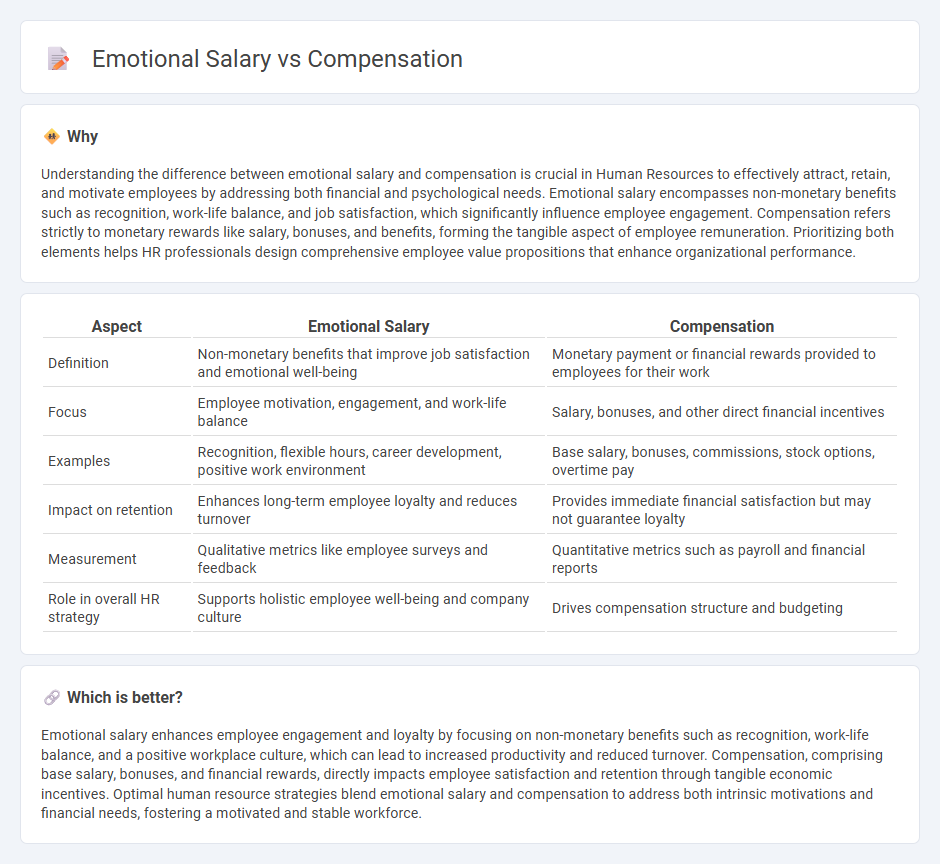
| Aspect | Emotional Salary | Compensation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Non-monetary benefits that improve job satisfaction and emotional well-being | Monetary payment or financial rewards provided to employees for their work |
| Focus | Employee motivation, engagement, and work-life balance | Salary, bonuses, and other direct financial incentives |
| Examples | Recognition, flexible hours, career development, positive work environment | Base salary, bonuses, commissions, stock options, overtime pay |
| Impact on retention | Enhances long-term employee loyalty and reduces turnover | Provides immediate financial satisfaction but may not guarantee loyalty |
| Measurement | Qualitative metrics like employee surveys and feedback | Quantitative metrics such as payroll and financial reports |
| Role in overall HR strategy | Supports holistic employee well-being and company culture | Drives compensation structure and budgeting |
Which is better?
Emotional salary enhances employee engagement and loyalty by focusing on non-monetary benefits such as recognition, work-life balance, and a positive workplace culture, which can lead to increased productivity and reduced turnover. Compensation, comprising base salary, bonuses, and financial rewards, directly impacts employee satisfaction and retention through tangible economic incentives. Optimal human resource strategies blend emotional salary and compensation to address both intrinsic motivations and financial needs, fostering a motivated and stable workforce.
Connection
Emotional salary, encompassing non-monetary benefits like recognition, work-life balance, and professional growth, directly influences employee motivation and job satisfaction, which in turn enhances the effectiveness of monetary compensation. Combining emotional salary with competitive financial rewards creates a holistic compensation strategy that attracts and retains top talent while boosting productivity. Organizations investing in both tangible pay and intangible emotional benefits foster greater employee engagement and loyalty.
Key Terms
Base Salary
Base salary represents the fixed monetary compensation employees receive for their work, serving as the foundational element of overall remuneration. Emotional salary encompasses non-monetary benefits such as recognition, work-life balance, and career growth opportunities that enhance employee motivation and satisfaction. Discover how integrating both base salary and emotional salary can drive employee engagement and retention.
Benefits
Compensation typically includes direct financial payments like salary, bonuses, and commissions, while emotional salary refers to non-monetary benefits such as recognition, work-life balance, and a positive company culture that enhance employee satisfaction. Benefits such as health insurance, flexible work hours, and career development opportunities blend both compensation and emotional salary elements, improving overall employee engagement and retention. Discover how integrating these benefits can transform your workplace experience and boost productivity.
Recognition
Compensation primarily refers to the monetary rewards employees receive, such as salary, bonuses, and benefits, while emotional salary centers on non-financial recognition like appreciation, workplace respect, and personal growth opportunities that boost employee motivation and satisfaction. Recognition as a core element of emotional salary significantly enhances engagement, reduces turnover, and fosters a positive organizational culture. Explore in-depth how integrating emotional salary strategies with traditional compensation can transform employee experience and drive business success.
Source and External Links
compensation | Wex | US Law | LII / Legal Information Institute - Compensation is payment or remuneration for work performed or for harm suffered, including fixed benefits or damages under workers' compensation laws.
COMPENSATION definition | Cambridge English Dictionary - Compensation is money paid to someone for a loss, damage, or problem, often in exchange or as a legal remedy.
What Does Compensation Mean? Definition & Examples - Sage - Compensation commonly refers to monetary payment earned by employees for services, including salary, commissions, incentives, or payments owed to injured parties.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com