Second chance hiring focuses on providing employment opportunities to individuals with criminal records, aiming to reduce recidivism and promote workforce diversity. Offender reintegration involves comprehensive support services to help formerly incarcerated individuals successfully reenter society, including housing, counseling, and job training. Explore more about how these strategies transform HR practices and community outcomes.
Why it is important
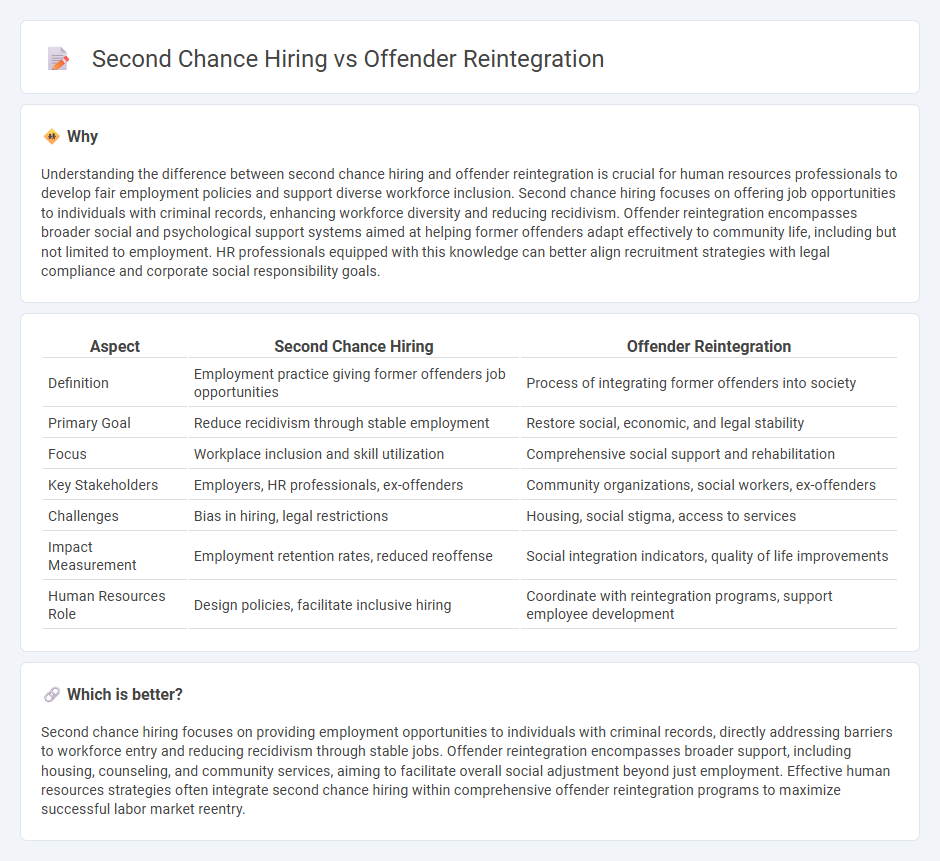
Understanding the difference between second chance hiring and offender reintegration is crucial for human resources professionals to develop fair employment policies and support diverse workforce inclusion. Second chance hiring focuses on offering job opportunities to individuals with criminal records, enhancing workforce diversity and reducing recidivism. Offender reintegration encompasses broader social and psychological support systems aimed at helping former offenders adapt effectively to community life, including but not limited to employment. HR professionals equipped with this knowledge can better align recruitment strategies with legal compliance and corporate social responsibility goals.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Second Chance Hiring | Offender Reintegration |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Employment practice giving former offenders job opportunities | Process of integrating former offenders into society |
| Primary Goal | Reduce recidivism through stable employment | Restore social, economic, and legal stability |
| Focus | Workplace inclusion and skill utilization | Comprehensive social support and rehabilitation |
| Key Stakeholders | Employers, HR professionals, ex-offenders | Community organizations, social workers, ex-offenders |
| Challenges | Bias in hiring, legal restrictions | Housing, social stigma, access to services |
| Impact Measurement | Employment retention rates, reduced reoffense | Social integration indicators, quality of life improvements |
| Human Resources Role | Design policies, facilitate inclusive hiring | Coordinate with reintegration programs, support employee development |
Which is better?
Second chance hiring focuses on providing employment opportunities to individuals with criminal records, directly addressing barriers to workforce entry and reducing recidivism through stable jobs. Offender reintegration encompasses broader support, including housing, counseling, and community services, aiming to facilitate overall social adjustment beyond just employment. Effective human resources strategies often integrate second chance hiring within comprehensive offender reintegration programs to maximize successful labor market reentry.
Connection
Second chance hiring directly supports offender reintegration by providing ex-offenders with employment opportunities that reduce recidivism rates and promote social stability. Human Resources teams play a crucial role in developing inclusive hiring policies and offering support programs tailored to align skills with job requirements for returning citizens. Data shows organizations adopting second chance hiring experience improved workforce diversity and community reputation, highlighting the strategic value of offender reintegration in HR practices.
Key Terms
**Offender Reintegration:**
Offender reintegration emphasizes structured support systems, such as housing, education, and mental health services, to help formerly incarcerated individuals successfully reenter society. This approach addresses barriers like stigma and lack of resources, reducing recidivism rates and promoting community stability. Discover how offender reintegration programs transform lives and foster safer communities.
Reentry Programs
Reentry programs prioritize offender reintegration by providing tailored support such as job training, counseling, and housing assistance to reduce recidivism and improve community safety. Second chance hiring focuses on employer-led initiatives to hire individuals with criminal records, promoting economic inclusion and workforce diversity. Explore how these strategies complement each other to enhance successful reentry outcomes.
Community Support
Offender reintegration emphasizes structured community support programs that facilitate transition from incarceration to society, reducing recidivism through mentorship and access to social services. Second chance hiring concentrates on employer-driven initiatives promoting workplace inclusion and fair hiring practices for former offenders, stimulating economic empowerment and social acceptance. Discover how these approaches complement each other to strengthen community resilience and reduce stigma.
Source and External Links
The Offender and Reentry: Supporting Active Participation in Reintegration - Reintegration focuses on stabilizing offenders in basic survival areas such as home and work, involving them actively in adjusting their post-release plans to maintain a crime-free lifestyle and strengthening community attachments over up to two years post-release.
Factors associated with successful reintegration for male offenders - Successful reintegration is influenced by factors including risk reduction interventions, family or religious support, cognitive-behavioral therapy, and overcoming barriers like prison victimization, with complex relationships affecting outcomes like recidivism, drug use, and housing.
AN EXPLORATION OF BARRIERS TO OFFENDER REINTEGRATION - Offender reintegration faces significant barriers such as homelessness, lack of employment, financial difficulties, discrimination due to criminal records, and social isolation, all of which challenge the successful social integration of ex-offenders into the community.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com