Ghost quitting refers to employees silently withdrawing effort and commitment without formally resigning, while disengagement describes a broader emotional and psychological detachment from work responsibilities. Both phenomena significantly impact productivity, morale, and retention rates within organizations. Explore strategies to identify and address these hidden workforce challenges effectively.
Why it is important
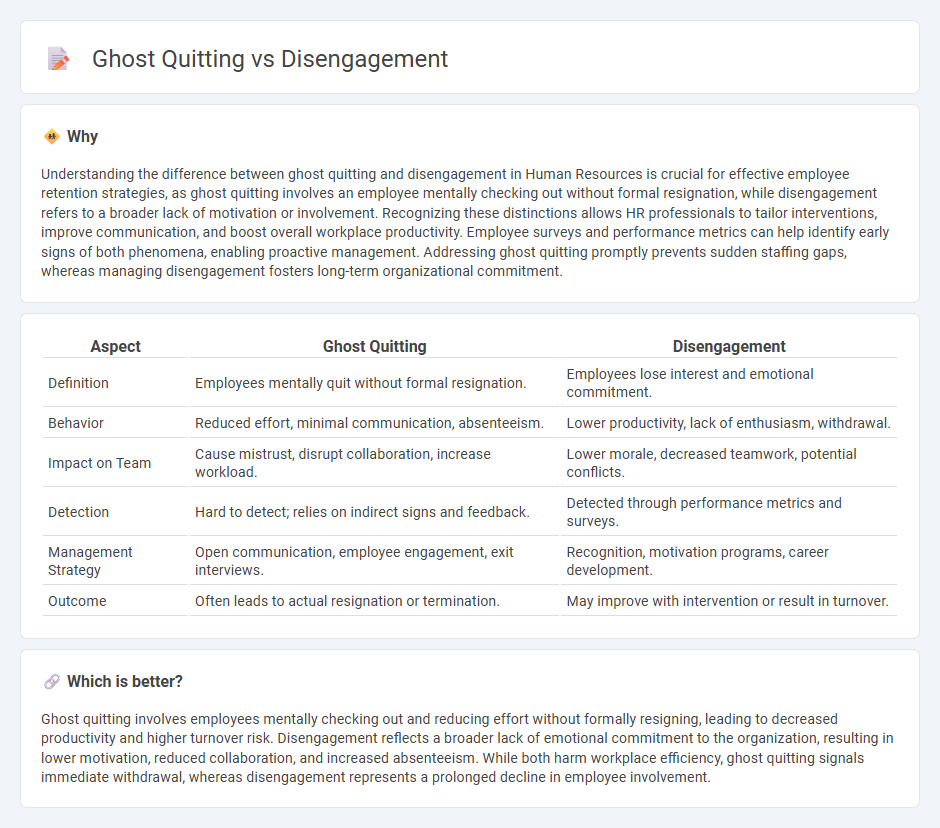
Understanding the difference between ghost quitting and disengagement in Human Resources is crucial for effective employee retention strategies, as ghost quitting involves an employee mentally checking out without formal resignation, while disengagement refers to a broader lack of motivation or involvement. Recognizing these distinctions allows HR professionals to tailor interventions, improve communication, and boost overall workplace productivity. Employee surveys and performance metrics can help identify early signs of both phenomena, enabling proactive management. Addressing ghost quitting promptly prevents sudden staffing gaps, whereas managing disengagement fosters long-term organizational commitment.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Ghost Quitting | Disengagement |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Employees mentally quit without formal resignation. | Employees lose interest and emotional commitment. |
| Behavior | Reduced effort, minimal communication, absenteeism. | Lower productivity, lack of enthusiasm, withdrawal. |
| Impact on Team | Cause mistrust, disrupt collaboration, increase workload. | Lower morale, decreased teamwork, potential conflicts. |
| Detection | Hard to detect; relies on indirect signs and feedback. | Detected through performance metrics and surveys. |
| Management Strategy | Open communication, employee engagement, exit interviews. | Recognition, motivation programs, career development. |
| Outcome | Often leads to actual resignation or termination. | May improve with intervention or result in turnover. |
Which is better?
Ghost quitting involves employees mentally checking out and reducing effort without formally resigning, leading to decreased productivity and higher turnover risk. Disengagement reflects a broader lack of emotional commitment to the organization, resulting in lower motivation, reduced collaboration, and increased absenteeism. While both harm workplace efficiency, ghost quitting signals immediate withdrawal, whereas disengagement represents a prolonged decline in employee involvement.
Connection
Ghost quitting, where employees silently withdraw effort without formally resigning, directly fuels disengagement in the workplace. This behavior results in reduced productivity, lower morale, and increased turnover risk, as disengaged employees are less committed to organizational goals. Understanding this connection is crucial for human resources to implement effective retention strategies and enhance employee engagement programs.
Key Terms
Employee Engagement
Disengagement in the workplace manifests as reduced productivity, lack of motivation, and emotional withdrawal, significantly impacting overall team performance. Ghost quitting refers to employees who continue to fulfill job descriptions superficially while mentally checking out, creating hidden risks for companies. Explore effective strategies for identifying and addressing these behaviors to enhance employee engagement and retention.
Turnover Intentions
Turnover intentions often stem from employee disengagement, characterized by reduced motivation and commitment, whereas ghost quitting involves employees withdrawing effort without formal resignation, leading to hidden productivity losses. Understanding the nuances between disengagement and ghost quitting helps organizations develop targeted retention strategies and improve workplace morale. Explore effective approaches to reduce turnover intentions and enhance employee engagement.
Silent Quitting
Silent quitting refers to employees who remain physically present at work but mentally withdraw by reducing effort and engagement, contrasting with ghost quitting where individuals abruptly leave without notice. Disengagement manifests through minimal participation, lack of enthusiasm, and decreased productivity, subtly impacting organizational performance. Explore more about recognizing and addressing silent quitting to foster a healthier workplace environment.
Source and External Links
Emotional Disengagement - Marshall Digital Scholar - Emotional disengagement is a behavioral pattern of denying or suppressing negative emotional experiences, leading to difficulties in connecting emotionally with others, impacting intimacy and family relationships.
DISENGAGEMENT definition | Cambridge English Dictionary - Disengagement is the act or fact of stopping involvement in something, such as social life, politics, or military forces withdrawing from an area.
Disengagement - Wikipedia - Disengagement refers to various concepts including apathy, social or moral disengagement, military withdrawal, and the disengagement theory in gerontology.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com