No code startups leverage visual development platforms to rapidly create and launch products without extensive coding knowledge, enabling faster innovation and reduced initial costs. Small businesses typically involve traditional operational models with higher dependency on manual processes and technical expertise. Explore the advantages and challenges of no code startups versus small businesses to determine the best entrepreneurial path for you.
Why it is important
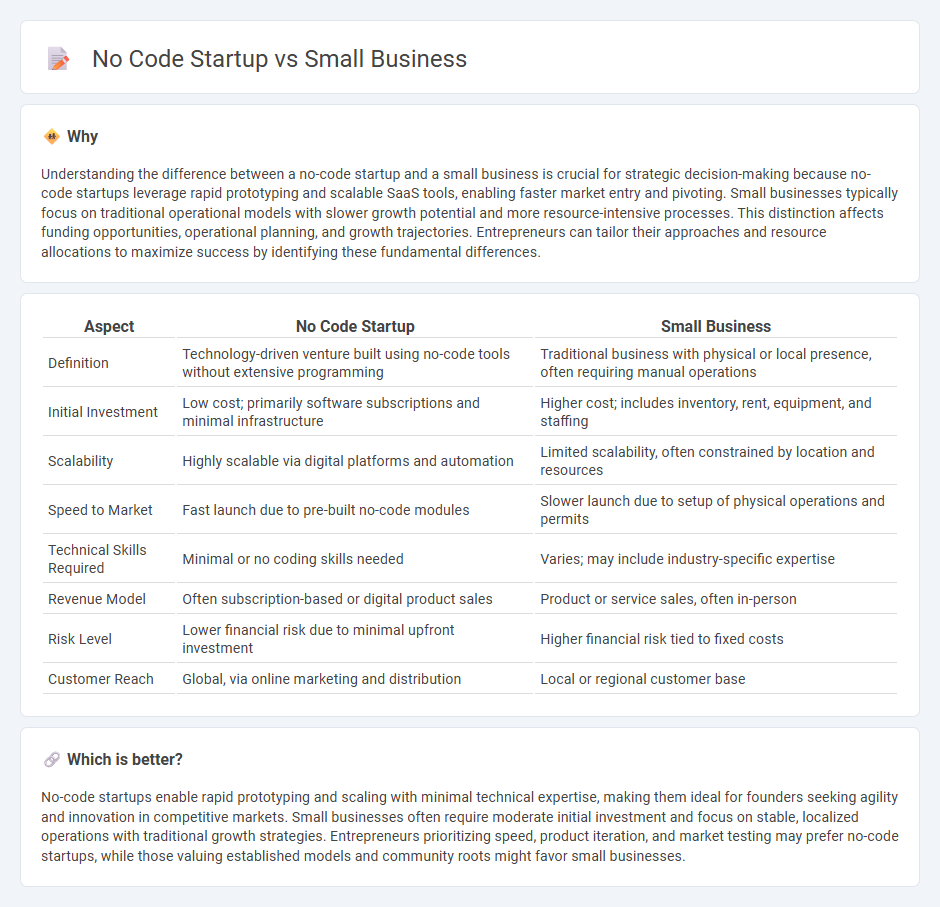
Understanding the difference between a no-code startup and a small business is crucial for strategic decision-making because no-code startups leverage rapid prototyping and scalable SaaS tools, enabling faster market entry and pivoting. Small businesses typically focus on traditional operational models with slower growth potential and more resource-intensive processes. This distinction affects funding opportunities, operational planning, and growth trajectories. Entrepreneurs can tailor their approaches and resource allocations to maximize success by identifying these fundamental differences.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | No Code Startup | Small Business |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Technology-driven venture built using no-code tools without extensive programming | Traditional business with physical or local presence, often requiring manual operations |
| Initial Investment | Low cost; primarily software subscriptions and minimal infrastructure | Higher cost; includes inventory, rent, equipment, and staffing |
| Scalability | Highly scalable via digital platforms and automation | Limited scalability, often constrained by location and resources |
| Speed to Market | Fast launch due to pre-built no-code modules | Slower launch due to setup of physical operations and permits |
| Technical Skills Required | Minimal or no coding skills needed | Varies; may include industry-specific expertise |
| Revenue Model | Often subscription-based or digital product sales | Product or service sales, often in-person |
| Risk Level | Lower financial risk due to minimal upfront investment | Higher financial risk tied to fixed costs |
| Customer Reach | Global, via online marketing and distribution | Local or regional customer base |
Which is better?
No-code startups enable rapid prototyping and scaling with minimal technical expertise, making them ideal for founders seeking agility and innovation in competitive markets. Small businesses often require moderate initial investment and focus on stable, localized operations with traditional growth strategies. Entrepreneurs prioritizing speed, product iteration, and market testing may prefer no-code startups, while those valuing established models and community roots might favor small businesses.
Connection
No code startups empower entrepreneurs to launch ventures rapidly by eliminating the need for traditional programming skills, thus lowering barriers to entry in the market. Small businesses leverage no code platforms to streamline operations, create custom tools, and automate workflows, increasing efficiency and reducing costs. This synergy accelerates innovation and growth, enabling more startups to scale effectively without heavy technical investments.
Key Terms
Bootstrapping
Bootstrap strategies for small businesses often rely on minimal initial investment and organic growth through customer revenue, while no-code startups leverage accessible platforms like Bubble or Webflow to rapidly develop products with limited technical skills. Both models emphasize cost-efficiency and resourcefulness, but no-code startups benefit from faster iteration and scalability compared to traditional small businesses. Explore how bootstrapping can uniquely empower your venture by learning more about these dynamic approaches.
MVP (Minimum Viable Product)
Small businesses often prioritize steady growth and customer relationships, while no code startups focus intensely on rapidly developing an MVP to validate product-market fit with minimal resources. No code platforms like Bubble and Adalo enable startups to launch functional prototypes quickly, reducing time-to-market and development costs compared to traditional methods. Explore how leveraging no code tools can accelerate your MVP development for a competitive edge.
Scalability
Small businesses typically rely on traditional growth models with limited scalability due to resource constraints, whereas no-code startups leverage scalable platforms to rapidly develop and iterate products with minimal technical overhead. No-code tools enable startups to automate workflows, integrate systems, and expand user bases efficiently, overcoming common scalability barriers faced by small businesses. Explore key strategies to maximize scalability in both small business and no-code startup environments for sustainable growth.
Source and External Links
Small business - Wikipedia - Small businesses are corporations, partnerships, or sole proprietorships with a small number of employees or less annual revenue, varying by country and industry, often qualifying for government support and preferential tax policies.
Small Business Administration - The SBA supports American small businesses by connecting entrepreneurs with lenders and funding, providing business advice, educational trainings, and low-interest disaster loans.
Small Business Centers - California offers no-cost or low-cost advising, training, and funding pathways for small businesses through over 150 centers statewide, including specialized support for veterans and women.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com