Micro private equity focuses on acquiring and growing small to mid-sized companies using private capital, emphasizing hands-on value creation and operational improvements. Search funds, in contrast, involve entrepreneurs raising investment to identify and acquire a single target company, often leading to direct management by the fund principals. Explore the distinct strategies and advantages of micro private equity versus search funds for informed investment decisions.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between micro private equity and search funds is crucial for entrepreneurs seeking tailored investment strategies and resource allocation. Micro private equity involves investing in very small businesses with potential for growth, while search funds focus on acquiring and operating a single company. This distinction helps entrepreneurs align their business goals with the appropriate funding model. Knowledge of these investment types improves decision-making and maximizes chances of business success.
Comparison Table
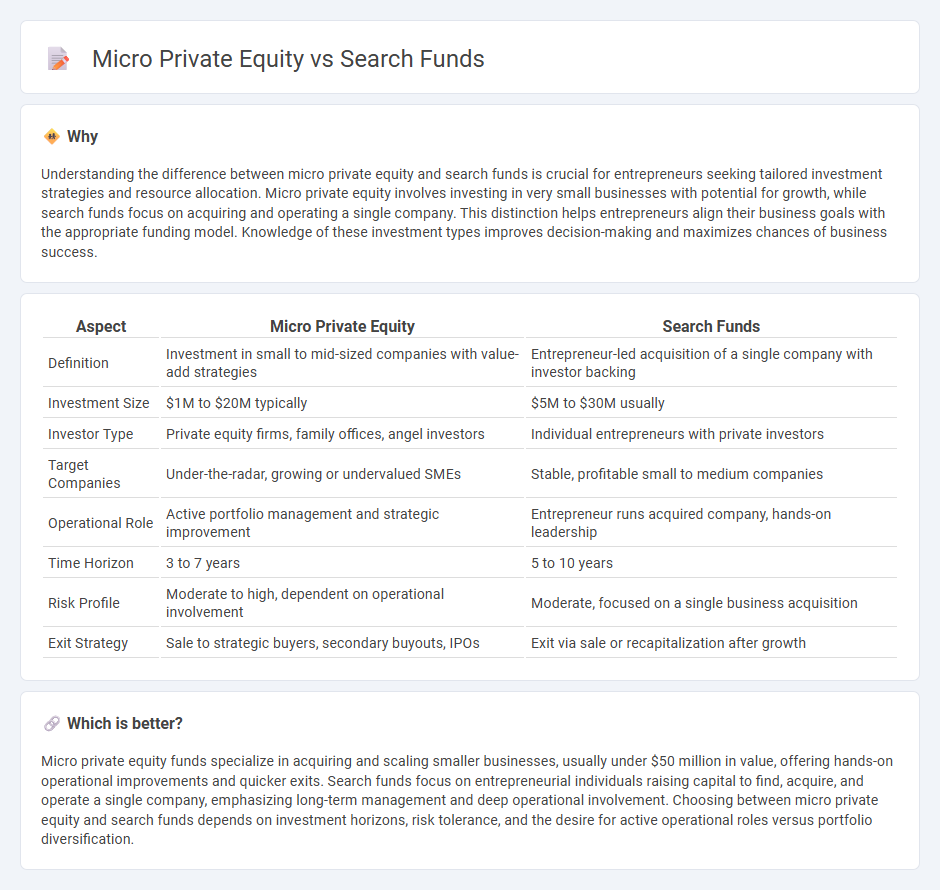
| Aspect | Micro Private Equity | Search Funds |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Investment in small to mid-sized companies with value-add strategies | Entrepreneur-led acquisition of a single company with investor backing |
| Investment Size | $1M to $20M typically | $5M to $30M usually |
| Investor Type | Private equity firms, family offices, angel investors | Individual entrepreneurs with private investors |
| Target Companies | Under-the-radar, growing or undervalued SMEs | Stable, profitable small to medium companies |
| Operational Role | Active portfolio management and strategic improvement | Entrepreneur runs acquired company, hands-on leadership |
| Time Horizon | 3 to 7 years | 5 to 10 years |
| Risk Profile | Moderate to high, dependent on operational involvement | Moderate, focused on a single business acquisition |
| Exit Strategy | Sale to strategic buyers, secondary buyouts, IPOs | Exit via sale or recapitalization after growth |
Which is better?
Micro private equity funds specialize in acquiring and scaling smaller businesses, usually under $50 million in value, offering hands-on operational improvements and quicker exits. Search funds focus on entrepreneurial individuals raising capital to find, acquire, and operate a single company, emphasizing long-term management and deep operational involvement. Choosing between micro private equity and search funds depends on investment horizons, risk tolerance, and the desire for active operational roles versus portfolio diversification.
Connection
Micro private equity firms invest in small to medium-sized businesses, providing capital and strategic guidance for growth. Search funds are a subset of entrepreneurial investment vehicles where entrepreneurs raise capital to acquire and manage a single private company. Both micro private equity and search funds focus on identifying undervalued or niche-market companies, using hands-on management to improve operations and increase value.
Key Terms
Acquisition
Search funds target acquiring a single company, often focusing on small to mid-sized businesses with strong cash flow and growth potential, while micro private equity firms invest in multiple smaller acquisitions, typically under $50 million, emphasizing portfolio diversification. Search fund entrepreneurs drive operations post-acquisition, blending hands-on management with strategic growth, whereas micro private equity operates more like traditional PE with external management teams. Explore how these acquisition models impact investment returns and management involvement to better align with your capital and operational goals.
Capital structure
Search funds typically employ a simple capital structure, relying heavily on equity investments from individual investors or small groups to finance the acquisition and growth of a single target company. Micro private equity funds, by contrast, often utilize a more complex capital structure, combining equity with various forms of debt to optimize returns and manage risk across multiple portfolio companies. Explore further to understand how these capital structures influence investment strategies and outcomes.
Operational involvement
Search funds prioritize hands-on operational involvement, where entrepreneurs actively manage and grow the acquired company to create value. Micro private equity firms typically focus on financial engineering and strategic guidance, often maintaining a more passive role in day-to-day operations. Explore detailed comparisons to understand which investment style aligns best with your business goals.
Source and External Links
Search fund - Wikipedia - A search fund is an investment vehicle that allows an entrepreneur to raise capital from investors to find, acquire, and operate a privately held company, typically involving two funding rounds: one for the search and another for acquisition capital.
Search Funds: A Rising Asset Class Outperforming PE and VC - Search funds are entrepreneurial investment vehicles where individuals raise capital to acquire owner-operated, profitable small businesses in need of succession, offering lower-risk leadership opportunities compared to typical venture capital or private equity investments.
Search Fund - Definition, History, How It Works - A search fund is a funding pool used by entrepreneurs to acquire businesses (usually valued $5 to $30 million) and run them as CEO, often targeting companies with retiring founders or family businesses with growth potential, developed initially at Stanford in 1984.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com