Bootstrapped SaaS companies leverage self-funding to develop scalable software solutions, prioritizing control and organic growth over external investment. Marketplace platforms connect buyers and sellers, creating value through network effects and often requiring significant upfront capital to establish liquidity and user trust. Explore the key differences and strategies behind these entrepreneurial models to optimize your startup approach.
Why it is important
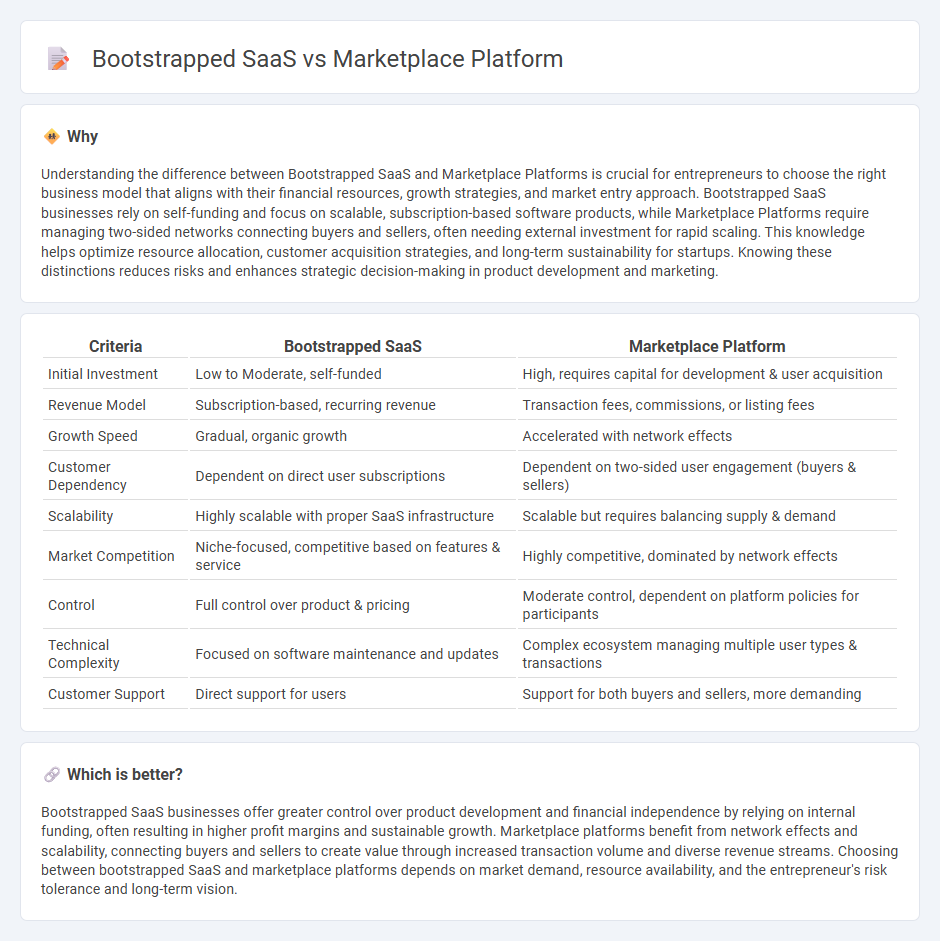
Understanding the difference between Bootstrapped SaaS and Marketplace Platforms is crucial for entrepreneurs to choose the right business model that aligns with their financial resources, growth strategies, and market entry approach. Bootstrapped SaaS businesses rely on self-funding and focus on scalable, subscription-based software products, while Marketplace Platforms require managing two-sided networks connecting buyers and sellers, often needing external investment for rapid scaling. This knowledge helps optimize resource allocation, customer acquisition strategies, and long-term sustainability for startups. Knowing these distinctions reduces risks and enhances strategic decision-making in product development and marketing.
Comparison Table
| Criteria | Bootstrapped SaaS | Marketplace Platform |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Investment | Low to Moderate, self-funded | High, requires capital for development & user acquisition |
| Revenue Model | Subscription-based, recurring revenue | Transaction fees, commissions, or listing fees |
| Growth Speed | Gradual, organic growth | Accelerated with network effects |
| Customer Dependency | Dependent on direct user subscriptions | Dependent on two-sided user engagement (buyers & sellers) |
| Scalability | Highly scalable with proper SaaS infrastructure | Scalable but requires balancing supply & demand |
| Market Competition | Niche-focused, competitive based on features & service | Highly competitive, dominated by network effects |
| Control | Full control over product & pricing | Moderate control, dependent on platform policies for participants |
| Technical Complexity | Focused on software maintenance and updates | Complex ecosystem managing multiple user types & transactions |
| Customer Support | Direct support for users | Support for both buyers and sellers, more demanding |
Which is better?
Bootstrapped SaaS businesses offer greater control over product development and financial independence by relying on internal funding, often resulting in higher profit margins and sustainable growth. Marketplace platforms benefit from network effects and scalability, connecting buyers and sellers to create value through increased transaction volume and diverse revenue streams. Choosing between bootstrapped SaaS and marketplace platforms depends on market demand, resource availability, and the entrepreneur's risk tolerance and long-term vision.
Connection
Bootstrapped SaaS and marketplace platforms are connected through their reliance on organic growth and efficient resource allocation to scale operations without external funding. Both models emphasize creating value through direct customer engagement, iterative product development, and sustainable revenue generation. Success in these platforms often hinges on leveraging community-driven network effects and optimizing user acquisition cost.
Key Terms
Network Effects
Marketplace platforms leverage strong network effects by connecting buyers and sellers, increasing value as user participation grows, resulting in enhanced liquidity and reduced transaction friction. Bootstrapped SaaS models often grow through customer retention and feature improvements but may lack the exponential user-driven growth characteristic of network effects. Explore more to understand how these dynamics influence scaling strategies and user engagement.
Revenue Model
Marketplace platforms generate revenue primarily through transaction fees, commissions, and listing charges, creating a steady income stream directly tied to user activity and sales volume. Bootstrapped SaaS typically relies on subscription-based revenue models, emphasizing recurring payments for software access, which fosters predictable cash flow and scalability without diluting ownership. Explore detailed comparisons to understand which revenue model aligns best with your business goals and growth strategy.
Customer Acquisition
Marketplace platforms leverage network effects to rapidly scale customer acquisition by connecting buyers and sellers in a centralized ecosystem, maximizing transactional volume and user engagement. Bootstrapped SaaS relies heavily on targeted digital marketing, organic growth, and customer retention strategies to build a loyal user base with limited external funding. Explore detailed strategies and metrics to optimize customer acquisition for your specific business model.
Source and External Links
Marketplace Builder | Create a Marketplace with CS-Cart - CS-Cart offers a powerful, fully customizable no-code marketplace builder ideal for various types of marketplaces such as product, service, rental, B2B, and digital goods, with features including vendor management, flexible commissions, multi-storefront support, payment integrations, and marketing tools.
What is a Marketplace Platform: Definition, Use Cases, and Features - A marketplace platform is an e-commerce website where multiple vendors create online stores on a common storefront, enabling buyers to shop a wide range of products or services online, with examples like Amazon, Etsy, and Airbnb, and includes seller onboarding, listing management, checkout, and user communication.
Best Marketplace Software: User Reviews from July 2025 - G2 - Marketplace software enables management of digital storefronts hosting multiple vendors, streamlining website design, vendor communication, and shipping, and differs from single-vendor e-commerce platforms by supporting multivendor functionality; products may be standalone or plugins for content management systems.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com