Embedded finance integrates financial services directly within non-financial platforms, streamlining customer experiences by eliminating the need for third-party intermediaries. Payment gateways act as secure online portals that facilitate transactions between merchants and customers, ensuring payment data is encrypted and processed efficiently. Discover how these technologies are transforming entrepreneurial opportunities and reshaping digital commerce.
Why it is important
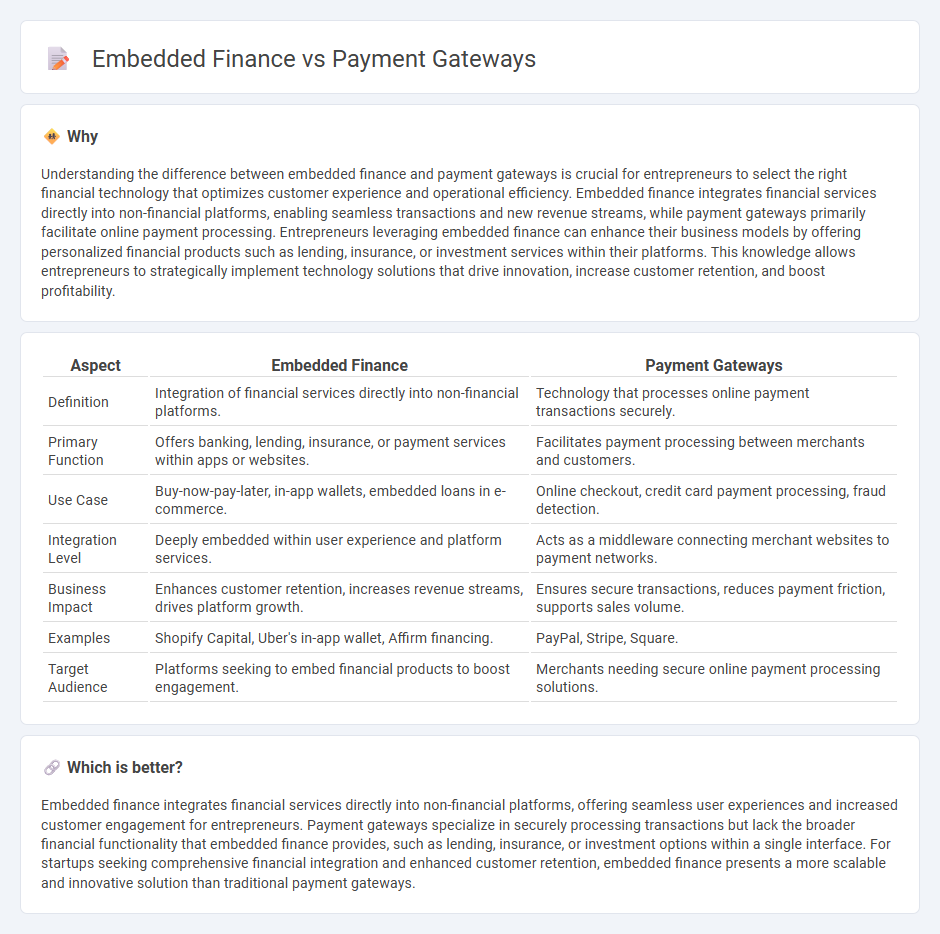
Understanding the difference between embedded finance and payment gateways is crucial for entrepreneurs to select the right financial technology that optimizes customer experience and operational efficiency. Embedded finance integrates financial services directly into non-financial platforms, enabling seamless transactions and new revenue streams, while payment gateways primarily facilitate online payment processing. Entrepreneurs leveraging embedded finance can enhance their business models by offering personalized financial products such as lending, insurance, or investment services within their platforms. This knowledge allows entrepreneurs to strategically implement technology solutions that drive innovation, increase customer retention, and boost profitability.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Embedded Finance | Payment Gateways |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Integration of financial services directly into non-financial platforms. | Technology that processes online payment transactions securely. |
| Primary Function | Offers banking, lending, insurance, or payment services within apps or websites. | Facilitates payment processing between merchants and customers. |
| Use Case | Buy-now-pay-later, in-app wallets, embedded loans in e-commerce. | Online checkout, credit card payment processing, fraud detection. |
| Integration Level | Deeply embedded within user experience and platform services. | Acts as a middleware connecting merchant websites to payment networks. |
| Business Impact | Enhances customer retention, increases revenue streams, drives platform growth. | Ensures secure transactions, reduces payment friction, supports sales volume. |
| Examples | Shopify Capital, Uber's in-app wallet, Affirm financing. | PayPal, Stripe, Square. |
| Target Audience | Platforms seeking to embed financial products to boost engagement. | Merchants needing secure online payment processing solutions. |
Which is better?
Embedded finance integrates financial services directly into non-financial platforms, offering seamless user experiences and increased customer engagement for entrepreneurs. Payment gateways specialize in securely processing transactions but lack the broader financial functionality that embedded finance provides, such as lending, insurance, or investment options within a single interface. For startups seeking comprehensive financial integration and enhanced customer retention, embedded finance presents a more scalable and innovative solution than traditional payment gateways.
Connection
Embedded finance integrates financial services such as payment gateways directly into non-financial platforms, streamlining transactions for entrepreneurs and enhancing customer experience. Payment gateways serve as the critical infrastructure enabling secure processing of online payments within embedded finance ecosystems, facilitating seamless checkout processes and reducing friction in digital commerce. This connection empowers entrepreneurs to offer instant credit, insurance, and transactional capabilities, driving business growth and customer retention.
Key Terms
Transaction Processing (Payment Gateways)
Payment gateways facilitate secure transaction processing by authorizing and capturing payments between merchants and customers, ensuring seamless payment acceptance across multiple platforms. Embedded finance integrates financial services directly into non-financial apps, streamlining user experience but often relying on payment gateways for transaction processing infrastructure. Explore how these technologies complement each other to optimize payment workflows and enhance customer satisfaction.
API Integration (Embedded Finance)
Payment gateways provide the infrastructure for processing online transactions, while embedded finance integrates financial services directly into non-financial platforms through API integration, streamlining user experience. API-driven embedded finance enables seamless access to payments, lending, insurance, or banking within apps, reducing friction and enhancing customer engagement. Explore how API integration in embedded finance can transform your business operations and customer interactions.
White-label Banking (Embedded Finance)
Payment gateways primarily facilitate online transaction processing by securely authorizing credit card and digital payments, whereas embedded finance integrates financial services like lending, insurance, and banking directly into non-financial platforms through white-label banking solutions. White-label banking enables businesses to offer customized financial products under their brand, enhancing customer experience and retention without building complex banking infrastructure. Explore how embedding financial services can transform your business model beyond traditional payment gateways.
Source and External Links
Payment Gateways in 2025: Main Types + How They Work - A payment gateway is a merchant service that processes credit card payments online and in-store, with popular providers including PayPal, Square, Stripe, and Apple Pay, each offering distinct features like fraud protection, mobile payment support, and in-person transaction solutions.
Payment Gateways: What They Are And How To Choose One - Payment gateways act as secure intermediaries for online transactions, encrypting payment data and connecting customers, merchants, and banks while supporting features like currency conversion and customizable API integrations.
Payment gateway - Wikipedia - A payment gateway facilitates electronic payment transactions by transferring data between a merchant's site or POS system and financial institutions, authorizing credit card or direct payments but without handling the money flow itself.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com