Sweat equity marketplaces enable entrepreneurs to exchange skills and services for ownership stakes, fostering collaboration and resource sharing in startup ecosystems. Bootstrapping involves self-funding and organic growth without external investment, emphasizing financial discipline and control. Explore these approaches to discover the best strategy for your entrepreneurial journey.
Why it is important
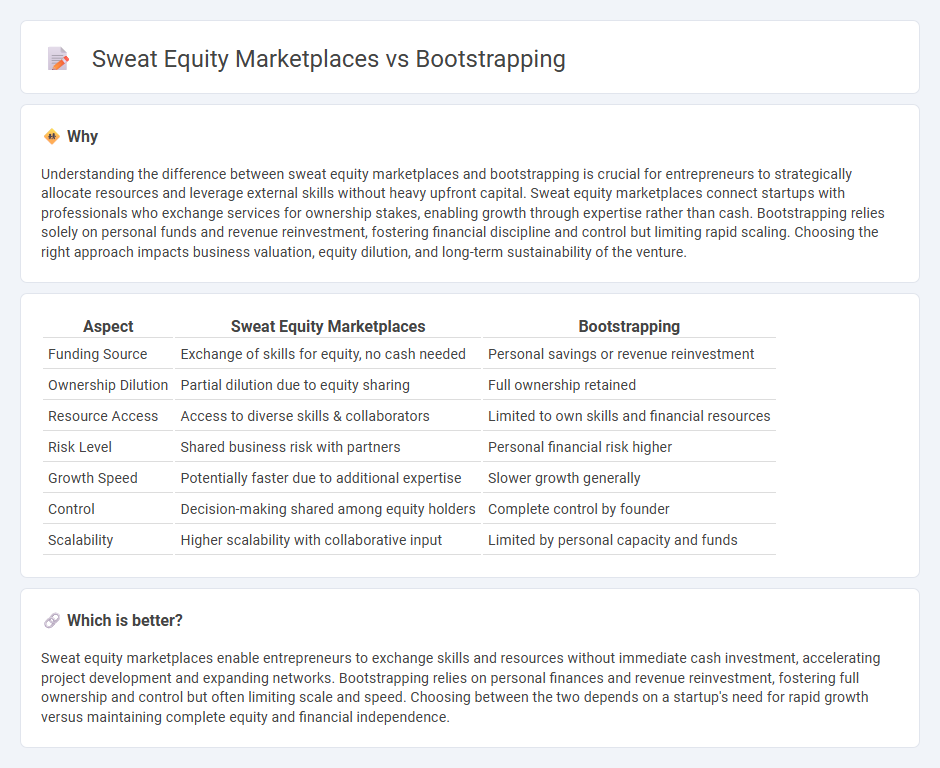
Understanding the difference between sweat equity marketplaces and bootstrapping is crucial for entrepreneurs to strategically allocate resources and leverage external skills without heavy upfront capital. Sweat equity marketplaces connect startups with professionals who exchange services for ownership stakes, enabling growth through expertise rather than cash. Bootstrapping relies solely on personal funds and revenue reinvestment, fostering financial discipline and control but limiting rapid scaling. Choosing the right approach impacts business valuation, equity dilution, and long-term sustainability of the venture.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Sweat Equity Marketplaces | Bootstrapping |
|---|---|---|
| Funding Source | Exchange of skills for equity, no cash needed | Personal savings or revenue reinvestment |
| Ownership Dilution | Partial dilution due to equity sharing | Full ownership retained |
| Resource Access | Access to diverse skills & collaborators | Limited to own skills and financial resources |
| Risk Level | Shared business risk with partners | Personal financial risk higher |
| Growth Speed | Potentially faster due to additional expertise | Slower growth generally |
| Control | Decision-making shared among equity holders | Complete control by founder |
| Scalability | Higher scalability with collaborative input | Limited by personal capacity and funds |
Which is better?
Sweat equity marketplaces enable entrepreneurs to exchange skills and resources without immediate cash investment, accelerating project development and expanding networks. Bootstrapping relies on personal finances and revenue reinvestment, fostering full ownership and control but often limiting scale and speed. Choosing between the two depends on a startup's need for rapid growth versus maintaining complete equity and financial independence.
Connection
Sweat equity marketplaces enable entrepreneurs to exchange skills and labor for ownership stakes, making bootstrapping more feasible by reducing upfront capital needs. These platforms facilitate resource pooling, allowing startups to leverage collective expertise without significant financial investment. Consequently, bootstrapped ventures can accelerate growth by converting sweat equity into tangible business value.
Key Terms
Self-funding
Self-funding through bootstrapping involves entrepreneurs using personal savings or revenue generated to finance their startup, preserving full ownership and control without relying on external investors. Sweat equity marketplaces allow founders and team members to contribute time and effort as a form of investment, gaining shares in the company instead of immediate cash. Explore more about how these self-funding methods can empower your startup growth and equity management.
Equity compensation
Bootstrapping involves funding a startup using personal savings or internal cash flow, minimizing reliance on external investment while retaining full ownership, whereas sweat equity marketplaces enable founders and early contributors to earn ownership shares through their time, skills, and effort instead of monetary investment. Equity compensation in sweat equity marketplaces aligns incentives by granting vesting shares that reflect the value of non-monetary contributions, enhancing team motivation and long-term commitment. Explore our detailed comparison of bootstrapping and sweat equity marketplaces to optimize your equity compensation strategy.
Marketplace platform
Bootstrapping a marketplace platform relies on self-funding and organic growth to validate business models while controlling expenses during early stages. Sweat equity marketplaces leverage participant contributions as intangible investments, fostering community-driven development and incentivizing platform stakeholders with ownership stakes. Explore in-depth strategies for maximizing marketplace value through bootstrapping or sweat equity models.
Source and External Links
Bootstrapping - Overview, Stages, and Advantages - Bootstrapping is the process of building a business from scratch with minimal external capital, relying mainly on internal financing, credit, and loans, progressing through stages from initial personal funds to customer-funded growth and possible credit for expansion.
Bootstrapping - Wikipedia - In business, bootstrapping means starting and growing a company with little or no external capital by using personal savings, reinvesting sales income, and cautiously managing expenses in stages like birth, sales funding, and outsourcing, sometimes leading to seeking loans or venture capital later.
Bootstrapping (statistics) - Wikipedia - Bootstrapping in statistics is a technique for estimating the distribution and accuracy of sample estimates by repeatedly resampling data with replacement, useful when parametric assumptions are questionable.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com