Decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs) operate through blockchain-based smart contracts, enabling collective decision-making without centralized control, unlike sole proprietorships, which rely on a single owner managing all business operations. DAOs offer enhanced transparency, automation, and community governance, contrasting with the simplicity and full ownership control found in sole proprietorships. Explore more to understand which entrepreneurial structure suits your business goals.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between a Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO) and a sole proprietorship is crucial for entrepreneurs to choose the optimal governance structure, legal liability framework, and funding mechanism. DAOs operate on blockchain technology, enabling decentralized decision-making and transparent smart contracts, while sole proprietorships are traditional, centralized businesses controlled by a single individual with unlimited liability. This knowledge helps entrepreneurs mitigate risks, optimize operational efficiency, and align with regulatory requirements. Selecting the appropriate business model impacts scalability, investor trust, and long-term sustainability in the dynamic entrepreneurial landscape.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO) | Sole Proprietorship |
|---|---|---|
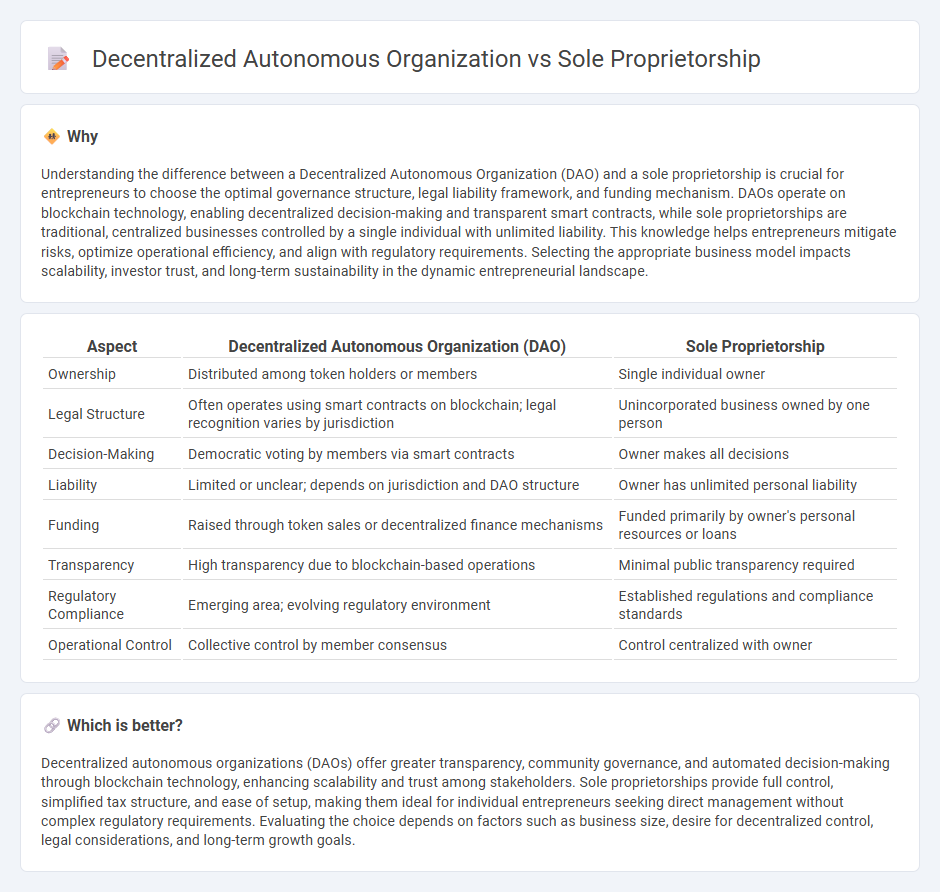
| Ownership | Distributed among token holders or members | Single individual owner |
| Legal Structure | Often operates using smart contracts on blockchain; legal recognition varies by jurisdiction | Unincorporated business owned by one person |
| Decision-Making | Democratic voting by members via smart contracts | Owner makes all decisions |
| Liability | Limited or unclear; depends on jurisdiction and DAO structure | Owner has unlimited personal liability |
| Funding | Raised through token sales or decentralized finance mechanisms | Funded primarily by owner's personal resources or loans |
| Transparency | High transparency due to blockchain-based operations | Minimal public transparency required |
| Regulatory Compliance | Emerging area; evolving regulatory environment | Established regulations and compliance standards |
| Operational Control | Collective control by member consensus | Control centralized with owner |
Which is better?
Decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs) offer greater transparency, community governance, and automated decision-making through blockchain technology, enhancing scalability and trust among stakeholders. Sole proprietorships provide full control, simplified tax structure, and ease of setup, making them ideal for individual entrepreneurs seeking direct management without complex regulatory requirements. Evaluating the choice depends on factors such as business size, desire for decentralized control, legal considerations, and long-term growth goals.
Connection
Decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs) and sole proprietorships both represent distinct entrepreneurial structures that enable individuals to operate businesses with varying degrees of autonomy and control. While sole proprietorships involve single individuals managing all aspects of a business, DAOs leverage blockchain technology to distribute decision-making authority among multiple stakeholders without centralized leadership. The connection lies in their shared emphasis on ownership and direct control, with DAOs offering a modern, decentralized evolution of the traditional sole proprietorship model.
Key Terms
Ownership structure
A sole proprietorship is owned and controlled by a single individual who assumes full responsibility for all liabilities and profits, ensuring centralized decision-making and accountability. Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) operate through blockchain technology, distributing ownership and control among token holders who participate in governance via smart contracts, promoting transparency and collective decision-making. Explore the nuances of ownership structures to make informed choices between these business models.
Decision-making process
In a sole proprietorship, the decision-making process is centralized, with the owner having full control over business operations and strategic choices, ensuring swift and singular authority. In contrast, a decentralized autonomous organization (DAO) leverages blockchain technology to enable collective decision-making through token-based voting, promoting transparency and democratic governance without central leadership. Explore how these contrasting structures impact efficiency and stakeholder involvement to understand which model suits your needs best.
Liability
Sole proprietorships expose owners to unlimited personal liability, making them personally responsible for all business debts and legal actions. In contrast, Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) offer limited liability protection by operating through smart contracts on blockchain networks, reducing individual stakeholder risk. Explore the key differences in liability models between these business structures to better understand your options.
Source and External Links
sole proprietorship | Wex | US Law | LII / Legal Information Institute - A sole proprietorship is an unregistered and unincorporated business owned by one person who assumes all assets, debts, and liabilities of the business, with no legal separation between owner and business and full personal liability for losses.
What is a Sole Proprietorship & How to Start One | Wolters Kluwer - Sole proprietorship is the simplest and most common business structure, where the owner has complete control, earns all profits, and is personally responsible for debts and liabilities, with no formal registration required.
Sole proprietorship - Wikipedia - A sole proprietorship (also called sole trader) is a business owned by one person who is personally liable for business debts, with easy setup and simpler tax filing, but no legal distinction between personal and business income or liability.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com