Solopreneurs independently manage all aspects of their business, leveraging personal skills and resources to drive growth, while franchisees operate under the established brand, benefiting from proven systems and support. The solopreneur model offers complete creative freedom and flexibility, contrasting with the franchisee's structured operational framework and shared risk. Discover key differences to determine which entrepreneurship path aligns with your goals.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between a solopreneur and a franchisee is crucial for entrepreneurs to choose the right business model that aligns with their risk tolerance, investment capacity, and desired level of control. Solopreneurs independently manage their startups, bearing all risks and rewards, while franchisees operate under an established brand with structured support but limited autonomy. Recognizing these distinctions helps optimize strategic decisions, operational planning, and financial forecasting for business success. Entrepreneurs equipped with this knowledge can better navigate legal obligations and growth opportunities inherent to each model.
Comparison Table
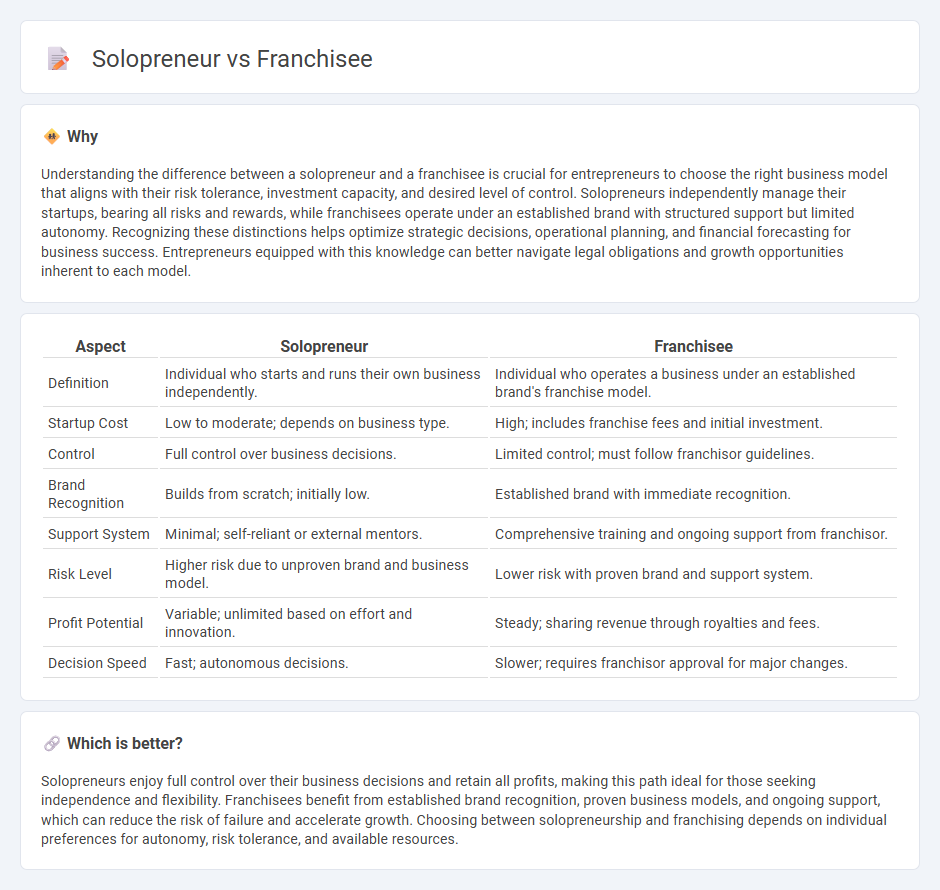
| Aspect | Solopreneur | Franchisee |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Individual who starts and runs their own business independently. | Individual who operates a business under an established brand's franchise model. |
| Startup Cost | Low to moderate; depends on business type. | High; includes franchise fees and initial investment. |
| Control | Full control over business decisions. | Limited control; must follow franchisor guidelines. |
| Brand Recognition | Builds from scratch; initially low. | Established brand with immediate recognition. |
| Support System | Minimal; self-reliant or external mentors. | Comprehensive training and ongoing support from franchisor. |
| Risk Level | Higher risk due to unproven brand and business model. | Lower risk with proven brand and support system. |
| Profit Potential | Variable; unlimited based on effort and innovation. | Steady; sharing revenue through royalties and fees. |
| Decision Speed | Fast; autonomous decisions. | Slower; requires franchisor approval for major changes. |
Which is better?
Solopreneurs enjoy full control over their business decisions and retain all profits, making this path ideal for those seeking independence and flexibility. Franchisees benefit from established brand recognition, proven business models, and ongoing support, which can reduce the risk of failure and accelerate growth. Choosing between solopreneurship and franchising depends on individual preferences for autonomy, risk tolerance, and available resources.
Connection
Solopreneurs and franchisees both operate independently but leverage distinctive business models to maximize growth and autonomy. Solopreneurs build and manage their own ventures from the ground up, while franchisees adopt established brand systems and business practices to reduce risk and accelerate profitability. Both roles emphasize entrepreneurial drive, decision-making authority, and commitment to business success.
Key Terms
Ownership Structure
Franchisees operate under an established brand with a predefined business model, benefiting from franchisor support and shared resources, while solopreneurs maintain full control and ownership of their independent ventures. Franchise ownership typically involves contractual obligations and fees, contrasting with the solopreneur's direct autonomy and decision-making power. Explore the nuances of ownership structures to determine the ideal path for your entrepreneurial goals.
Support System
Franchisees benefit from robust support systems, including comprehensive training, marketing assistance, and operational guidance from the franchisor, which significantly reduces the risks associated with starting a business. Solopreneurs operate independently, relying primarily on self-acquired knowledge and external networks for support, which can lead to greater flexibility but increased vulnerability. Discover more about choosing the ideal business model based on support system advantages.
Autonomy
Franchisees operate under the established brand and business model of a franchisor, which limits their autonomy but provides structured support and proven systems. Solopreneurs enjoy full control over all business decisions, allowing maximum autonomy but requiring complete responsibility for success and risk. Explore the advantages and challenges of each to determine which path aligns with your entrepreneurial goals.
Source and External Links
What is a Franchisee? | HR & Payroll Glossary - Paylocity - A franchisee is an independent business owner who has purchased the rights to operate using an existing company's brand, name, knowledge, and intellectual property, paying fees and royalties while adhering to franchisor guidelines.
Franchising - Wikipedia - Franchising is a business expansion strategy where a franchisor licenses its trademark, know-how, and business model to a franchisee in exchange for fees, with franchisees typically having fewer legal and economic advantages compared to franchisors.
Defining the Role and Responsibilities of a Franchisee - Entrepreneur - Franchisees are required to fund, operate, and manage the franchise according to franchisor standards, assuming the role of brand representatives and maintaining business viability through compliance and sales efforts.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com