Bootstrapped SaaS businesses leverage self-funding to maintain full control and scalability while minimizing external influence, ensuring organic growth driven by innovation and customer feedback. Franchise models offer rapid market expansion through franchisor support and a proven business blueprint but require adherence to established protocols and shared revenue. Explore the distinct advantages and challenges of both models to determine the best entrepreneurial path.
Why it is important
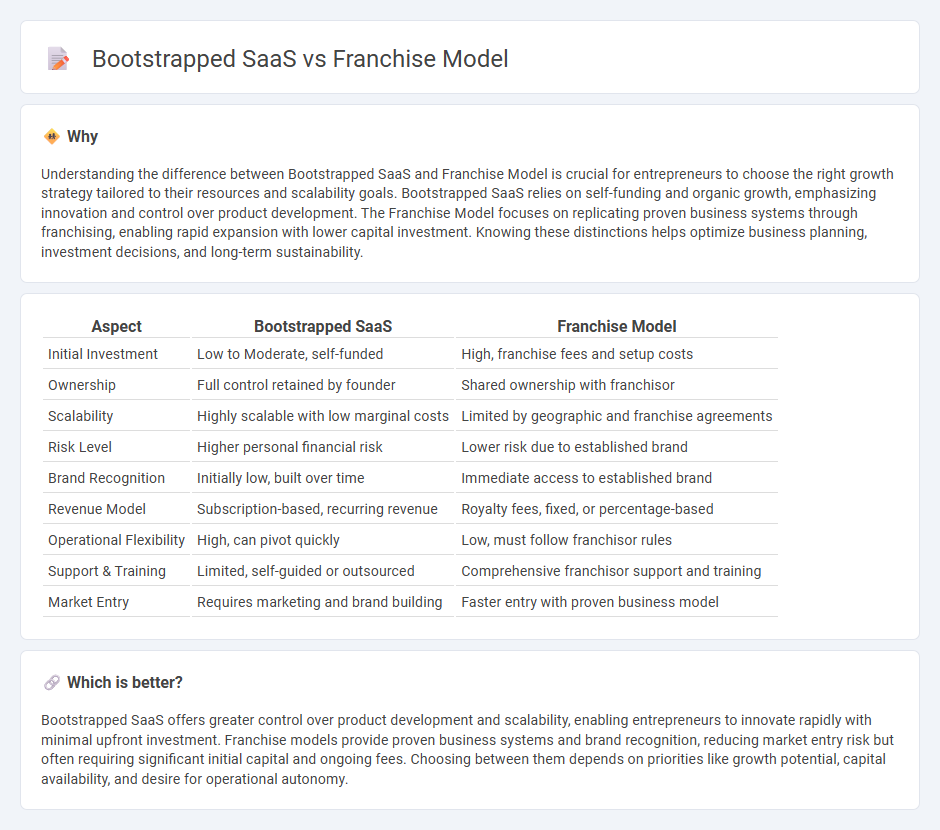
Understanding the difference between Bootstrapped SaaS and Franchise Model is crucial for entrepreneurs to choose the right growth strategy tailored to their resources and scalability goals. Bootstrapped SaaS relies on self-funding and organic growth, emphasizing innovation and control over product development. The Franchise Model focuses on replicating proven business systems through franchising, enabling rapid expansion with lower capital investment. Knowing these distinctions helps optimize business planning, investment decisions, and long-term sustainability.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Bootstrapped SaaS | Franchise Model |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Investment | Low to Moderate, self-funded | High, franchise fees and setup costs |
| Ownership | Full control retained by founder | Shared ownership with franchisor |
| Scalability | Highly scalable with low marginal costs | Limited by geographic and franchise agreements |
| Risk Level | Higher personal financial risk | Lower risk due to established brand |
| Brand Recognition | Initially low, built over time | Immediate access to established brand |
| Revenue Model | Subscription-based, recurring revenue | Royalty fees, fixed, or percentage-based |
| Operational Flexibility | High, can pivot quickly | Low, must follow franchisor rules |
| Support & Training | Limited, self-guided or outsourced | Comprehensive franchisor support and training |
| Market Entry | Requires marketing and brand building | Faster entry with proven business model |
Which is better?
Bootstrapped SaaS offers greater control over product development and scalability, enabling entrepreneurs to innovate rapidly with minimal upfront investment. Franchise models provide proven business systems and brand recognition, reducing market entry risk but often requiring significant initial capital and ongoing fees. Choosing between them depends on priorities like growth potential, capital availability, and desire for operational autonomy.
Connection
Bootstrapped SaaS companies often adopt franchise models to scale their operations efficiently by leveraging established systems and brand recognition, minimizing initial capital expenditures. This connection allows entrepreneurs to maintain control while accessing proven market strategies, facilitating sustainable growth. Franchise structures provide a replicable framework that aligns well with the iterative development and customer-centric approach inherent in bootstrapped SaaS ventures.
Key Terms
Royalty Fees
Franchise models in SaaS often require ongoing royalty fees, typically ranging between 5% to 10% of gross revenue, which can impact profitability and cash flow. In contrast, bootstrapped SaaS ventures avoid royalty payments, enabling founders to retain full revenue but requiring significant upfront capital and resource allocation. Explore detailed comparisons and strategic insights to choose the best funding and growth approach for your SaaS business.
Equity Ownership
Equity ownership in franchise models typically remains with the franchisor, limiting the franchisee's stake while ensuring brand consistency and support. In bootstrapped SaaS companies, founders retain full equity, enabling complete control over business decisions and profit distribution. Discover how equity structures impact growth and control in your business strategy.
Initial Capital
Franchise models typically require substantial initial capital to cover franchise fees, setup costs, and compliance with brand standards, often ranging from $50,000 to over $500,000. Bootstrapped SaaS startups usually demand significantly less upfront investment, mainly allocated toward product development, cloud infrastructure, and marketing, sometimes starting with under $10,000. Explore deeper comparisons on financing strategies by diving into detailed analyses of franchise and bootstrapped SaaS models.
Source and External Links
Types of Franchise Business Models - Legalkart - Franchise models include Company Owned Company Operated (COCO), Company Owned Franchise Operated (COFO), Franchise Owned Company Operated (FOCO), and Franchise Owned Franchise Operated (FOFO), differing in ownership and operational responsibility between franchisor and franchisee.
Types of Franchise Models Explained - HigherVisibility - Other franchise models include product distribution franchises where franchisees sell franchisor products often exclusively, and manufacturing franchises where franchisees manufacture and distribute products under franchisor guidelines.
A Consumer's Guide to Buying a Franchise - The franchise business model grants franchisees the right to operate using the franchisor's system and name for a fee, with ongoing royalties and support, including training, marketing, and operational assistance.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com