No code startups leverage platforms like Bubble and Webflow to rapidly build and launch products without extensive coding, enabling entrepreneurs to focus on market validation and customer feedback. Direct-to-consumer (DTC) startups prioritize selling products directly to customers via online channels, streamlining distribution and fostering brand loyalty through personalized experiences. Explore the strategic differences and growth opportunities between no code and DTC startups to optimize your entrepreneurial journey.
Why it is important
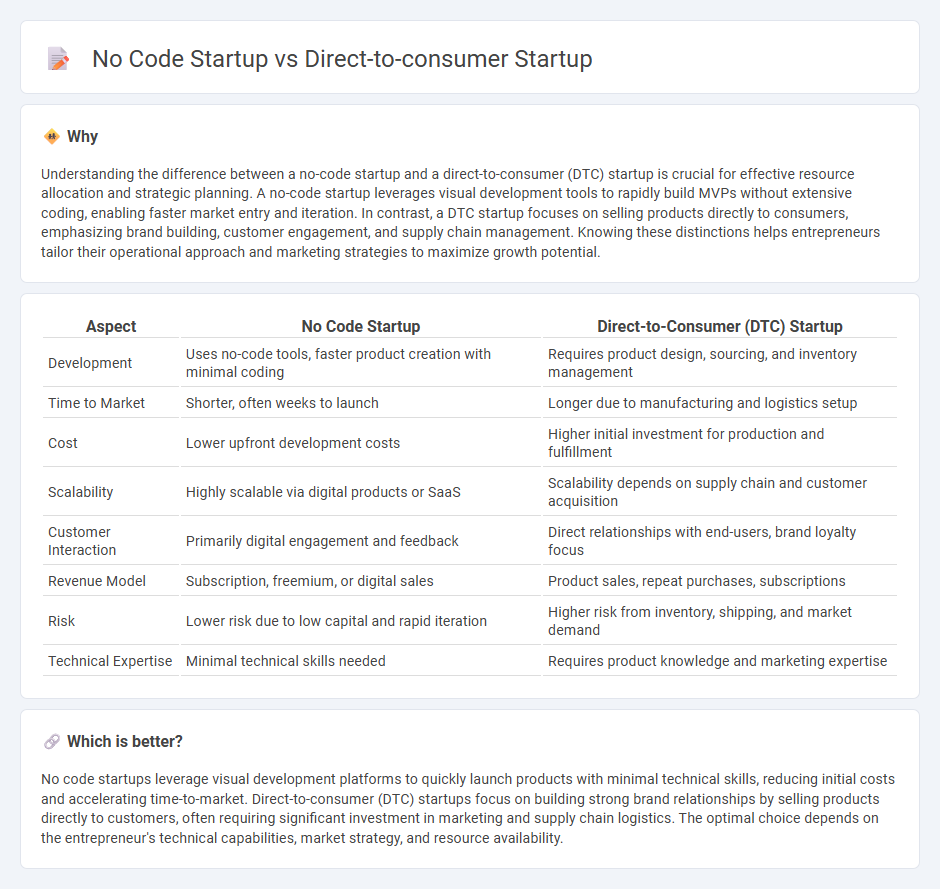
Understanding the difference between a no-code startup and a direct-to-consumer (DTC) startup is crucial for effective resource allocation and strategic planning. A no-code startup leverages visual development tools to rapidly build MVPs without extensive coding, enabling faster market entry and iteration. In contrast, a DTC startup focuses on selling products directly to consumers, emphasizing brand building, customer engagement, and supply chain management. Knowing these distinctions helps entrepreneurs tailor their operational approach and marketing strategies to maximize growth potential.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | No Code Startup | Direct-to-Consumer (DTC) Startup |
|---|---|---|
| Development | Uses no-code tools, faster product creation with minimal coding | Requires product design, sourcing, and inventory management |
| Time to Market | Shorter, often weeks to launch | Longer due to manufacturing and logistics setup |
| Cost | Lower upfront development costs | Higher initial investment for production and fulfillment |
| Scalability | Highly scalable via digital products or SaaS | Scalability depends on supply chain and customer acquisition |
| Customer Interaction | Primarily digital engagement and feedback | Direct relationships with end-users, brand loyalty focus |
| Revenue Model | Subscription, freemium, or digital sales | Product sales, repeat purchases, subscriptions |
| Risk | Lower risk due to low capital and rapid iteration | Higher risk from inventory, shipping, and market demand |
| Technical Expertise | Minimal technical skills needed | Requires product knowledge and marketing expertise |
Which is better?
No code startups leverage visual development platforms to quickly launch products with minimal technical skills, reducing initial costs and accelerating time-to-market. Direct-to-consumer (DTC) startups focus on building strong brand relationships by selling products directly to customers, often requiring significant investment in marketing and supply chain logistics. The optimal choice depends on the entrepreneur's technical capabilities, market strategy, and resource availability.
Connection
No-code startups accelerate entrepreneurship by enabling founders to rapidly build and launch direct-to-consumer (D2C) businesses without extensive technical skills. These startups leverage no-code platforms to create customizable e-commerce websites and marketing tools that streamline customer engagement and product delivery. The synergy between no-code tools and D2C models reduces time-to-market and operational costs, fostering innovation and scalability in entrepreneurial ventures.
Key Terms
Direct-to-Consumer Startup:
Direct-to-consumer startups prioritize building direct relationships with end customers by bypassing traditional retail channels, leveraging personalized marketing strategies and e-commerce platforms to maximize customer engagement and data insights. These startups often focus on product differentiation, brand loyalty, and customer experience to drive growth and profitability in competitive markets. Explore the unique advantages and challenges of direct-to-consumer startups to understand their strategic impact on modern retail.
Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC)
Direct-to-consumer startups often face higher Customer Acquisition Costs (CAC) due to extensive marketing, advertising, and brand-building efforts required to reach individual customers. No code startups typically experience lower CAC by targeting niche developer communities or businesses through organic growth and partnerships, leveraging product-led growth strategies. Explore deeper insights on CAC optimization for both startup types to refine your acquisition strategy.
Brand Positioning
Direct-to-consumer startups prioritize brand positioning through personalized customer experiences, unique value propositions, and strong emotional connections to build loyalty and trust. No-code startups focus on positioning by emphasizing flexibility, accessibility, and innovation in technology that empowers non-technical users to create solutions quickly. Explore deeper insights into how brand positioning differentiates each startup model and drives market success.
Source and External Links
DTC marketplace: Your direct to consumer strategy - COAX Software - A direct-to-consumer (DTC) startup is a brand that sells products directly to end consumers through digital platforms, bypassing wholesalers and retailers, allowing them to manage the entire customer journey and often achieve competitive pricing and strong brand connection; the DTC market has seen explosive growth, reaching billions in sales and shifting retail norms since the late 2000s.
20 Fast-Growing DTC Startups 2025 | TRUiC - DTC startups are rapidly growing companies that leverage digital channels to sell directly to customers, building closer relationships and often disrupting traditional retail by cutting out the middleman; examples and key success factors include funding, founder vision, and personalized customer experiences.
The Ultimate Guide to Direct To Consumer (DTC) - Brightpearl - DTC startups are transforming the retail sector by adopting this sales strategy to bypass traditional distribution, achieving rapid revenue growth and new market entry, supported by omnichannel approaches and technologies, as shown by brands like Finlay London; the model is increasingly adopted worldwide with significant economic impact.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com