Solopreneurs independently manage every aspect of their business, leveraging agility and personal vision to drive growth, while corporate entrepreneurs innovate within established organizations, balancing creativity with company resources and structures. Both paths demand strategic risk-taking, resilience, and a deep understanding of market dynamics to succeed. Explore the nuances of solopreneurship and corporate entrepreneurship to determine the best fit for your professional ambitions.
Why it is important
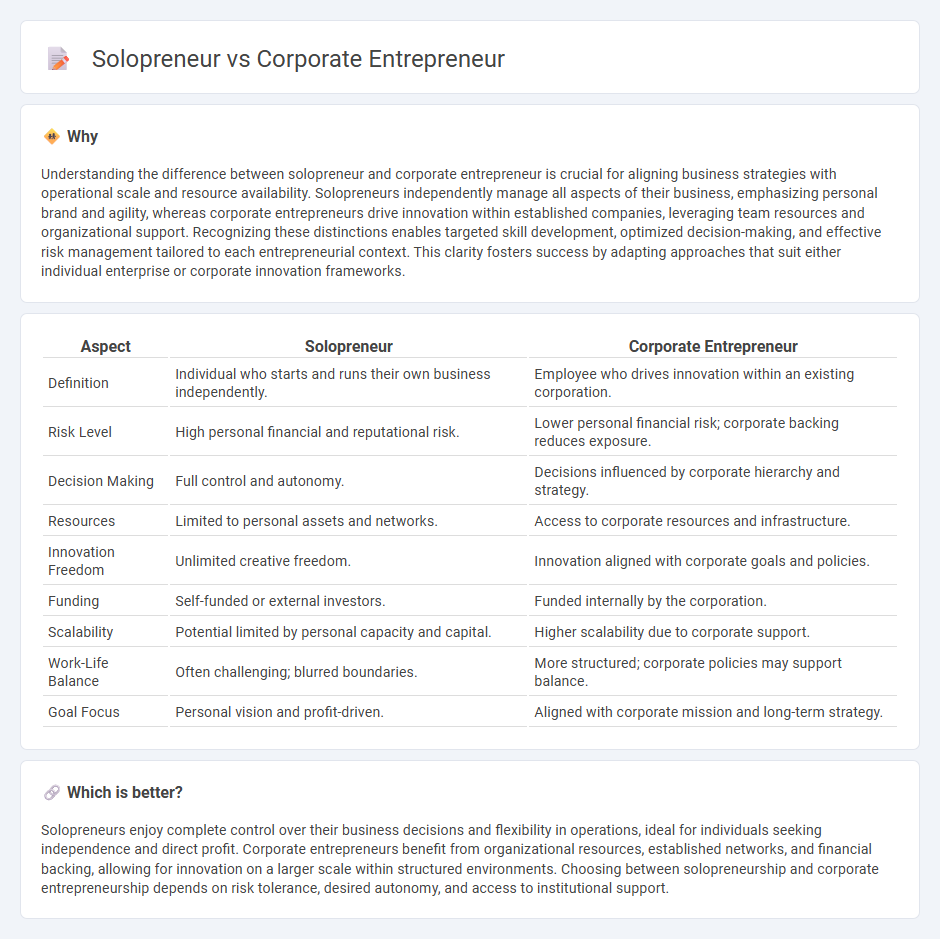
Understanding the difference between solopreneur and corporate entrepreneur is crucial for aligning business strategies with operational scale and resource availability. Solopreneurs independently manage all aspects of their business, emphasizing personal brand and agility, whereas corporate entrepreneurs drive innovation within established companies, leveraging team resources and organizational support. Recognizing these distinctions enables targeted skill development, optimized decision-making, and effective risk management tailored to each entrepreneurial context. This clarity fosters success by adapting approaches that suit either individual enterprise or corporate innovation frameworks.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Solopreneur | Corporate Entrepreneur |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Individual who starts and runs their own business independently. | Employee who drives innovation within an existing corporation. |
| Risk Level | High personal financial and reputational risk. | Lower personal financial risk; corporate backing reduces exposure. |
| Decision Making | Full control and autonomy. | Decisions influenced by corporate hierarchy and strategy. |
| Resources | Limited to personal assets and networks. | Access to corporate resources and infrastructure. |
| Innovation Freedom | Unlimited creative freedom. | Innovation aligned with corporate goals and policies. |
| Funding | Self-funded or external investors. | Funded internally by the corporation. |
| Scalability | Potential limited by personal capacity and capital. | Higher scalability due to corporate support. |
| Work-Life Balance | Often challenging; blurred boundaries. | More structured; corporate policies may support balance. |
| Goal Focus | Personal vision and profit-driven. | Aligned with corporate mission and long-term strategy. |
Which is better?
Solopreneurs enjoy complete control over their business decisions and flexibility in operations, ideal for individuals seeking independence and direct profit. Corporate entrepreneurs benefit from organizational resources, established networks, and financial backing, allowing for innovation on a larger scale within structured environments. Choosing between solopreneurship and corporate entrepreneurship depends on risk tolerance, desired autonomy, and access to institutional support.
Connection
Solopreneurs and corporate entrepreneurs share a core mindset centered on innovation, risk-taking, and value creation within their respective environments. Both leverage entrepreneurial skills such as opportunity recognition, resource management, and strategic decision-making to drive growth and competitive advantage. Their connection lies in the application of entrepreneurial principles, where solopreneurs operate independently while corporate entrepreneurs innovate intrapreneurially to transform established organizations.
Key Terms
Resources
Corporate entrepreneurs leverage extensive organizational resources such as established networks, capital, and technology platforms to innovate within a company's ecosystem. Solopreneurs rely primarily on personal assets, skills, and limited external support, often facing constraints in scaling due to resource scarcity. Explore how these distinct resource dynamics influence entrepreneurial success and growth strategies.
Autonomy
Corporate entrepreneurs, often referred to as intrapreneurs, operate within established organizations, leveraging resources while navigating corporate structures to innovate. Solopreneurs maintain complete autonomy, controlling every aspect of their business from strategy to execution without external oversight. Explore key differences in autonomy and decision-making to understand which path aligns with your entrepreneurial goals.
Risk-sharing
Corporate entrepreneurs benefit from risk-sharing within established organizational structures, leveraging resources, networks, and financial support to mitigate individual exposure. Solopreneurs face the full spectrum of business risks alone, managing finances, market uncertainties, and operational challenges without external backing. Explore in-depth insights on risk-sharing dynamics between corporate entrepreneurs and solopreneurs.
Source and External Links
Understanding Corporate Entrepreneurship - Corporate entrepreneurship is a business approach within companies that creates new opportunities through four core models: opportunist, enabler, advocate, and producer, enabling growth, innovation, and competitive advantage but also posing challenges like resource allocation and change resistance.
Corporate entrepreneur - NOSCO - A corporate entrepreneur (or intrapreneur) is an individual who develops new ideas and innovation projects inside an existing company, often working under management backing but with lower personal risk than independent entrepreneurs.
Why Is Corporate Entrepreneurship Important? - Corporate entrepreneurship (intrapreneurship) is crucial for generating new businesses or products within organizations, combining startup energy with corporate resources to enhance innovation, productivity, and even support sustainability efforts.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com