Secondment involves temporarily assigning an employee to a different department or organization to gain specific experience while maintaining their original employment status. Apprenticeship combines on-the-job training with classroom instruction to develop specialized skills and certifications for a defined trade or profession. Explore the differences and benefits of secondment versus apprenticeship to determine the best fit for career growth.
Why it is important
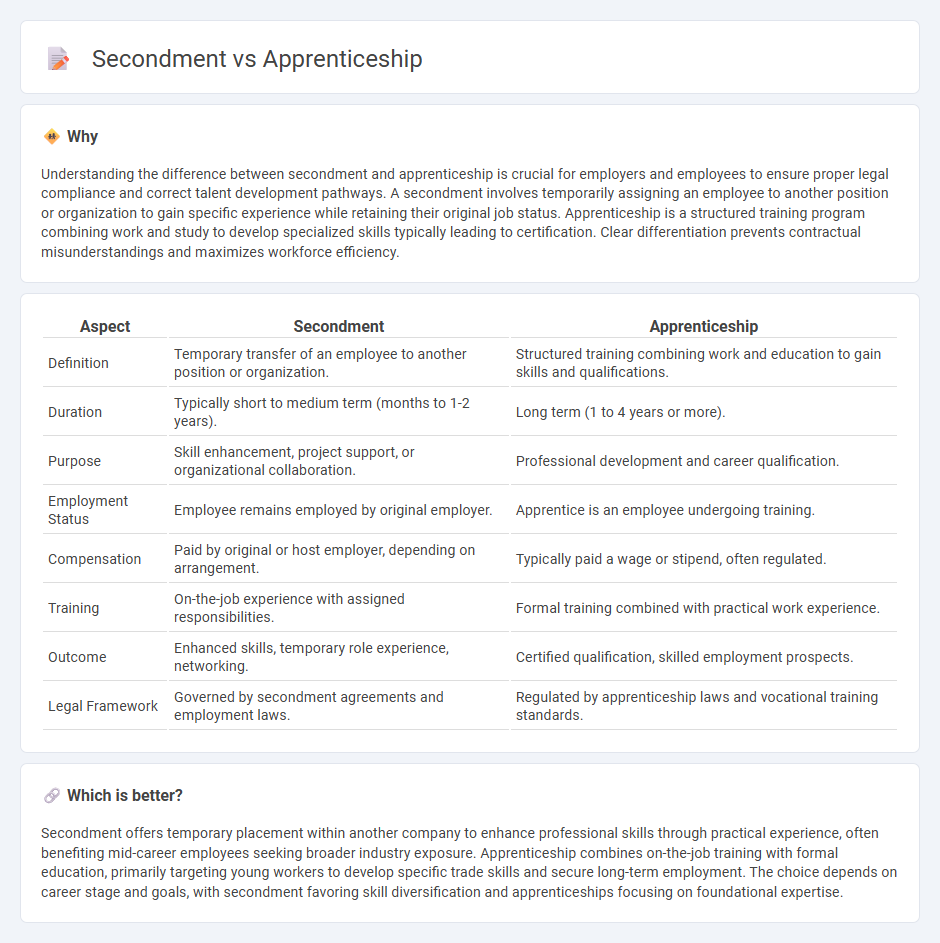
Understanding the difference between secondment and apprenticeship is crucial for employers and employees to ensure proper legal compliance and correct talent development pathways. A secondment involves temporarily assigning an employee to another position or organization to gain specific experience while retaining their original job status. Apprenticeship is a structured training program combining work and study to develop specialized skills typically leading to certification. Clear differentiation prevents contractual misunderstandings and maximizes workforce efficiency.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Secondment | Apprenticeship |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Temporary transfer of an employee to another position or organization. | Structured training combining work and education to gain skills and qualifications. |
| Duration | Typically short to medium term (months to 1-2 years). | Long term (1 to 4 years or more). |
| Purpose | Skill enhancement, project support, or organizational collaboration. | Professional development and career qualification. |
| Employment Status | Employee remains employed by original employer. | Apprentice is an employee undergoing training. |
| Compensation | Paid by original or host employer, depending on arrangement. | Typically paid a wage or stipend, often regulated. |
| Training | On-the-job experience with assigned responsibilities. | Formal training combined with practical work experience. |
| Outcome | Enhanced skills, temporary role experience, networking. | Certified qualification, skilled employment prospects. |
| Legal Framework | Governed by secondment agreements and employment laws. | Regulated by apprenticeship laws and vocational training standards. |
Which is better?
Secondment offers temporary placement within another company to enhance professional skills through practical experience, often benefiting mid-career employees seeking broader industry exposure. Apprenticeship combines on-the-job training with formal education, primarily targeting young workers to develop specific trade skills and secure long-term employment. The choice depends on career stage and goals, with secondment favoring skill diversification and apprenticeships focusing on foundational expertise.
Connection
Secondment and apprenticeship both enhance workforce skills through practical, on-the-job training, allowing employees to gain diverse experience and industry knowledge. Secondment temporarily assigns workers to different roles or departments within or outside their organization, complementing apprenticeships that combine formal education with hands-on learning. These approaches foster employee development, increase adaptability, and support talent retention by bridging theoretical knowledge with real-world applications.
Key Terms
Training
Apprenticeships provide structured, long-term training programs combining on-the-job experience with academic learning to develop specific skill sets. Secondments offer temporary assignments where employees gain practical exposure to different roles or departments, enhancing adaptability and cross-functional expertise. Explore how these training methods impact professional growth and organizational development.
Temporary assignment
Temporary assignments, including apprenticeships and secondments, offer practical work experience with distinct frameworks: apprenticeships emphasize structured training combined with employment, while secondments involve temporary transfers within or between organizations for skill enhancement. Apprenticeships often result in certification and are designed for skill acquisition in specific trades, whereas secondments provide exposure to new roles or projects, promoting professional development and networking opportunities. Explore detailed comparisons and benefits of these temporary assignments to determine the ideal strategy for workforce development.
Skill development
Apprenticeship programs provide hands-on training combined with theoretical education, enabling individuals to develop specialized skills within a structured curriculum. Secondments offer temporary assignments in different roles or departments, promoting skill diversification and real-world experience through exposure to varied work environments. Explore the advantages of each approach to enhance your career growth and skill development strategies.
Source and External Links
Apprenticeship for Career Seekers - Apprenticeship Colorado - Apprenticeships combine paid hands-on training with learning, offering well-paying job opportunities with mentorship and career pathways across various industries, with a national average starting salary of $80K and strong employment rates.
Apprenticeship Programs - California Community Colleges - California apprenticeship programs integrate paid on-the-job training with classroom instruction to prepare workers for skilled careers in traditional and emerging industries, supported by state funding to expand opportunities.
Apprenticeship.gov: Homepage - The official US government resource connecting career seekers, employers, and educators to apprenticeship programs nationwide, highlighting benefits such as high employment retention, average starting salaries around $80K, and over 800,000 apprentices annually.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com