Ghost jobs are deceptive listings that inflate hiring numbers without real positions available, misleading job seekers and skewing employment data. Mass layoffs, conversely, reflect significant workforce reductions driven by economic downturns or organizational restructuring, impacting job stability and market confidence. Explore more insights on how these phenomena affect labor trends and economic health.
Why it is important
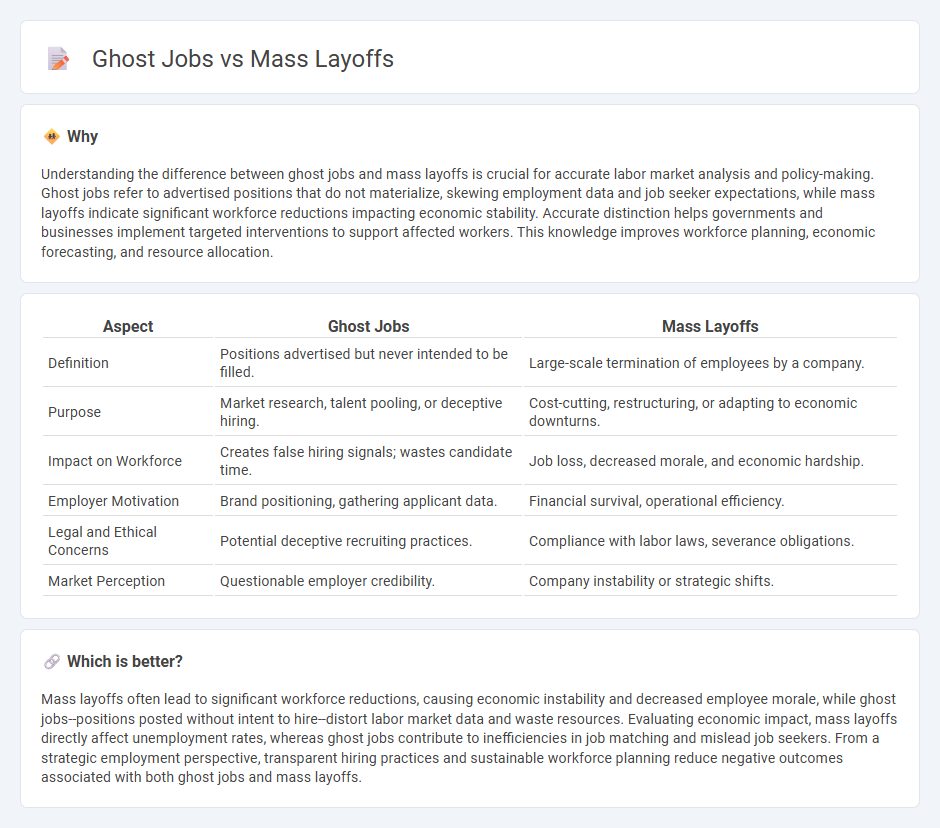
Understanding the difference between ghost jobs and mass layoffs is crucial for accurate labor market analysis and policy-making. Ghost jobs refer to advertised positions that do not materialize, skewing employment data and job seeker expectations, while mass layoffs indicate significant workforce reductions impacting economic stability. Accurate distinction helps governments and businesses implement targeted interventions to support affected workers. This knowledge improves workforce planning, economic forecasting, and resource allocation.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Ghost Jobs | Mass Layoffs |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Positions advertised but never intended to be filled. | Large-scale termination of employees by a company. |
| Purpose | Market research, talent pooling, or deceptive hiring. | Cost-cutting, restructuring, or adapting to economic downturns. |
| Impact on Workforce | Creates false hiring signals; wastes candidate time. | Job loss, decreased morale, and economic hardship. |
| Employer Motivation | Brand positioning, gathering applicant data. | Financial survival, operational efficiency. |
| Legal and Ethical Concerns | Potential deceptive recruiting practices. | Compliance with labor laws, severance obligations. |
| Market Perception | Questionable employer credibility. | Company instability or strategic shifts. |
Which is better?
Mass layoffs often lead to significant workforce reductions, causing economic instability and decreased employee morale, while ghost jobs--positions posted without intent to hire--distort labor market data and waste resources. Evaluating economic impact, mass layoffs directly affect unemployment rates, whereas ghost jobs contribute to inefficiencies in job matching and mislead job seekers. From a strategic employment perspective, transparent hiring practices and sustainable workforce planning reduce negative outcomes associated with both ghost jobs and mass layoffs.
Connection
Ghost jobs, which are unfilled or falsely advertised positions, distort labor market data and create misleading signals about employment opportunities. Mass layoffs often trigger a surge in ghost jobs as companies post openings without intent to hire immediately, aiming to maintain market confidence or comply with reporting requirements. This phenomenon complicates accurate workforce analysis and hinders effective labor policy development.
Key Terms
Worker Displacement
Mass layoffs result in large-scale job losses leading to significant worker displacement and economic instability, while ghost jobs refer to positions that appear open but are not genuinely available, creating misleading employment prospects. Both phenomena contribute to workforce uncertainty and complicate job market transparency, impacting worker morale and economic recovery efforts. Explore deeper insights into how these challenges reshape employment landscapes and affect displaced workers.
Job Market Transparency
Mass layoffs signal significant workforce reductions affecting thousands of employees across industries, often indicating economic downturns or corporate restructuring, while ghost jobs represent misleading job postings that create false impressions of hiring activity, undermining job market transparency. Understanding the distinction between these phenomena is crucial for job seekers and policymakers to navigate employment opportunities accurately and develop informed labor market strategies. Explore comprehensive insights on how mass layoffs and ghost jobs impact transparency in the job market and influence future employment trends.
Labor Demand Manipulation
Mass layoffs often indicate a sharp decline in labor demand, reflecting company efforts to reduce workforce costs amid economic challenges. In contrast, ghost jobs represent inflated or fictitious labor demand, where employers list vacancies without genuine intent to hire, manipulating market perceptions. Explore deeper insights into how labor demand manipulation impacts job market dynamics and economic policies.
Source and External Links
Companies that announced Major Layoffs and Hiring Freezes - Since early 2025, over 2,000 companies, including Dyson, Stellantis, Tesla, and Apple, have announced mass layoffs totaling thousands of jobs as part of restructuring and cost-cutting efforts.
2025 United States federal mass layoffs - Wikipedia - The 2025 federal mass layoffs in the US involve more than 275,000 civil service job cuts, including confirmed layoffs, buyouts, and planned reductions affecting 12% of the federal workforce, driven by policy changes and agency closures.
Mass Layoff Statistics Home Page : U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics - The Mass Layoff Statistics program tracks monthly and quarterly data on establishments with at least 50 initial claims for unemployment insurance due to mass layoffs, providing official labor market separation data.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com