Ghost work involves individuals completing fragmented, often invisible digital tasks for companies, while outsourcing delegates entire business processes to external organizations. Ghost workers typically perform microtasks through online platforms, enabling companies to scale operations flexibly without directly hiring employees. Explore deeper insights into how ghost work and outsourcing reshape the modern employment landscape.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between ghost work and outsourcing is crucial for effective workforce management and ethical labor practices. Ghost work involves invisible, often low-paid tasks performed by individuals typically unknown to end-users, while outsourcing delegates entire business processes to external companies, impacting operational control and cost structures. Recognizing these distinctions helps businesses optimize productivity, ensure compliance with labor laws, and maintain transparent employment standards. Accurate knowledge fosters better strategic decisions regarding resource allocation and employee rights protection.
Comparison Table
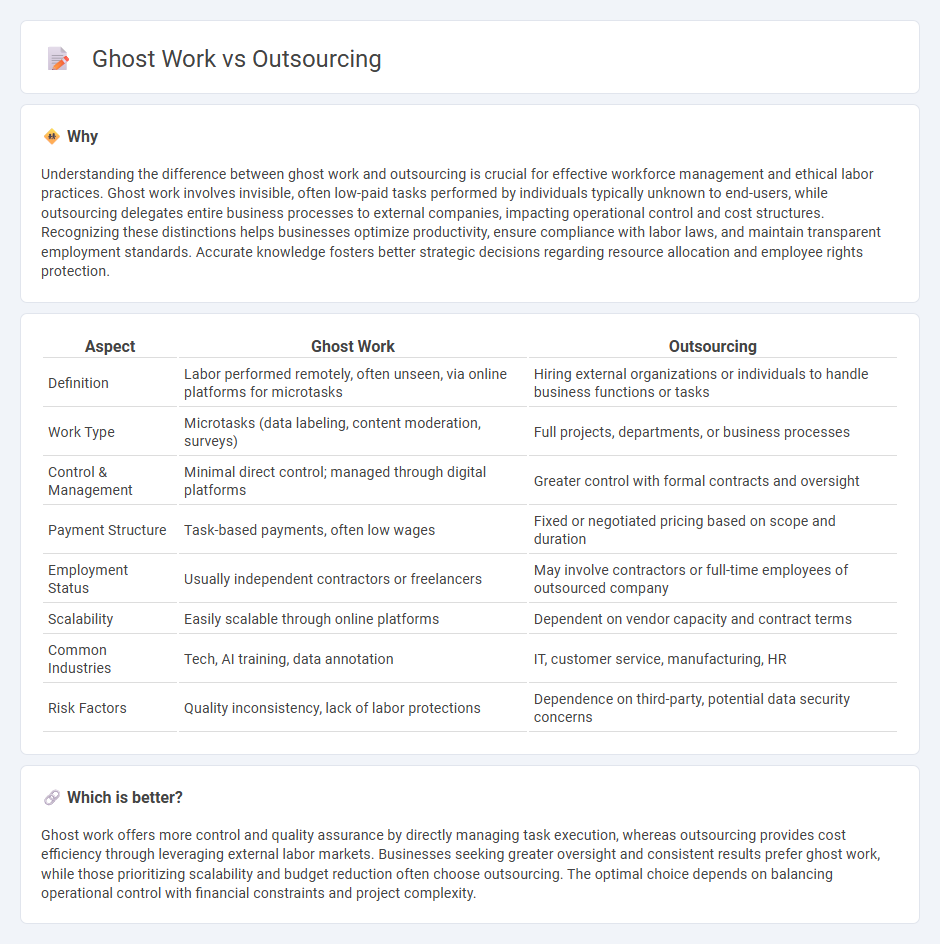
| Aspect | Ghost Work | Outsourcing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Labor performed remotely, often unseen, via online platforms for microtasks | Hiring external organizations or individuals to handle business functions or tasks |
| Work Type | Microtasks (data labeling, content moderation, surveys) | Full projects, departments, or business processes |
| Control & Management | Minimal direct control; managed through digital platforms | Greater control with formal contracts and oversight |
| Payment Structure | Task-based payments, often low wages | Fixed or negotiated pricing based on scope and duration |
| Employment Status | Usually independent contractors or freelancers | May involve contractors or full-time employees of outsourced company |
| Scalability | Easily scalable through online platforms | Dependent on vendor capacity and contract terms |
| Common Industries | Tech, AI training, data annotation | IT, customer service, manufacturing, HR |
| Risk Factors | Quality inconsistency, lack of labor protections | Dependence on third-party, potential data security concerns |
Which is better?
Ghost work offers more control and quality assurance by directly managing task execution, whereas outsourcing provides cost efficiency through leveraging external labor markets. Businesses seeking greater oversight and consistent results prefer ghost work, while those prioritizing scalability and budget reduction often choose outsourcing. The optimal choice depends on balancing operational control with financial constraints and project complexity.
Connection
Ghost work refers to tasks performed by invisible or anonymous online laborers, often outsourced to remote workers across the globe. Outsourcing leverages this model by transferring specific job functions, such as data entry or content moderation, to external contractors or platforms that utilize ghost workers. This practice reduces costs and increases flexibility for companies while raising concerns about job security and labor rights for the ghost workforce.
Key Terms
Contracting
Outsourcing involves hiring external companies or freelancers through formal contracts to complete specific business tasks, often emphasizing clear deliverables and legal accountability. Ghost work refers to hidden, often undocumented labor where workers perform microtasks without formal recognition or contractual agreements, making tracking and regulation challenging. Explore the detailed contrasts between outsourcing and ghost work in contracting to optimize resource management.
Gig Economy
Outsourcing in the gig economy involves delegating entire projects or tasks to third-party firms or freelancers, whereas ghost work refers to invisible, often low-paid tasks performed by gig workers behind the scenes, such as content moderation or data tagging. The gig economy relies heavily on these models to increase flexibility while managing costs and scalability. Explore deeper insights into how outsourcing and ghost work shape the future of the gig economy.
Invisible Labor
Invisible labor encompasses unpaid or underrecognized tasks critical to organizational success, often classified under outsourcing and ghost work. Outsourcing involves delegating specific business functions to external agencies, while ghost work refers to hidden, human-performed digital tasks like content moderation and data labeling that support AI and online platforms. Explore the nuances of these labor forms to better understand their impact on economies and workforce dynamics.
Source and External Links
What Is Outsourcing? (Including Types and Advantages) | Indeed.com - Outsourcing is a strategic practice where organizations contract third-party companies or contractors to perform tasks or create goods, commonly used to reduce labor costs and improve efficiency by leveraging external expertise in areas like customer support, accounting, and engineering.
What is Outsourcing and How Does it Work? - TechTarget - Outsourcing involves a company hiring a third-party service provider to perform operations or services, which can be done onsite or remotely, focusing on maintaining a trusted partnership and managing service contracts effectively.
What is Outsourcing? Definition, Advantages, and Examples - Outsourcing helps businesses reduce costs and improve performance by contracting non-core activities to specialized external providers, allowing companies to focus on their main activities and manage challenges such as communication and economic impact.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com