Career cushioning enhances job security by encouraging diverse skill development and proactive networking, while talent hoarding limits organizational growth through withholding expertise and resources. Understanding these contrasting approaches reveals their impact on personal career advancement and company innovation. Discover how balancing career cushioning and talent hoarding can optimize employment strategies.
Why it is important
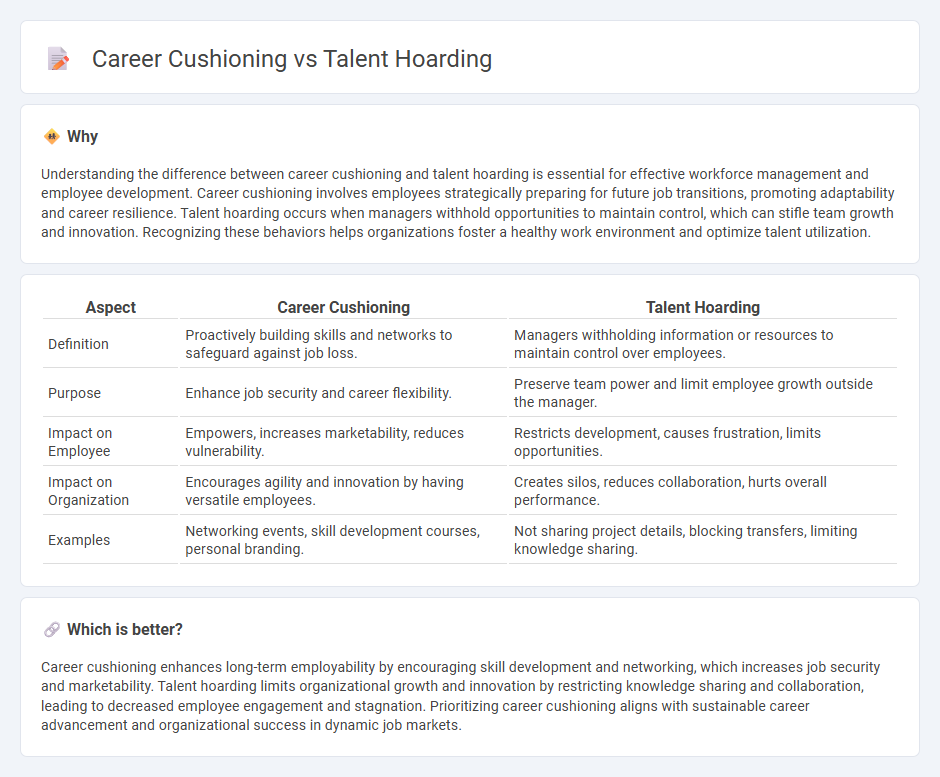
Understanding the difference between career cushioning and talent hoarding is essential for effective workforce management and employee development. Career cushioning involves employees strategically preparing for future job transitions, promoting adaptability and career resilience. Talent hoarding occurs when managers withhold opportunities to maintain control, which can stifle team growth and innovation. Recognizing these behaviors helps organizations foster a healthy work environment and optimize talent utilization.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Career Cushioning | Talent Hoarding |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Proactively building skills and networks to safeguard against job loss. | Managers withholding information or resources to maintain control over employees. |
| Purpose | Enhance job security and career flexibility. | Preserve team power and limit employee growth outside the manager. |
| Impact on Employee | Empowers, increases marketability, reduces vulnerability. | Restricts development, causes frustration, limits opportunities. |
| Impact on Organization | Encourages agility and innovation by having versatile employees. | Creates silos, reduces collaboration, hurts overall performance. |
| Examples | Networking events, skill development courses, personal branding. | Not sharing project details, blocking transfers, limiting knowledge sharing. |
Which is better?
Career cushioning enhances long-term employability by encouraging skill development and networking, which increases job security and marketability. Talent hoarding limits organizational growth and innovation by restricting knowledge sharing and collaboration, leading to decreased employee engagement and stagnation. Prioritizing career cushioning aligns with sustainable career advancement and organizational success in dynamic job markets.
Connection
Career cushioning involves employees building fallback options to secure job continuity, while talent hoarding occurs when managers retain skilled workers to maintain team performance and avoid knowledge loss. Both practices reflect underlying job insecurity and influence workforce stability by creating environments where talent mobility is limited. Organizations experiencing high levels of career cushioning often see increased talent hoarding as a response to retain critical expertise.
Key Terms
Internal Mobility
Talent hoarding restricts internal mobility by limiting employee opportunities for growth and collaboration within organizations. Career cushioning encourages proactive skill development and networking, enabling employees to smoothly transition across roles internally. Discover effective strategies to balance organizational needs with empowering internal mobility.
Job Security
Talent hoarding restricts employee growth by limiting opportunities within an organization, hindering overall career advancement and job security. Career cushioning involves strategic skill development and networking to build a safety net, enhancing long-term employment stability. Explore effective strategies to balance these approaches for optimizing job security and professional growth.
Employee Retention
Talent hoarding occurs when managers deliberately retain high-performing employees to protect their team's expertise, limiting growth opportunities elsewhere, whereas career cushioning involves employees discreetly preparing backup plans to safeguard their career progression in uncertain environments. Both practices impact employee retention by creating either stagnation or disengagement, potentially reducing organizational agility and long-term commitment. Explore effective strategies to balance talent utilization and career development for sustainable retention.
Source and External Links
Talent Hoarding in Organizations: Two Researched-Based Studies - Shares two scientific studies analyzing the impact of talent hoarding on the internal mobility of workers within organizations.
Talent Hoarding in Organizations - AWS - Provides first empirical evidence of talent hoarding where managers limit workers from seeking promotions to preserve team productivity, causing talent misallocation and contributing to inequality.
How to Manage the Problem of Talent Hoarding - Wowledge - Explains talent hoarding as managers restricting employee mobility by hiding their skills and performance from other parts of the organization, thus limiting career advancement and skill development opportunities.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com