Ghost work involves remote, digital tasks performed anonymously through online platforms, often lacking traditional job security and benefits. Shift work requires employees to work scheduled time blocks, frequently in industries like healthcare or manufacturing, with defined hours and direct supervision. Explore the differences in work structure and employee experience to better understand these employment models.
Why it is important
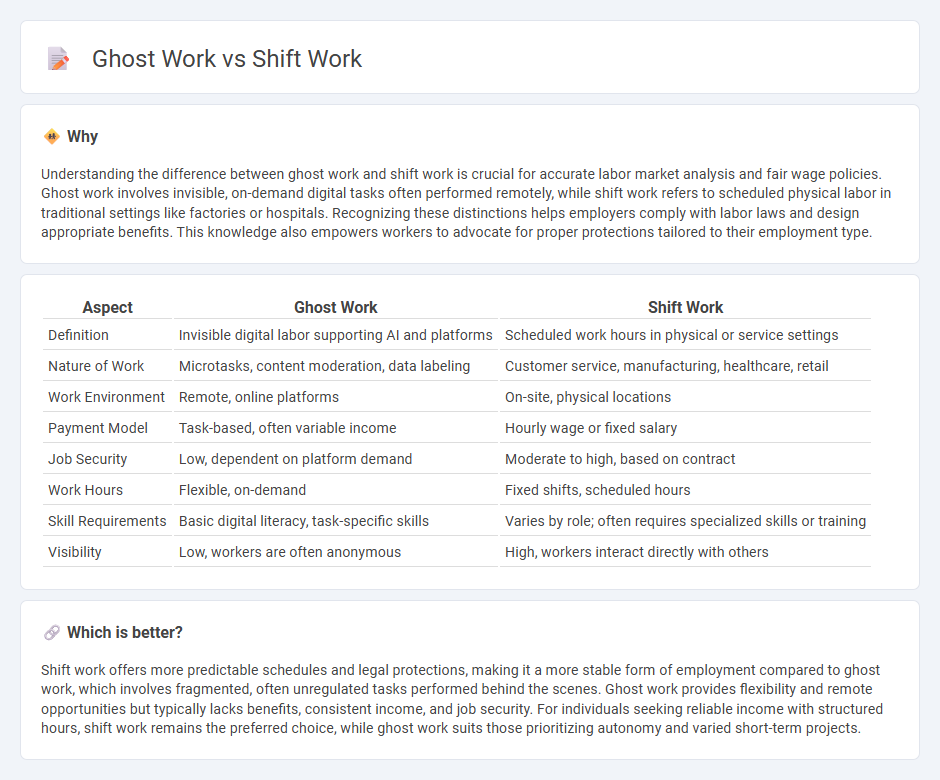
Understanding the difference between ghost work and shift work is crucial for accurate labor market analysis and fair wage policies. Ghost work involves invisible, on-demand digital tasks often performed remotely, while shift work refers to scheduled physical labor in traditional settings like factories or hospitals. Recognizing these distinctions helps employers comply with labor laws and design appropriate benefits. This knowledge also empowers workers to advocate for proper protections tailored to their employment type.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Ghost Work | Shift Work |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Invisible digital labor supporting AI and platforms | Scheduled work hours in physical or service settings |
| Nature of Work | Microtasks, content moderation, data labeling | Customer service, manufacturing, healthcare, retail |
| Work Environment | Remote, online platforms | On-site, physical locations |
| Payment Model | Task-based, often variable income | Hourly wage or fixed salary |
| Job Security | Low, dependent on platform demand | Moderate to high, based on contract |
| Work Hours | Flexible, on-demand | Fixed shifts, scheduled hours |
| Skill Requirements | Basic digital literacy, task-specific skills | Varies by role; often requires specialized skills or training |
| Visibility | Low, workers are often anonymous | High, workers interact directly with others |
Which is better?
Shift work offers more predictable schedules and legal protections, making it a more stable form of employment compared to ghost work, which involves fragmented, often unregulated tasks performed behind the scenes. Ghost work provides flexibility and remote opportunities but typically lacks benefits, consistent income, and job security. For individuals seeking reliable income with structured hours, shift work remains the preferred choice, while ghost work suits those prioritizing autonomy and varied short-term projects.
Connection
Ghost work involves invisible labor performed by remote digital workers, often on-demand and task-based, closely aligning with the intermittent hours of shift work. Both ghost work and shift work provide flexible schedules but blur traditional employer-employee boundaries, impacting job security and benefits. The rise of gig economy platforms has intensified this connection by enabling widespread deployment of shift-like ghost work across industries such as customer service and content moderation.
Key Terms
Scheduling
Shift work involves pre-set schedules with fixed start and end times, ensuring predictable workforce management and labor allocation. Ghost work refers to on-demand task-based labor, where scheduling is flexible, often driven by digital platforms matching real-time demand. Explore the differences in scheduling strategies and implications for workforce efficiency and worker well-being.
Gig economy
Shift work in the gig economy involves predefined hours and structured schedules, often seen in ride-sharing and delivery services, whereas ghost work refers to invisible, crowd-sourced digital labor such as content moderation and data labeling. The gig economy's rise has amplified demand for both types, emphasizing flexibility in shift work and anonymity in ghost work. Explore how these distinct labor models reshape modern employment and workforce dynamics.
Flexibility
Shift work offers structured schedules with predetermined hours, providing a clear routine but less adaptability for sudden personal needs. Ghost work involves on-demand, often remote tasks performed asynchronously, granting greater flexibility to choose when and where to work. Explore how these work models impact work-life balance and productivity to determine which suits your lifestyle best.
Source and External Links
What is Shift Work? Types of Shifts, Jobs and Pros and Cons - Shift work involves rotating schedules including overnight, early morning, or longer hours over fewer days; it is common in industries operating over 10 hours daily to maintain productivity without overtime costs.
Shift work - Shift work is designed to keep operations running 24/7, commonly using 8- or 12-hour shifts with slow or fast rotation, where forward rotating shifts better align with workers' circadian rhythms.
What Is Shift Work? - Shift work refers to work outside 7 am-6 pm hours, offering benefits like suited schedules for night owls and better wages, but also causing sleep problems, life disruptions, and increased risks of drowsy driving accidents.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com