Fractional work offers professionals a chance to divide their expertise across multiple companies, creating diversified income streams unlike traditional part-time jobs that typically involve fixed hours for a single employer. This approach maximizes flexibility and leverages specialist skills for strategic business impacts, contrasting with the often routine nature of part-time employment. Explore how fractional work reshapes modern employment landscapes and career growth opportunities.
Why it is important
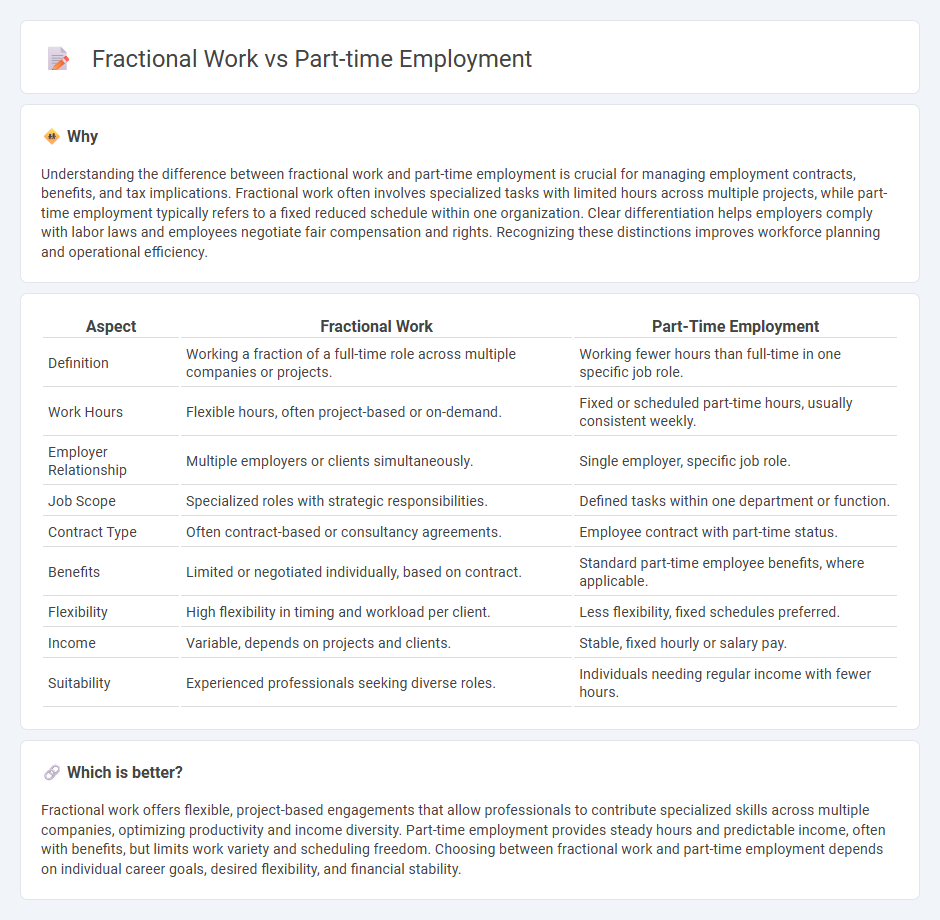
Understanding the difference between fractional work and part-time employment is crucial for managing employment contracts, benefits, and tax implications. Fractional work often involves specialized tasks with limited hours across multiple projects, while part-time employment typically refers to a fixed reduced schedule within one organization. Clear differentiation helps employers comply with labor laws and employees negotiate fair compensation and rights. Recognizing these distinctions improves workforce planning and operational efficiency.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Fractional Work | Part-Time Employment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Working a fraction of a full-time role across multiple companies or projects. | Working fewer hours than full-time in one specific job role. |
| Work Hours | Flexible hours, often project-based or on-demand. | Fixed or scheduled part-time hours, usually consistent weekly. |
| Employer Relationship | Multiple employers or clients simultaneously. | Single employer, specific job role. |
| Job Scope | Specialized roles with strategic responsibilities. | Defined tasks within one department or function. |
| Contract Type | Often contract-based or consultancy agreements. | Employee contract with part-time status. |
| Benefits | Limited or negotiated individually, based on contract. | Standard part-time employee benefits, where applicable. |
| Flexibility | High flexibility in timing and workload per client. | Less flexibility, fixed schedules preferred. |
| Income | Variable, depends on projects and clients. | Stable, fixed hourly or salary pay. |
| Suitability | Experienced professionals seeking diverse roles. | Individuals needing regular income with fewer hours. |
Which is better?
Fractional work offers flexible, project-based engagements that allow professionals to contribute specialized skills across multiple companies, optimizing productivity and income diversity. Part-time employment provides steady hours and predictable income, often with benefits, but limits work variety and scheduling freedom. Choosing between fractional work and part-time employment depends on individual career goals, desired flexibility, and financial stability.
Connection
Fractional work and part-time employment both offer flexible work arrangements that cater to employees seeking reduced hours compared to full-time positions. These employment models support workforce diversity, allowing individuals to balance personal commitments while maintaining career growth. Businesses leverage fractional and part-time roles to optimize labor costs and access specialized skills on a demand-driven basis.
Key Terms
Working Hours
Part-time employment typically involves a fixed schedule with fewer hours than full-time, often ranging between 20 to 30 hours per week, allowing employees to maintain consistent availability. Fractional work refers to specialized professional services delivered on a workload or project basis with flexible hours tailored to specific organizational needs, often involving high-level expertise distributed across multiple clients. Explore in-depth comparisons to understand which work model aligns best with your time management and career goals.
Contract Type
Part-time employment typically involves a fixed schedule and hours below full-time, governed by traditional labor contracts with defined benefits and protections. Fractional work, by contrast, is based on project-specific or retainer contracts that allocate a proportional share of an employee's expertise without full-time commitment or standard benefits. Explore the differences in contract types to determine the best fit for your staffing strategy.
Benefits Eligibility
Part-time employment typically offers limited benefits eligibility, often excluding health insurance and retirement plans, whereas fractional work arrangements provide proportional benefits aligned with hours worked or project scope. Fractional workers might gain access to tailored benefits packages through specialized agencies or contracts, enhancing flexibility without sacrificing coverage quality. Explore the distinct benefits landscapes and eligibility criteria to optimize your employment strategy effectively.
Source and External Links
Understanding Part-Time Jobs: Definition, Benefits, and Opportunities - A part-time job is defined as employment with fewer than 30 hours per week, offering flexibility, work-life balance, and additional income, though it may come with limited benefits and career advancement opportunities.
Part-Time vs Full-Time: How Many Hours & How to Classify? - Part-time employment is generally considered as working between 1 to 34 hours per week, often paid hourly or prorated salary, with fewer benefits compared to full-time employees.
Part Time jobs in Draper, Ut - Indeed - Thousands of part-time job openings in Draper, UT, are available across various fields like retail, food service, and clerical roles, often offering flexible schedules.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com