A career lattice emphasizes upward, lateral, and diagonal movements within an organization, allowing employees to develop diverse skills and broaden their experience beyond traditional vertical promotions. In contrast, a horizontal career move involves shifting roles at the same level within or across departments to gain specialized knowledge or explore new functions. Explore more to understand how these strategies impact long-term career growth and adaptability.
Why it is important
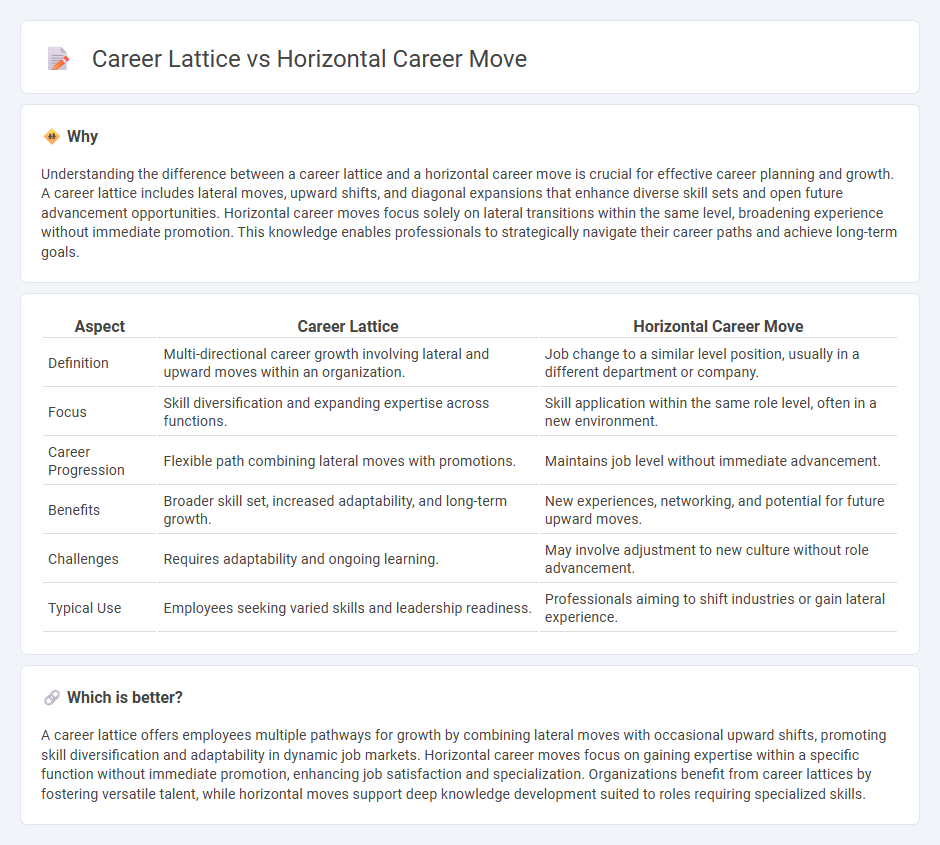
Understanding the difference between a career lattice and a horizontal career move is crucial for effective career planning and growth. A career lattice includes lateral moves, upward shifts, and diagonal expansions that enhance diverse skill sets and open future advancement opportunities. Horizontal career moves focus solely on lateral transitions within the same level, broadening experience without immediate promotion. This knowledge enables professionals to strategically navigate their career paths and achieve long-term goals.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Career Lattice | Horizontal Career Move |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Multi-directional career growth involving lateral and upward moves within an organization. | Job change to a similar level position, usually in a different department or company. |
| Focus | Skill diversification and expanding expertise across functions. | Skill application within the same role level, often in a new environment. |
| Career Progression | Flexible path combining lateral moves with promotions. | Maintains job level without immediate advancement. |
| Benefits | Broader skill set, increased adaptability, and long-term growth. | New experiences, networking, and potential for future upward moves. |
| Challenges | Requires adaptability and ongoing learning. | May involve adjustment to new culture without role advancement. |
| Typical Use | Employees seeking varied skills and leadership readiness. | Professionals aiming to shift industries or gain lateral experience. |
Which is better?
A career lattice offers employees multiple pathways for growth by combining lateral moves with occasional upward shifts, promoting skill diversification and adaptability in dynamic job markets. Horizontal career moves focus on gaining expertise within a specific function without immediate promotion, enhancing job satisfaction and specialization. Organizations benefit from career lattices by fostering versatile talent, while horizontal moves support deep knowledge development suited to roles requiring specialized skills.
Connection
Career lattice and horizontal career moves are interconnected concepts emphasizing diverse pathways for professional growth beyond traditional vertical promotions. The career lattice model encourages lateral moves, skill diversification, and cross-functional experiences to enhance adaptability and long-term career development. Horizontal career moves serve as strategic steps within the lattice framework, enabling employees to expand their expertise and increase organizational value without necessarily advancing in rank.
Key Terms
Lateral Transfer
A horizontal career move, or lateral transfer, involves shifting to a role with similar responsibilities and level within an organization, enabling skill diversification without hierarchical advancement. The career lattice model emphasizes a combination of lateral moves, promotions, and sometimes backward steps to build a broad skill set and adaptability across functions. Explore the strategic benefits of lateral transfers and how they fit within the career lattice framework to enhance professional growth.
Skill Diversification
A horizontal career move involves shifting to a different role at the same organizational level to gain new skills and experiences, enhancing versatility. Career lattice strategies expand this concept by incorporating both lateral and diagonal moves, promoting comprehensive skill diversification and broader professional development. Explore how embracing these approaches can accelerate your career growth.
Cross-Functional Experience
Horizontal career moves involve shifting to roles at the same level within the same function, enhancing expertise without altering hierarchical status. In contrast, a career lattice emphasizes cross-functional experience by navigating laterally across different departments, broadening skill sets and fostering organizational versatility. Explore how embracing a career lattice can accelerate professional growth through diverse cross-functional challenges.
Source and External Links
Vertical vs. Lateral Career Growth: What's The Difference? - Deel - A horizontal (lateral) career move involves broadening your skill set by taking on new roles or challenges in different fields without necessarily getting a promotion or pay raise, helping develop a wider range of competencies.
Understanding lateral vs. vertical career moves - University of Phoenix - A horizontal career move means learning new skills in a different department at a similar level, which can increase your organizational value though it might not immediately boost your salary.
It's still movement - why you should consider a horizontal career move - A horizontal career move lets you build new skills, expand your network within the company, and position yourself better for future promotions or external opportunities while staying at a similar responsibility and pay level.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com